Page Family Dentistry Uses Social Media Channels To Interact With Patients
2014-03-15
As Providence, RI family dentists, Dr. Marc Page and Dr. Lawrence Page have recently announced the recent launch of his practice's new social media sites. Page Family dentistry's new Facebook and Twitter pages, two increasingly popular social media channels, were created in order to improve the practice's communication with current and potential patients on the Web.
Social networking continues to remain as an important Internet tool for dentists. Now patients have the ability to participate in ongoing online conversations with their Providence, RI family dentists and ...
Littleton Family Dentist Helps Patients With Updated Health Tips
2014-03-15
At Southwest Family Dentistry, Dr. Robert Madden strives to improve his patients' knowledge of oral health by offering newsletters, an educational blog and helpful health tips. As a family dentist in Littleton, Dr. Madden prides himself in his ability to provide superior dental health care services. To further improve his patients' understanding of important health topics, he also offers "Health Tips" via his practice website.
The current health tips offered by Dr. Madden are on the topic of "Tooth Demineralization." As stated by Dr. Madden, many ...
Requesting Appointments Just Got A Lot Easier!
2014-03-15
Patients no longer need to interrupt their busy schedules to make an appointment with Dr. Lars Johnson of Forest Edge Dental by calling the office. By maintaining an up-to-date, interactive website, children's dentist in Hoffman Estates, Dr. Johnson, is pleased to offer a new way for patients to make their next appointment with his office - online appointment requests.
With problems arising at any point of the day, patients can now request appointments online via the practice's website. When symptoms arise, patients can simply submit an appointment request via the practice's ...
Salt Lake City Cosmetic Dentists Offer 24 Hour Emergency Care For Patients
2014-03-15
When an emergency arises, Dr. Jack Brauer, Dr. Anthony Tidwell, Dr. Gary Findley and Dr. Jacob Froerer of Olympus View Dental are readily available as Salt Lake City emergency dentists to provide patients with the dental care they need in a timely matter. Serving the community for many years, these emergency dentists in Salt Lake City will gladly accept emergency patients the same day with their 24-hour emergency care.
If patients experience a dental emergency, these Salt Lake City emergency dentists encourage patients to call as soon as possible for an appointment. ...
Milton Chiropractic and Rehabilitation, Inc. Offers Chiropractic Care For Sports Injuries In Quincy
2014-03-15
Highly competitive sports can post a higher risk of injuries, especially among children. Whether a patient participates in football, weightlifting, gymnastics, wrestling or any other competitive sport, they run the risk of injury. If a patient suffers from a sports injury in Quincy, Dr. David Smith encourages him or her to visit Milton Chiropractic & Rehabilitation, Inc. for further care.
Finding relief from pain is important for patients to maintain a healthy, active lifestyle. While participation in sports or exercise is an important step in maintaining your health, ...
Simon Dental Care Offers Dental Implants For Mesa Residents In Need Of A Smile Restoration
2014-03-15
Patients who are missing a tooth or multiple teeth might benefit from dental implants, as they offer the stability a smile needs. Dental implants fuse to the bone, helping replacement teeth to feel more natural than other conventional restoration options. Candidates for dental implants need to have healthy gums and adequate bone to support the implant.
A thorough evaluation by Dr. Preethy Kunthara, a dentist in Mesa, will help to determine whether a patient is a good candidate for dental implants. So if a patient is self-conscious about missing teeth or wearing dentures, ...
Charlottesville Dentist Enhances Patient Educational Knowledge Through Educational Resources
2014-03-15
Leading Charlottesville dentist, Dr. Tore Steinberg, is pleased to introduce new educational resources via his practice's patient friendly and easy to use website. Patients can now easily access dental information to better understand the importance of maintaining proper dental health.
The new patient education library for Dr. Steinberg offers an array of informational dental articles and topics such as cosmetic procedures, dental problems, pain management and treatment options. Whether patients have questions about tooth pain or want more information on a cosmetic procedure ...
Join Northwest ENT and Allergy Care in Milwaukie on Facebook and Twitter
2014-03-15
Preferred Milwaukie, OR ENT doctor, Dr. Adrian Varela is pleased to announce the launch of Northwest ENT & Allergy Care's Facebook and Twitter pages to improve patient relations. The Facebook and Twitter accounts were created to allow patients to easily access more valuable information about the practice, in addition to communicating with other patients about their previous procedures and visits to Northwest ENT & Allergy Care.
With the recent addition of the new Facebook and Twitter pages, patients have the ability to gain important information regarding an ...
Urgent Care Clinic In Falls Church Utilizes Practice Website For Increased Communication
2014-03-15
For more than 12 years, Falls Church urgent care clinic has been serving the community with reliable medical care through the help of warmth and professional staff with years of experience. Dr. Rizwan Dar maintains and operates Loehmann's Walk-In-Clinic to help the community with their need for urgent, walk-in medical care. Through the availability of Loehmann's Walk-In-Clinic's technologically advanced website, patients can search the Internet for a variety of medical information they might need, in particular medical information related to urgent care medicine.
"I ...
How To Tell Your Children About Divorce
2014-03-15
Divorce is one of the most difficult challenges most people face - including the children involved. The good news is that most of the time, families that feel their lives torn apart by divorce come through the experience without lasting effects. Even well-adjusted children, however, may have long-lasting memories of the moment their parents told them about an upcoming divorce.
That's one reason it's important to tell your children about divorce in a way that is caring and age-appropriate and presents a unified front between you and your soon-to-be ex-spouse. Another ...
Chamber Orchestra Performs 'All Mozart' with Philadelphia Orchestra Flutist Jeffrey Khaner and Conductor Matthias Bamert
2014-03-15
Celebrating the most influential composer of the Classical Era, former Music Director of the London Mozart Players and the Malaysian Symphony Orchestra, Matthias Bamert, leads the Chamber Orchestra in three eminent works by Mozart, including the celebrated Symphony No. 40 in G minor - the most intensely expressive and powerful of all Mozart's symphonies. Maestro Bamert will be joined by Jeffrey Khaner, Principal Flute of the Philadelphia Orchestra for Flute Concerto No. 2 in D minor, which unbeknownst to many, is an arrangement of Mozart's Oboe Concerto in C major.
MARCH ...
Doggone Safe Announces the International Dog Bite Prevention Challenge 2014
2014-03-15
Doggone Safe today announced the International Dog Bite Prevention Challenge. It challenges its presenters to visit schools and educate 50,000 children about dog safety during the months of March to May. The Challenge is to celebrate Dog Bite Prevention Week (May 18-24, 2014). Non-profit Doggone Safe has presenters in 17 countries, 11 Canadian provinces and 43 states in the USA.
Dog bites to children are considered to be a serious public health problem by public health agencies and veterinary medical associations worldwide. Statistics show that most bites are by the ...
ATS releases guidelines on the management of pulmonary hypertension of sickle cell disease
2014-03-15
The American Thoracic Society has developed clinical practice guidelines to help clinicians identify and manage patients with sickle cell disease who are at increased risk for mortality from pulmonary hypertension.
"With the development of new treatments, many patients with sickle cell disease are now surviving long enough to develop pulmonary hypertension, with an estimated prevalence of 6 to 11 percent," said Elizabeth S. Klings, MD, associate professor of medicine at the Boston University School of Medicine and chair of the committee that produced the guidelines. ...
Contagious yawning may not be linked to empathy; still largely unexplained
2014-03-14
DURHAM, N.C. -- While previous studies have suggested a connection between contagious yawning and empathy, new research from the Duke Center for Human Genome Variation finds that contagious yawning may decrease with age and is not strongly related to variables like empathy, tiredness and energy levels.
The study, published March 14 in the journal PLOS ONE, is the most comprehensive look at factors influencing contagious yawning to date.
The researchers said a better understanding of the biology involved in contagious yawning could ultimately shed light on illnesses ...
School sick days could be reduced with safe drinking water
2014-03-14
Providing free drinking water in schools could be key to helping people in developing countries lift themselves out of poverty according to research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
Research published today shows that schools providing clean water report fewer children off sick. It is the first study to investigate whether providing drinking water in schools can reduce absenteeism.
Researchers looked at absentee rates in eight schools in Cambodia – half of which received treated drinking water, and half of which did not. The 26-week study period spanned two ...
Specialized care improves treatment outcomes in patients with sleep apnea
2014-03-14
DARIEN, IL – A new study of patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) found that treatment outcomes were better when patients received care from sleep specialists and accredited sleep centers.
Results show that sleep apnea patients who received care from board certified sleep medicine physicians and accredited sleep centers were two times more likely to be adherent to positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy than those who received care from non-accredited centers and non-certified physicians. Patient satisfaction also was associated with physician certification, and ...
NASA's TRMM satellite eyeing Tropical Cyclone Gillian's rebirth
2014-03-14
VIDEO:
On March 14, 2014, at 1 a.m. EDT this simulated 3-D flyby of the TRMM satellite showed rain falling at the rate of over 116 mm/4.5 inches per hour (red),...
Click here for more information.
Heavy rainfall rates and powerful towering thunderstorms were spotted in what appeared to be the rebirth process of Tropical Cyclone Gillian in the Gulf of Carpentaria between Australia's Northern Territory and Queensland.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite called TRMM ...
Parents receiving heart disease diagnosis for infants need better information
2014-03-14
LOS ANGELES – Based on a survey of parents of children with congenital heart disease, physicians delivering the diagnosis need to do a better job of showing compassion, ensuring parents understand all their options and providing easily understandable information, according to a new study published in the February edition of the journal, Pediatric Cardiology.
Researchers at Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute (LA BioMed) worked with the California Heart Connection, a nonprofit organization of parents of children with congenital heart disease, to conduct an online ...
Tension triggers muscle building
2014-03-14
In order to move the body, skeletal muscles are pulling on the skeleton. For efficient muscle and skeletal movements it is essential that the muscle contracts only along a defined axis, for instance for the leg movement along the thigh. Such a directed contraction is achieved by the myofibrils that span through the entire length of the muscle. At both ends, the myofibrils are anchored to the tendon cells, which themselves are linked to the skeleton. "Thereby, the entire force is transduced from the muscle to the skeleton," Frank Schnorrer describes. How can the regular ...
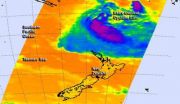
NASA sees an extra-tropical Lusi north of New Zealand
2014-03-14
NASA's Aqua satellite caught an infrared picture of Tropical Cyclone Lusi after it transitioned into an extra-tropical storm, north of New Zealand. Gale Warnings are in effect in Northern New Zealand.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Lusi on March 13 at 13:41 UTC/9:41 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured infrared data on the storm that revealed it had become a cold-core system. When a storm becomes extra-tropical and its core changes from warm to cold, the strongest winds spread out and the storm expands.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center ...
Salad at concession stands!?
2014-03-14
Pep-rallies, the marching band, cheers and chants, and savory, indulgent foods sold at the concession stand are all beloved features of the American high school sports tradition.
In contrast to the nutrition requirements on breakfast and lunches sold in school cafeterias, foods sold at concession stands do not follow the standard nutrition guidelines because they are typically sold for fundraising purposes. Is there something that can be done to improve the healthful features of concession stand food, and preserve the profits they generate? According to this new study ...
Older age at onset of Type 1 diabetes associated with lower brain connectivity
2014-03-14
SAN FRANCISCO, March 14, 2014 – Children and adolescents older than age 8 at the onset of type 1 diabetes had weaker brain connectivity when tested later in life relative to those who had earlier ages of diagnosis, University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences researchers discovered.
The findings, presented today at the American Psychosomatic Society's annual meeting, were made by analyzing the brain scans of 44 middle-age adults diagnosed with type 1 diabetes as children.
"Adolescence is a time when the brain matures and makes connections in networks responsible ...
Study: Losing or gaining weight after joint replacement affects how well patients do
2014-03-14
While many overweight patients have the best intentions to lose weight after joint replacement, a study at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) finds that although some are able to achieve this goal, equal numbers of patients actually gain weight after hip or knee replacement. Researchers also determined that patients who lose weight do better in terms of function and activity level two years down the road.
"Our findings represent the first report to present evidence that weight loss is associated with improved clinical outcomes, while weight gain is associated with inferior ...
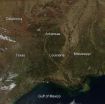
Southeastern fires consist of prescribed and wild
2014-03-14
According to the Southern Area Coordination Center, which monitors and coordinates response to incidents throughout the Southeast, there are currently seven large fires burning in this area of the country. Six of them are located in the state of Oklahoma and the seventh is in the Gulf area of Louisiana. These fires currently have burned over 7,600 acres. The majority of the fires on this image, though, are not wildfires, but are prescribed fires. The Chicasaw Journal of Mississippi wrote this regarding prescribed fires: "Prescribed fire, also known as controlled burning, ...
Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ER
2014-03-14
WASHINGTON (March 14, 2014) —George Washington University (GW) researchers report dramatic increases in prescriptions of opioid analgesics, such as Percocet, Vicodin, oxycodone and Dilaudid, during U.S. emergency department visits from 2001 to 2010. These findings were not explained by higher visit rates for painful conditions, which only increased modestly during the time period. This report was published today in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
"This trend is especially concerning given dramatic increases in opioid-related overdoses and fatalities in recent ...
[1] ... [3851]
[3852]
[3853]
[3854]
[3855]
[3856]
[3857]
[3858]
3859
[3860]
[3861]
[3862]
[3863]
[3864]
[3865]
[3866]
[3867]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.