Growing rice the sustainable way: LEGATO holds its 3rd annual conference
2014-03-19
In a world facing the challenges of climate change, demographic boom and deficit in food resources, the word "sustainable" and the concept behind it become increasingly relevant. Sustainability in the way humanity uses available resources is key to a brighter and greener future.
In the context of sustainable food production, there is a clear need for crop productivity increases and diversification. Optimising rice ecosystem functions and services in Southeast Asia and their stabilisation under future land use and climate change, is the main focus of the project LEGATO ...
Radiation damage at the root of Chernobyl's ecosystems
2014-03-19
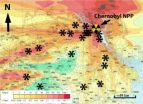
Radiological damage to microbes near the site of the Chernobyl disaster has slowed the decomposition of fallen leaves and other plant matter in the area, according to a study just published in the journal Oecologia. The resulting buildup of dry, loose detritus is a wildfire hazard that poses the threat of spreading radioactivity from the Chernobyl area.
Tim Mousseau, a professor of biology and co-director of the Chernobyl and Fukushima Research Initiatives at the University of South Carolina, has done extensive research in the contaminated area surrounding the Chernobyl ...
Research reveals true value of cover crops to farmers, environment
2014-03-19
Planting cover crops in rotation between cash crops -- widely agreed to be ecologically beneficial -- is even more valuable than previously thought, according to a team of agronomists, entomologists, agroecologists, horticulturists and biogeochemists from Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
"As society places increasing demands on agricultural land beyond food production to include ecosystem services, we needed a new way to evaluate 'success' in agriculture," said Jason Kaye, professor of biogeochemistry. "This research presents a framework for considering ...
Researchers identify potential new therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar
2014-03-19
DALLAS – March 19, 2014 – A UT Southwestern Medical Center study has identified a new potential therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar, a finding that could help the estimated 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes.
Researchers showed that lipid molecules called phosphatidic acids enhance glucose production in the liver. These findings suggest that inhibiting or reducing production of phosphatidic acids may do the opposite.
“This study establishes a role for phosphatidic acids in enhancing glucose production by the liver and identifies enzymes involved ...
NASA sees ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian affect Indonesia
2014-03-19
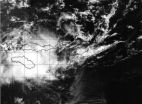
The remnants of former Tropical Cyclone Gillian moved out of the Southern Pacific Ocean and into the Indian Ocean only to trigger warnings and watches for part of Indonesia on March 19. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the stubborn storm and took a visible image of the re-organizing tropical low pressure area.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Gillian's remnants on March 19 at 05:30 UTC/1:30 a.m. EDT and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible picture of the storm. The image showed that the storm appeared to be well-defined, ...
Satellite sees newborn So. Pacific Tropical Storm Mike
2014-03-19
NOAA's GOES-West satellite caught the birth of Tropical Storm Mike in the Southern Pacific Ocean on March 19. Mike's formation has generated warnings for the Southern Cook Islands.
NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite captured an infrared image of newborn Tropical Storm Mike in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean on March 19 at 1200 UTC/8 a.m. EDT. Mike appeared to be a compact, rounded tropical storm with bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. NOAA's GOES-West satellite sits in a fixed orbit in space capturing visible and infrared imagery of all weather over the western ...
The scientific legacy of colonialism in Africa
2014-03-19
Colonial legacy has a significant impact on scientific productivity across the continent of Africa, according to a study by researchers at the University of Lomé, in Togo. Writing in the International Journal of Education Economics and Development, the team suggests that Africa performs relatively poorly compared with other regions of the world. Moreover, their analysis of data for the period 1994 to 2009 shows that African nations with a British colonial legacy are much more productive than countries with French or other history. This, the team adds, correlates with superior ...
French Alps Property Market Witnesses a Surge in Interest From International Buyers
2014-03-19
Demand for property in the Alps is on the increase with a growing number of foreigners looking to invest in resorts such as Chamonix, according to new figures.
Property agents in Chamonix, a resort in France's Savoie region and one of the key Alpine winter destinations, are reporting soaring property demand, much of which is being driven by the international buyers. The real estate agents also revealed an increase in property prices of more than eight per cent during 2013. This surge in interest can be attributed to the infrastructure upgrades in Chamonix and also to ...
Catching the early spread of breast cancer
2014-03-19
DALLAS, March 19, 2014 — When cancer spreads from one part of the body to another, it becomes even more deadly. It moves with stealth and can go undetected for months or years. But a new technology that uses "nano-flares" has the potential to catch these lurking, mobilized tumor cells early on. Today, scientists presented the latest advances in nano-flare technology as it applies to the detection of metastatic breast cancer cells.
The report was one of more than 10,000 at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). The meeting is taking ...
Noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool shows unprecedented detection rates
2014-03-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. — March 17, 2014 — Results of a clinical trial of Cologuard show unprecedented rates of precancer and cancer detection by a noninvasive test. The detection rates are similar to those reported for colonoscopy. The results were published in the March 20 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). Cologuard was co-developed by Mayo Clinic and Exact Sciences.
Cologuard, is a noninvasive sDNA test for the early detection of colorectal precancer and cancer. The Cologuard test is based on a stool sample that is analyzed for DNA signatures of precancer ...
New, noninvasive, stool-based colorectal cancer screening test
2014-03-19
(New York, March 19, 2014) – A new, non-invasive, stool-based screening test detected 92% of colorectal cancer (CRC), according to a multicenter trial published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine. The new test, which is not yet approved by the FDA, allows patients to collect a sample at home without the need for bowel preparation or diet restrictions.
Unlike other available stool-based CRC screening tests, which rely solely on detecting occult blood in the stool, this new test, called "Cologuard", developed and patented by Exact Sciences, detects both ...
Work shines light on Hox genes responsible for firefly lantern development
2014-03-19
It's difficult to identify a single evolutionary novelty in the animal kingdom that has fascinated and intrigued mankind more than the lantern of the firefly. Yet to this day, nothing has been known about the genetic foundation for the formation and evolution of this luminescent structure.
But now, new work from a former Indiana University Bloomington graduate student and his IU Ph.D. advisor offers for the first time a characterization of the developmental genetic basis of this spectacular morphological novelty -- the firefly's photic organ -- and the means by which this ...
Winners and losers in globalization of world's economy, health and education
2014-03-19
Globalization has made the world a better and more equal place for many more people than was the case a few decades ago. However, it has also created two well-defined worlds of poor countries and wealthy nations, according to Vanesa Jordá and José María Sarabia of the University of Cantabria in Spain. In an article published in Springer's journal Applied Research in Quality of Life, they studied the distribution of well-being over the last wave of globalization between 1980 and 2011.
Well-being is generally described as the state of being happy, healthy or prosperous. ...
Magnetic behavior discovery could advance nuclear fusion
2014-03-19
ANN ARBOR—Inspired by the space physics behind solar flares and the aurora, a team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Princeton has uncovered a new kind of magnetic behavior that could help make nuclear fusion reactions easier to start.
Fusion is widely considered the ultimate goal of nuclear energy. While fission leaves behind radioactive waste that must be stored safely, fusion generates helium, a harmless element that is becoming scarce. Just 250 kilograms of fusion fuel can match the energy production of 2.7 million tons of coal.
Unfortunately, it ...
Increased risk of relapse omitting RT in early PET scan negative Hodgkin lymphoma
2014-03-19
Interim analysis of the intergroup EORTC-LYSA-FIL 20051 H10 trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology indicates an increased risk of early relapse when omitting radiotherapy in early PET scan negative patients with stage I/II Hodgkin's lymphoma. Early outcome, however, was excellent in both arms, and the final analysis should reveal whether these initial findings are maintained over time.
Dr. J.M.M. Raemaekers of the Radboud university medical center Nijmegen, The Netherlands, and central coordinator of the study says, "The standard treatment for patients with ...
Study finds forest corridors help plants disperse their seeds
2014-03-19
A forest in South Carolina, a supercomputer in Ohio and some glow-in-the-dark yarn have helped a team of field ecologists conclude that woodland corridors connecting patches of endangered plants not only increase dispersal of seeds from one patch to another, but also create wind conditions that can spread the seeds for much longer distances.
The idea for the study emerged from modern animal conservation practices, where landscape connectivity – the degree to which landscapes facilitate movement – is being used to counteract the impacts of habitat loss and fragmentation ...
Inflammation mobilizes tumor cells
2014-03-19
Researchers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have discovered a novel feedback mechanism that provides a mechanistic link between chronic inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Malignant tumors pose a major threat to survival largely because they shed mobile cells that can form secondary tumors in other tissues. This process requires a fundamental change in the character of cells within the primary tumor, insofar as members of a localized cell mass must be converted into actively migrating cells that invade into the surrounding tissue and blood vessels, and ...
IU, Regenstrief study: New noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool highly accurate
2014-03-19
INDIANAPOLIS -- An Indiana University and Regenstrief Institute study of nearly 10,000 average-risk, asymptomatic men and women from 90 sites across the United States reports that a multi-target stool DNA test -- a new noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool that has not yet been approved for sale by the Food and Drug Administration -- detects 92.3 percent of colon cancers, compared to only 73.8 percent of cancers detected by a fecal immunochemical test, the most commonly used noninvasive test today.
Study results were published online March 19 and in the April ...
Earliest evidence of limb bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million year old fish
2014-03-19
This week in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, a team of French and Swedish researchers present the earliest fossil evidence for the presence of bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million-year-old fish.
Long bones, which are found in the limb of tetrapods, are not only important for locomotion and supporting the weight of the body, but also host the bone marrow. The latter plays a major role in haematopoiesis, i.e. the formation of blood cells. In a healthy adult human, about a hundred billion to one trillion new blood cells are produced every day to maintain ...
Internists must play a larger role in managing menopausal symptoms
2014-03-19
New Rochelle, NY, March 19, 2014—The number of menopausal women is projected to reach 50 million by 2020. With changing views on appropriate therapies to control symptoms and new treatments available and on the horizon, most internists lack the core competencies and experience to meet the needs of women entering menopause, according to a provocative Commentary published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
The ...
Genetic test could improve colon cancer screening
2014-03-19
A non-invasive test that includes detection of the genetic abnormalities related to cancer could significantly improve the effectiveness of colon cancer screening, according to research published by a team of scientists including David Ransohoff, MD, professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine and UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center member. The large-scale, cross-sectional study was published online today in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The study compared two different types of tests used for screening colorectal cancer: a non-invasive, multitarget ...
Strategies for teaching common core to teens with autism show promise
2014-03-19
Scientists at UNC's Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) report that high school students with autism can learn under Common Core State Standards (CCSS), boosting their prospects for college and employment. Newly published recommendations from FPG's team also provide strategies for educating adolescents with autism under a CCSS curriculum.
"The number of students with autism who enter high school settings continues to grow," said Veronica P. Fleury, lead author and postdoctoral research associate with FPG's Center on Secondary Education for Students with ...
New technique makes LEDs brighter, more resilient
2014-03-19
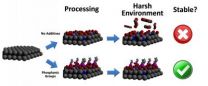
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new processing technique that makes light emitting diodes (LEDs) brighter and more resilient by coating the semiconductor material gallium nitride (GaN) with a layer of phosphorus-derived acid.
"By coating polar GaN with a self-assembling layer of phosphonic groups, we were able to increase luminescence without increasing energy input," says Stewart Wilkins, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work. "The phosphonic groups also improve stability, making the GaN less likely ...
Chemo-free treatment a possibility for leukemia/lymphoma
2014-03-19
Patients with terminal forms of leukaemia and lymphoma who have run out of treatment options could soon benefit from a new drug, which not only puts an end to chemotherapy and has virtually no side effects but also improves a patient's life expectancy and quality of life.
It has been described as a breakthrough in cancer treatment by a leading professor in haematology, who presented the findings of the Phase 1 trial at an international conference in New Orleans in December 2013.
Professor Simon Rule, Consultant Haematologist at Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust and researcher ...
Neuroscience 'used and abused'
2014-03-19
Influential policy-informing 'evidence' that children's brains are irreversibly 'sculpted' by parental care is based on questionable evidence.
The researchers warn that the success that advocates of 'brain-based' parenting have had in influencing government policy could undermine parent-child relationships.
The study identified that although there is a lack of scientific foundation to many of the claims of 'brain-based' parenting, the idea that years 0-3 are neurologically critical is now repeated in policy documents and has been integrated into professional training ...
[1] ... [3831]
[3832]
[3833]
[3834]
[3835]
[3836]
[3837]
[3838]
3839
[3840]
[3841]
[3842]
[3843]
[3844]
[3845]
[3846]
[3847]
... [8814]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.