Research brings new control over topological insulator
2014-03-20
An international team of scientists investigating the electronic properties of ultra-thin films of new materials – topological insulators (TIs) - has demonstrated a new method to tune their unique properties using strain.
Topological insulators are new materials with surfaces that host a new quantum state of matter and are insensitive to contaminants, defects and impurities. Surface electrons in TIs behave like massless Dirac particles in a similar way to electrons in graphene. Moreover, surface currents in topological insulators also preserve their spin orientation and ...
E3-production -- sustainable manufacturing
2014-03-20
This news release is available in German.
Industrial manufacturing is pivotal to Germany's prosperity. Not only does manufacturing account for a quarter of GDP, it provides a third of jobs as well. Yet rising raw material and energy costs, coupled with a demographic shift, pose significant challenges for industry. Keeping manufacturing operations in Germany will require a fundamental shift away from maximum profit from minimal capital investment toward maximum added value from minimum resources.
Initiating and effecting this change is what Fraunhofer's E3-production ...
Resin infiltration effects in a caries-active environment -- 2 year results
2014-03-20
Alexandria, Va., USA – Today during the 43rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the American Association for Dental Research, held in conjunction with the 38th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, Mathilde C. Peters, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA, will present research titled "Resin Infiltration Effects in a Caries-Active Environment – 2 Year Results."
The objective of this study was to compare carious lesion changes after resin infiltration of approximal non-cavitated lesions in a high caries risk population after two years. Resin infiltration ...
Thermal conductance can be controlled like waves using nanostructures
2014-03-20
Thermal conduction is a familiar everyday phenomenon. In a hot sauna, for instance, you can sit comfortably on a wooden bench that has a temperature of 100C (212F), but if you touch a metallic nail with the same temperature, you will hurt yourself. The difference of these two experiences is due to the fact that some materials, such as metals, conduct heat well, whereas some other materials, such as wood, do not. It is therefore commonly thought that thermal conductance is simply a materials parameter. Now, researchers at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, led by Professor ...
Oldest fossil evidence of modern African venomous snakes found in Tanzania
2014-03-20
ATHENS, Ohio (March 19, 2014)—Ohio University scientists have found the oldest definitive fossil evidence of modern, venomous snakes in Africa, according to a new study published March 19 in the journal PLOS ONE.
The newly discovered fossils demonstrate that elapid snakes—such as cobras, kraits and sea snakes—were present in Africa as early as 25 million years ago, said lead author Jacob McCartney, a postdoctoral researcher in the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine. He's part of a team that has been examining the Rukwa Rift Basin of Tanzania over ...
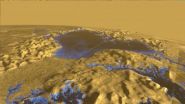
Surface of Titan Sea is mirror smooth, Stanford scientists find
2014-03-20
New radar measurements of an enormous sea on Titan offer insights into the weather patterns and landscape composition of the Saturnian moon. The measurements, made in 2013 by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, reveal that the surface of Ligeia Mare, Titan's second largest sea, possesses a mirror-like smoothness, possibly due to a lack of winds.
"If you could look out on this sea, it would be really still. It would just be a totally glassy surface," said Howard Zebker, professor of geophysics and of electrical engineering at Stanford who is the lead author of a new study detailing ...
Parents should try to find middle ground to keep teens safe online
2014-03-20
Parents might take a lesson from Goldilocks and find a balanced approach to guide their teens in making moral, safe online decisions, according to Penn State researchers.
In a study on parenting strategies and online adolescent safety, the researchers found evidence that suggests that parents should try to establish a middle ground between keeping their teens completely away from the internet not monitoring their online activities at all.
"It's a Goldilocks problem," said Pamela Wisniewski, a postdoctoral scholar in information sciences and technology. "Overly restrictive ...
Low levels of oxgen, nitric oxide worsen sickle cell disease
2014-03-20
Low levels of both oxygen and the powerful blood vessel dilator nitric oxide appear to have an unfortunate synergy for patients with sickle cell disease, researchers report.
Their studies indicate that the two conditions common in sickle cell disease, dramatically increase red blood cells' adhesion to the lining of blood vessels walls and the debilitating pain crises that can result.
The good news is that restoring normal levels of nitric oxide can substantially reduce red blood cell adhesion, said Dr. Tohru Ikuta, a molecular hematologist at the Medical College of ...
School hearing tests do not detect noise exposure hearing loss
2014-03-20
School hearing tests cannot effectively detect adolescent high-frequency hearing loss, which is typically caused by loud noise exposure, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine.
The Pennsylvania Department of Health mandates school-administered hearing screens for children in kindergarten to third, seventh and 11th grades. The school screenings primarily focus on low-frequency hearing loss. This is logical for young children, who are more likely to develop low-frequency hearing loss due to fluid in the ear after a bad cold or an ear infection. Adolescents, ...
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria among children in the United States on the rise
2014-03-20
(Chicago)--Infections caused by a specific type of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are on the rise in U.S. children, according to new study published in the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. While still rare, the bacteria are increasingly found in children of all ages, especially those 1-5 years old, raising concerns about dwindling treatment options.
"Some infections in children that have typically been treated with oral antibiotics in the past may now require hospitalization, treatment with intravenous drugs, or both, as there may not be an oral treatment ...
Obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on cancer outcomes
2014-03-20
Both obesity and diabetes have adverse effects on outcomes in breast cancer patients who receive chemotherapy as primary treatment before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy), according to research to be presented at the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday). Although a high body mass index (BMI) is known to have a negative impact on cancer development and prognosis, until now there has been uncertainty as to whether having a high BMI had an equal effect on patients with different types of breast tumours.
Dr Caterina Fontanella, MD, a trainee in ...
Deaths from breast cancer fall in Europe
2014-03-20
Improvements in treatment, as well as enhanced access to care, underlie the sustained decreases in breast cancer mortality seen in 30 European countries [1] from 1989 to 2010. But there are notable variations between different countries that cannot be explained simply by the resources devoted to cancer care, and these differences need to be studied further, according to research to be presented to the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) tomorrow (Friday).
Professor Philippe Autier, from the International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France, told a press ...
In the genome of loblolly pine lies hope for better resistance to a damaging disease
2014-03-20
"The project was a huge undertaking because at 22 gigabases, the loblolly pine genome is about eight times larger than the human genome," said C. Dana Nelson, SRS Southern Institute for Forest Genetics (SIFG) project leader and research geneticist. "The group chose loblolly pine both because of its economic importance, and the knowledge gained from 60 years of breeding the species and managing millions of trees in genetic trials."
As part of the project, researchers identified a candidate for a gene involved in resistance to fusiform rust, a disease that infects southern ...
Regular physical activity reduces breast cancer risk irrespective of age
2014-03-20
Glasgow, UK: Practising sport for more than an hour day reduces the risk of contracting breast cancer, and this applies to women of any age and any weight, and also unaffected by geographical location, according to research presented to the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9). Compared with the least active women, those with the highest level of physical activity reduced their risk of breast cancer by 12%, researchers say
Professor Mathieu Boniol, Research Director at the International Prevention Research Institute, Lyon, France, reported to a press conference ...
Scientists discover potential way to make graphene superconducting
2014-03-20
Scientists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University have discovered a potential way to make graphene – a single layer of carbon atoms with great promise for future electronics – superconducting, a state in which it would carry electricity with 100 percent efficiency.
Researchers used a beam of intense ultraviolet light to look deep into the electronic structure of a material made of alternating layers of graphene and calcium. While it's been known for nearly a decade that this combined material is superconducting, the ...
Stellar Slate of Industry Speakers at the Inaugural Internet of Things Asia 2014
2014-03-20
The first-ever Internet of Things (IoT) Asia 2014 to be held at Singapore EXPO Convention & Exhibition Centre from 21-22 April will feature a dynamic slate of international and local speakers from leading companies in the IoT field. Jointly organised by Singapore Industrial Automation Association (SIAA) and Singex Exhibitions, the event has a confirmed line-up of over 40 industry experts and practitioners in the IoT & machine-to-machine (M2M) field as speakers.
Comprising a trade exhibition and conference, IoT Asia 2014 is the first event in the Asia Pacific ...
Nicholls Auction Marketing Group announces the Auction of 27 Valuable Lake Gaston Building Lots
2014-03-20
"This is an amazing opportunity for you to own gorgeous home sites on picturesque Lake Gaston," said John Nicholls, president of the company.. "The auction will be conducted at Kahill's Restaurant in South Hill, VA.Nicholls. Make plans to now to purchase these great lake properties."
"The 27 lots include 22 waterfront and 5 interior lots, most with community water/sewer and boat slips/covered boat houses," said Mr. Sid Smyth, NAMG Auction Coordinator. "Two of the lots (26.5+/- and 7.7+/- acres) highlights include notable timber." ...
Phillip and Divine Fry Announce Their Training and Certification as Air Duct Cleaning Specialists
2014-03-20
Mold consultants Phillip and Divine Fry completed their classroom and hands-on training and certification on March 7, 2014, as Certified Air Duct Cleaning Specialists in the RotoMasters Certified Training program in Dallas, Texas, to enable the Frys to provide effective cleaning and environmental decontamination of heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) air supply and return ducts.
"Our Certified Air Duct Cleaning Specialist training and certification helps us to better serve our EnviroFry residential and commercial clients in Michigan, Indiana, Ohio, ...
PacNet Services Showcasing International Payment Solutions at ad:tech San Francisco
2014-03-20
ad:tech is the leading digital marketing event for 8,500+ marketing and technology professionals from all over the world - a marketplace for buying and selling, a community for networking, a forum for exchanging ideas and an opportunity for contributing to industry trends and initiatives. The payment experts at PacNet are looking forward to adding their international payment processing expertise to the mix on the show floor.
PacNet will be on hand at booth 2630, ready to discuss how an effective payment strategy can boost sales and lift response rates for international ...
Village Frame Shoppe Launches CanvasGnome.com, A Full Service Photo to Canvas Printing Website
2014-03-20
The Village Frame Shoppe of St. Albans, Vermont has just announced the launch of their new Photo to Canvas printing website, CanvasGnome.com.
"After the high demand for our canvas photo printing services on the local level, we decided it was time to take our product to a larger market", stated Dan Pattullo, "That's when we decided to launch our new business venture."
CanvasGnome.com is an online service that provides photo to canvas printing to artists, photographers and the consumer market. A user can log onto CanvasGnome, upload their photo file, ...
Kenneth Copeland Ministries Reaches Millions of People Around the World with Sennheiser and Neumann
2014-03-20
Kenneth Copeland Ministries has been an important contributor in the Christian community since 1967, reaching over 60 million people through its various faith-based outreach activities. In addition to the KCM broadcasts, which reach an international audience of over 100 countries, the Ministry regularly provides humanitarian and disaster assistance through its KCM Relief Fund, which recently helped provide Haiti with $2.7 million of medical supplies and 7,000 pounds of antibiotics. KCM broadcasts its meetings from various arenas, conferences centers and ballrooms around ...
Marc Caron, Professor at Duke University Medical Center, to Give Keynote Address on Functional Selectivity at GPCR Structure, Function and Drug Discovery Conference, May 22-23, 2014 in Cambridge, MA
2014-03-20
Dr. Marc Caron, Professor of Cell Biology at the Duke University Medical Center, will give the keynote presentation at the GPCR Structure, Function and Drug Discovery Conference, to be held May 22-23, 2014 in Cambridge, MA.
Dr. Caron, who has focused his research on mechanisms and regulation of G protein-coupled receptors and on the mechanisms of neurotransmission as controlled by neurotransmitter transporters, will speak about "Approaches to Validate and Exploit Functional Selectivity of GPCRs."
Though the recent genomic revolution has provided great hope ...
StarPrime.com Introduces New and Improved Interactive Advertising Model
2014-03-20
Los Angeles, CA, MARCH 17, 2014 - StarPrime.com, an incentivized, interactive shopping and rewards website, is challenging the way advertisements are being perceived by consumers and are giving away capital for every ad watched. Anytime a StarPrime user makes a purchase, shares something from the site, and/or invites their friends to join, they receive AdTime credits. AdTime is a user's time limit to watch ads, so that they can start earning Primes (StarPrime points). Primes can be used to enter for a chance to win prizes in StarPrime's sweepstakes section and/or can be ...
Secure Decisions Wins U.S. Department of Homeland Security Phase II Software Assurance Contract
2014-03-20
Secure Decisions, a division of Applied Visions and developer of visual analytic tools for cyber security, has received a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) Phase II award from the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to improve the security of software applications. Under this DHS Science & Technology (S&T) Directorate contract, Secure Decisions will continue development of the Code Ray software assurance risk management framework, to correlate the results of static and dynamic software analysis tools towards the goal of improving software vulnerability ...
Brentano to Show Color, Pattern at HD Expo
2014-03-20
Brentano will show their true colors at the Hospitality Design Expo in May. The textile house will debut dramatic new fire retardant draperies from the upcoming fall Affinity collection -- in addition to the heavy duty upholstery, outdoor and novelty fabrics expected from Brentano. From geometrics and stripes to organic shapes modeled after tree bark and gingko leaves, all of the fabrics have two things in common: They're bright! And they're Brentano.
"We looked at the new Affinity patterns and colors, and these were the ones that popped," says National Sales ...
[1] ... [3847]
[3848]
[3849]
[3850]
[3851]
[3852]
[3853]
[3854]
3855
[3856]
[3857]
[3858]
[3859]
[3860]
[3861]
[3862]
[3863]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.