Democrats, Republicans see each other as mindless -- unless they pose a threat
2014-03-18
We are less likely to humanize members of groups we don't belong to—except, under some circumstances, when it comes to members of the opposite political party. A study by researchers at New York University and Harvard Business School suggests that we are more prone to view members of the opposite political party as human if we view those individuals as threatening.
"It's hardly surprising that we dehumanize those who are not part of our groups," says Jay Van Bavel, an assistant professor in NYU's Department of Psychology and one of the study's co-authors. "However, what ...
Research on the protein gp41 could help towards designing future vaccinations against HIV
2014-03-18
This news release is available in Spanish. Researchers from the University of Granada have discovered, for the first time, an allosteric interaction (that is, a regulation mechanism whereby enzymes can be activated or de-activated) between this protein, which forms part of the sheath of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and the antibody 2F5 (FAB), a potent virus neutralizer. This important scientific breakthrough could help specialists to understand the mechanisms behind generating immune responses and help towards the design of future vaccines against the HIV ...
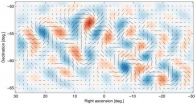
First direct evidence of cosmic inflation
2014-03-18
Almost 14 billion years ago, the universe we inhabit burst into existence in an extraordinary event that initiated the Big Bang. In the first fleeting fraction of a second, the universe expanded exponentially, stretching far beyond the view of our best telescopes. All this, of course, was just theory.
Researchers from the BICEP2 collaboration today announced the first direct evidence for this cosmic inflation. Their data also represent the first images of gravitational waves, or ripples in space-time. These waves have been described as the "first tremors of the Big Bang." ...
Immunologists present improved mass spectrometric method for proteomic analyses
2014-03-18
When it comes to analyzing cell components or body fluids or developing new medications, there is no way around mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry is a highly sensitive method of measurement that has been used for many years for the analysis of chemical and biological materials. Scientists at the Institute of Immunology of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have now significantly improved this analytical method that is widely employed within their field. They have also developed a software program for the integrated analysis of ...
UNH research: Positive memories of exercise spur future workouts
2014-03-18
DURHAM, N.H. – Getting motivated to exercise can be a challenge, but new research from the University of New Hampshire shows that simply remembering a positive memory about exercise may be just what it takes to get on the treadmill. This is the first study to explore how positive memories can influence future workouts.
"This study underscores the power of memory's directive influence in a new domain with practical applications: exercise behaviors. These results provide the first experimental evidence that autobiographical memory activation can be an effective tool in ...
Male, stressed, and poorly social
2014-03-18
Stress, this enemy that haunts us every day, could be undermining not only our health but also our relationships with other people, especially if we are men. In fact, stressed women apparently become more "prosocial". These are the main findings of a study carried out with the collaboration of Giorgia Silani, from the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) of Trieste. The study was coordinated by the Social Cognitive Neuroscience Unit of the University of Vienna and saw the participation of the University of Freiburg.
"There's a subtle boundary between the ...
What's so bad about feeling happy?
2014-03-18
Why is being happy, positive and satisfied with life the ultimate goal of so many people, while others steer clear of such feelings? It is often because of the lingering belief that happiness causes bad things to happen, says Mohsen Joshanloo and Dan Weijers of the Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand. Their article, published in Springer's Journal of Happiness Studies, is the first to review the concept of aversion to happiness, and looks at why various cultures react differently to feelings of well-being and satisfaction.
"One of these cultural phenomena ...
Study fingers chickens, quail, in spread of H7N9 influenza virus
2014-03-18
Among the copious species of poultry in China, quail and chickens are the likely sources of infection of H7N9 influenza virus to humans, according to a paper published ahead of print in the Journal of Virology.
"Knowing the likely poultry species lets us target our interventions better to prevent human infections," says corresponding author David Suarez, of the United States Department of Agriculture.
The H7N9 avian influenza virus was first reported in humans in March 2013 in China. Since then over 375 human cases have been confirmed and over 100 have died. Only ...
New understanding of why chromosome errors are high in women's eggs
2014-03-18
A new study from the University of Southampton has provided scientists with a better understanding of why chromosome errors are high in women's eggs.
It is estimated that up to 60 per cent of eggs are affected by errors in how their chromosomes divide, making it the leading cause of infertility. Chromosome errors also lead to conditions such as Down Syndrome and early pregnancy loss.
By using state-of-the-art imaging techniques, the Southampton researchers examined the most important process present in all cells to prevent chromosome errors – the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint ...
Some truth to the 'potent pot myth'
2014-03-18
New research from The Netherlands shows that people who smoke high-potency cannabis end up getting higher doses of the active ingredient (THC). Although they reduce the amount they puff and inhale to compensate for the higher strength, they still take in more THC than smokers of lower potency cannabis.
For the past decade or more, the common sense idea that high strength cannabis leads to higher doses of THC and therefore poses a greater risk of unwanted effects such as dependency has been challenged and labelled the 'potent pot myth'. It has been argued that smokers ...
A new algorithm improves the efficiency of small wind turbines
2014-03-18
Small wind turbines tend to be located in areas where wind conditions are more unfavourable. "The control systems of current wind turbines are not adaptative; in other words, the algorithms lack the capacity to adapt to new situations," explained Iñigo Kortabarria, one of the researchers in the UPV/EHU'sAPERT research group. That is why "the aim of the research was to develop a new algorithm capable of adapting to new conditions or to the changes that may take place in the wind turbine," added Kortabarria. That way, the researchers have managed to increase the efficiency ...
Simulations predict blast scenarios, have crossover animation appeal in Disney's 'Frozen'
2014-03-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Simulation-based engineering science (SBES) allows researchers to predict the effects of building explosions and analyze the response of building materials to those threats. Using a $400,000, five-year CAREER grant from the National Science Foundation, researchers at the University of Missouri developed the Material Point Method (MPM) a computer-generated tool that not only creates blast scenarios that informs blast and impact resistant materials and design, but also is crossing over into Hollywood animation—most recently, Disney's Oscar-winning animated ...
Exposure to snuff smoke in non-smokers fell by 90 percent after the tobacco control laws
2014-03-18
Researchers of the Tobaco Control Unit of the Catalan Institute of Oncology (ICO) and the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) evaluated exposure to snuff smoke in nonsmokers before the entry into force of the first Spanish smoking ban and after the launch of the second law (2011 ) in the city of Barcelona.
Salivary cotinine
Cotinine is a nicotine derived substance that is used as a marker of exposure to snuff smoke in nonsmokers. Researchers at the ICO- IDIBELL measured the concentration of this substance in the saliva of those surveyed and found to have ...
In IBS, non-GI issues are more powerful than symptoms in patients' health perceptions
2014-03-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Social relationships, fatigue and other coexisting medical problems have a stronger effect on how patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) rate their overall health than the severity of their gastrointestinal symptoms, a University at Buffalo study has found.
"Our findings suggest that in IBS patients and possibly patients with other diseases as well, health perceptions depend to a much larger extent on non-biomedical factors than those of us who are health care providers have ever suspected," says lead author Jeffrey Lackner, PsyD, associate professor ...
Sorption energy storage and conversion for cooling and heating
2014-03-18
In many industrialized countries, city skylines are dominated by imposing glass façades and skyscrapers made of concrete and steel. There is a drawback to these magnificent structures, though – they often get very hot in the summer, so they mostly need elaborate and costly air conditioning systems. And these already account for some 14 percent of Germany's annual energy consumption. Experts reckon that total cooling requirements in buildings will triple by 2020.
Cooling and heating using metal organic frameworks
Thermally driven cooling systems are one possible alternative ...
What factors contribute to sexual assault in the military and what can be done to prevent it?
2014-03-18
New Rochelle, NY, March 18, 2014–Recent high-profile cases have drawn attention to the problem of sexual assault in the U.S. military, the effects on survivors, and the actions and response of military leadership. Issues such as why there is more sexual assault in the military than in the general population, why it is under-reported, and what preventive approaches should the military adopt are explored in a provocative Roundtable Discussion published in the preview issue of Violence and Gender, a new peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article ...
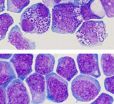
Major breakthrough in developing new cancer drugs: Capturing leukemic stem cells
2014-03-18
This news release is available in French.
The Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer (IRIC) at the Université de Montréal (UdeM), in collaboration with the Maisonneuve-Rosemont Hospital's Quebec Leukemia Cell Bank, recently achieved a significant breakthrough thanks to the laboratory growth of leukemic stem cells, which will speed up the development of new cancer drugs.
In a recent study published in Nature Methods, the scientists involved describe how they succeeded in identifying two new chemical compounds that allow to maintain leukemic stem cells ...
Getting rid of bad vibrations
2014-03-18
Whether you're looking at hairy spider legs, the alien-like faces of ants, or the spiky-looking surfaces of pollen – a scanning electron microscope delivers high-resolution images that are rich in detail. But you can't get perfect images unless you protect the microscope from vibration. If someone walking across the room or an elevator going up and down between nearby floors makes the table shake, you're unlikely to get good results. The simplest way to quell vibrations is to put the microscope on a granite base – a stone so heavy that it dampens vibrations occurring at ...
Who's afraid of math? Study finds some genetic factors
2014-03-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study of math anxiety shows how some people may be at greater risk to fear math not only because of negative experiences, but also because of genetic risks related to both general anxiety and math skills.
The study, which examined how fraternal and identical twins differ on measures of math anxiety, provides a revised view on why some children – and adults – may develop a fear of math that makes it more difficult for them to solve math problems and succeed in school.
"We found that math anxiety taps into genetic predispositions in two ways: people's ...
Suppressing unwanted memories reduces their unconscious influence on behavior
2014-03-18
Researchers part-funded by the Medical Research Council (MRC) have shown that, contrary to what was previously assumed, suppressing unwanted memories reduces their unconscious influences on subsequent behaviour, and have shed light on how this process happens in the brain.
The study, published online in PNAS, challenges the idea that suppressed memories remain fully preserved in the brain's unconscious, allowing them to be inadvertently expressed in someone's behaviour. The results of the study suggest instead that the act of suppressing intrusive memories helps to disrupt ...
Lessons from a meadow
2014-03-18
For almost 40 years, field scientists strapped on cross-country skis, shouldered backpacks with supplies and set out over three miles of snow and rocks to a field station by a meadow high in the Rocky Mountains as soon as the snow began melting. Every other day, they counted each flower they found, identified the plant it belonged to and kept meticulous records of their observations.
Their observations provide the longest-running scientific study of its kind and tell a story of biological change that teaches scientists new lessons about phenology – the timing of biological ...
Supplements not associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease in elderly
2014-03-18
Bottom Line: Daily dietary supplements of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (also found in fish) or lutein and zeaxanthin (nutrients found in green leafy vegetables) were not associated with reduced risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in elderly patients with the eye disease age-related macular degeneration.
Author: The writing group for the Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) clinical trial.
Background: Diet studies have suggested that increased intake of fish, a source of omega (ω)-3 fatty acids, can reduce rates of cardiac death, death from all other ...
Study finds high utilization of neuroimaging for headaches despite guidelines
2014-03-18
Bottom Line: Neuroimaging for headaches is frequently ordered by physicians during outpatient visits, despite guidelines that recommend against such routine procedures.
Author: Brian C. Callaghan, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
Background: Most headaches are due to benign causes, and multiple guidelines have recommended against routine neuroimaging for headaches.
How the Study Was Conducted: The authors analyzed National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data for all headache visits for patients 18 years or older ...
The frozen truth about glaciers, climate change and our future
2014-03-18
Lewis Owen has been scraping out icy fragments of history's truth from one of the most glaciated regions on Earth for the past 25 years.
His frequent excursions to Tibet and the Himalayas have led the University of Cincinnati professor of geology to some cold, hard facts.
Owen knows climate change is immortal – fluctuating across millennia, patiently building toward moments when circumstances are ripe for apocalypse. It was true thousands of years ago, when rapid climate change had profound effects on landscapes and the creatures that lived on them. That scenario could ...
Rice study: Simple changes to homework improved student learning
2014-03-18
A new study offers evidence that simple and inexpensive changes to existing courses can help students learn more effectively.
The study from Rice University and Duke University found that making a few changes to homework assignments in an upper-level undergraduate engineering course at Rice led to improved scores on exams. The study appears this week in the journal Educational Psychology Review.
The findings by a team from Rice's Center for Digital Learning and Scholarship and Duke's Department of Psychology and Neuroscience demonstrate how technology and cognitive ...
[1] ... [3852]
[3853]
[3854]
[3855]
[3856]
[3857]
[3858]
[3859]
3860
[3861]
[3862]
[3863]
[3864]
[3865]
[3866]
[3867]
[3868]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.