Large feathered dinosaur species discovered in North America
2014-03-19
Fossils found in western North America reveal a new species of large-bodied, feathered oviraptorosaurian theropod dinosaur from the latest Cretaceous Period, according to a paper published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 19, 2014 by Matthew Lamanna from Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pennsylvania and colleagues.
Known for their beaks, long necks, and relatively short tails, the bird-like oviraptorosaurian group contains dinosaurs with body sizes ranging from a few kilograms to more than one metric ton. The scientists described three well-preserved partial ...
Fossilized bighorn sheep poop reveals early Holocene population
2014-03-19
Genetic analysis of ancient poop found off the coast of Mexico suggests bighorn sheep may be native to the island, according to a paper published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 19, 2014 by Benjamin Wilder from University of California Riverside and colleagues.
Bighorn sheep were not thought to inhabit Tiburón Island, the largest island in the Gulf of California and Mexico, prior to their introduction in 1975. Scientists discovered fossilized dung in the mountains of Tiburón Island that challenges that assumption. Scientists compared the pellet-shaped poop ...
Bighorn sheep went extinct on desert island in Gulf of California, study finds
2014-03-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Using ancient DNA analysis and other techniques, a research team led by conservation biologists at the University of California, Riverside has determined that bighorn sheep, so named for their massive spiral horns, became extinct on Tiburón Island, a large and mostly uninhabited island just off Sonora, Mexico, in the Gulf of California, sometime in the last millennium — specifically between the 6th and 19th centuries.
The result, published March 19 in PLOS ONE, is a surprise because conventional wisdom among wildlife biologists and the indigenous Seri ...
A 'chicken from hell' dinosaur
2014-03-19
SALT LAKE CITY, March 19, 2014 – Scientists from Carnegie and Smithsonian museums and the University of Utah today unveiled the discovery, naming and description of a sharp-clawed, 500-pound, bird-like dinosaur that roamed the Dakotas with T. rex 66 million years ago and looked like an 11 ½-foot-long "chicken from hell."
"It was a giant raptor, but with a chicken-like head and presumably feathers. The animal stood about 10 feet tall, so it would be scary as well as absurd to encounter," says University of Utah biology postdoctoral fellow Emma Schachner, a co-author of ...
Smithsonian collaborates with paleontologist team to reveal new large, feathered dinosaur
2014-03-19
A team of scientists from the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History, the Carnegie Museum of Natural History and the University of Utah has described an unusual bird-like dinosaur previously unknown to science, resembling a cross between a modern emu and a reptile. The new species, Anzu wyliei, lived 68 to 66 million years ago and was identified from three partial skeletons collected from the Upper Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation in North and South Dakota. The species belongs to Oviraptorosauria, a group of dinosaurs mostly known from fossils found in Central ...
Paleontologists announce discovery of Anzu wyliei
2014-03-19
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania…A team of researchers has announced the discovery of a bizarre, bird-like dinosaur, named Anzu wyliei, that provides paleontologists with their first good look at a dinosaur group that has been shrouded in mystery for almost a century. Anzu was described from three specimens that collectively preserve almost the entire skeleton, giving scientists a remarkable opportunity to study the anatomy and evolutionary relationships of Caenagnathidae (pronounced SEE-nuh-NAY-thih-DAY)—the long-mysterious group of theropod dinosaurs to which Anzu belongs. The ...
High-frequency breathing support for premature babies could lead to better lung function
2014-03-19
A new study led by researchers at King's College London has found that premature babies supported immediately after birth by high-frequency oscillation - a type of breathing support - had better lung function as adolescents than those who received conventional ventilation. The children ventilated with the high frequency method also showed higher academic achievement in three of eight school subjects.
The findings of the research, funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Programme and the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre ...
Studies advance potential use Of MRI magnetic fields to treat balance disorders
2014-03-19
Expanding on earlier research, Johns Hopkins researchers report that people with balance disorders or dizziness traceable to an inner-ear disturbance show distinctive abnormal eye movements when the affected ear is exposed to the strong pull of an MRI's magnetic field.
The researchers first reported in 2011 in the journal Current Biology that an MRI's magnetic field pushes on the inner ear fluid responsible for maintaining balance, causing subjects undergoing MRI scans to have jerky eye movements and dizziness.
Two new studies now suggest that these strong magnets could ...
New guidelines deem 13 million more Americans eligible for statins
2014-03-19
DURHAM, N.C. – New guidelines for using statins to treat high cholesterol and prevent cardiovascular disease are projected to result in 12.8 million more U.S. adults taking the drugs, according to a research team led by Duke Medicine scientists.
The findings for the first time quantify the impact of the American Heart Association's new guidelines, which were issued in November and generated both controversy and speculation about who should be given a prescription for statins.
In an analysis of health data published online March 19, 2014, in the New England Journal ...
Tracking endangered leatherback sea turtles by satellite, key habitats identified
2014-03-19
AMHERST, Mass. ¬– A first-of-its-kind satellite tagging study of migrating New England leatherback turtles in the North Atlantic offers a greatly improved understanding of their seasonal high-use habitats, diving activity and response to key ocean and environmental features in relation to their search behavior. Leatherbacks are considered endangered species in all the world's oceans.
The study, part of doctoral research by Kara Dodge supervised by her advisor, Molly Lutcavage of the University of Massachusetts Amherst's Large Pelagics Research Center (LPRC) in Gloucester, ...
North Shore-LIJ Cancer Institute doctors' editorial published
2014-03-19
LAKE SUCCESS, NY – Two North Shore-LIJ Cancer Institute doctors, world-renowned for their research in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), weigh in on a German study of a new drug therapy for CLL in the March 20 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine, the North Shore-LIJ Health System announced today.
CLL is one of the most common forms of blood cancers, usually affecting those later in life. In an editorial written by Kanti Rai, MD, chief of CLL Research and Treatment Program for the health system, and Jacqueline Barrientos, MD, a research hematologist on staff ...
Dry future climate could reduce orchid bee habitat
2014-03-19
ITHACA, N.Y. – During Pleistocene era climate changes, neotropical orchid bees that relied on year-round warmth and wet weather found their habitats reduced by 30 to 50 percent, according to a Cornell University study that used computer models and genetic data to understand bee distributions during past climate changes.
In previous studies, researchers have tracked male and female orchid bees and found that while females stay near their nests, male orchid bees travel, with one study concluding they roam as far as 7 kilometers per day. These past findings, corroborated ...
Diabetes in middle age may lead to brain cell loss later in life
2014-03-19
MINNEAPOLIS – People who develop diabetes and high blood pressure in middle age are more likely to have brain cell loss and other damage to the brain, as well as problems with memory and thinking skills, than people who never have diabetes or high blood pressure or who develop it in old age, according to a new study published in the March 19, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Middle age was defined as age 40 to 64 and old age as age 65 and older.
"Potentially, if we can prevent or control diabetes and high blood ...
Ruling with an iron fist could make your child pack on pounds
2014-03-19
If you're rigid with rules and skimpy on affection and dialogue with your kids, they have a greater chance of being obese, according to research presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology & Prevention/Nutrition, Physical Activity & Metabolism Scientific Sessions 2014.
Researchers followed a nationally representative group of 37,577 Canadian children aged 0 to 11. They compared kids whose parents are generally affectionate, have reasonable discussions about behavior with their child and set healthy boundaries (authoritative) with those whose parents were ...
Program taught in American Sign Language helps deaf achieve healthier weight
2014-03-19
A group of deaf adults using American Sign Language in a healthy lifestyle program successfully lost weight, according to a study presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology & Prevention/Nutrition, Physical Activity & Metabolism Scientific Sessions 2014.
In the first randomized trial of lifestyle modification or weight reduction with deaf people using American Sign Language (ASL), participants had moderate improvements in their weight and level of physical activity after a 16-week program.
"Existing mainstream programs focused on weight and weight-related ...
Spices and herbs intervention helps adults reduce salt intake
2014-03-19
Teaching people how to flavor food with spices and herbs is considerably more effective at lowering salt intake than having them do it on their own, according to research presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology & Prevention/Nutrition, Physical Activity & Metabolism Scientific Sessions 2014.
In the first phase of the study, 55 volunteers ate a low-sodium diet for four weeks. Researchers provided all foods and calorie-containing drinks. Salt is the main source of sodium in food.
In the second phase, half of the study volunteers participated in a 20-week ...
US women unfamiliar with most stroke warning signs
2014-03-19
Many U.S. women don't know most of the warning signs of a stroke, according to research presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology and Prevention/Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism 2014 Scientific Sessions.
The study is also published in the American Heart Association journal, Stroke.
In a phone survey of 1,205 U.S. women:
More than half (51 percent) of the women identified sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the face, arms or legs as a warning sign of a stroke.
Less than half (44 percent) identified difficulty speaking or garbled speech ...
Researchers identify impaired new learning in persons with Parkinson's disease
2014-03-19
West Orange, NJ. March 20, 2014. Kessler Foundation scientists collaborated with colleagues in Spain to study memory and learning in patients with Parkinson Disease (PD). They found that the Parkinson group's ability to learn new information was significantly poorer when compared with the control group. The article was published ahead of print on February 24: Chiaravalloti ND, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Deluca J, Rusu O, Pena J, García-Gorostiaga I, Ojeda N. The source of the memory impairment in Parkinson's disease: Acquisition versus retrieval. Movement Disorders 2014 Feb 24. ...
Analysis: Industry-sponsored academic inventions spur increased innovation
2014-03-19
Industry-sponsored, academic research leads to innovative patents and licenses, says a new analysis led by Brian Wright, University of California, Berkeley professor of agricultural and resource economics.
The finding calls into question assumptions that corporate support skews science toward inventions that are less accessible and less useful to others than those funded by the government or non-profit organizations.
The analysis, based on a study of two decades of records from the University of California system, is in today's science journal Nature.
The National ...
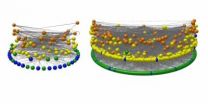
NASA's Van Allen Probes reveal zebra stripes in space
2014-03-19
Scientists have discovered a new, persistent structure in one of two radiation belts surrounding Earth. NASA's twin Van Allen Probes spacecraft have shown that high-energy electrons in the inner radiation belt display a persistent pattern that resembles slanted zebra stripes. Surprisingly, this structure is produced by the slow rotation of Earth, previously considered incapable of affecting the motion of radiation belt particles, which have velocities approaching the speed of light.
Scientists had previously believed that increased solar wind activity was the primary ...
Sometimes less is more for hungry dogs
2014-03-19
Hungry dogs would be expected to choose alternatives leading to more food rather than less food. But just as with humans and monkeys, they sometimes show a "less is more" effect. Thus conclude Kristina Pattison and Thomas Zentall of the University of Kentucky in the US, who tested the principle by feeding baby carrots and string cheese to ten dogs of various breeds. The findings are published in Springer's journal Animal Cognition.
The research was conducted on dogs that would willingly eat cheese and baby carrots when offered, but showed a preference for the cheese. ...
Alzheimer's prevention trial to monitor reactions to higher disease risk status
2014-03-19
PHILADELPHIA - A new clinical trial will soon begin testing whether early medical intervention in people at risk for Alzheimer's can slow down progression of disease pathology before symptoms emerge, as outlined in Science Translational Medicine. For the first time, people with no Alzheimer's disease symptoms will be told of their risk status before being asked to join the randomized controlled trial. As part of the overall prevention trial, Penn Medicine neurodegenerative ethics experts will monitor how learning about their risk of developing Alzheimer's impacts trial ...
NJIT physicist helps to discover a new structure in Earth's radiation belt
2014-03-19
An NJIT physicist is a collaborator in the discovery of a new structure in Earth's inner radiation belt -- a zebra-striped structure of highly energized electrons that could endanger humans in space and also damage low-earth navigation and communication satellites.
And surprisingly, the new structure is produced not by solar activity but by Earth's slow rotation. Scientists had previously thought Earth's rotation couldn't affect the motion of radiation belt particles. The data supporting these discoveries comes from a measuring device aboard the two NASA Van Allen Probes ...
Scientists describe gut bacteria that cause sepsis in preterm infants
2014-03-19
Researchers studying intestinal bacteria in newborns have characterized the gut bacteria of premature infants who go on to develop sepsis, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition caused by bacteria in the bloodstream. Their findings suggest new strategies for the early detection and prevention of severe bloodstream infections. The research was funded by several components of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)—the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), ...
Ancient food webs developed modern structure soon after mass extinction
2014-03-19
Researchers from the Santa Fe Institute and the Smithsonian Institution have pieced together a highly detailed picture of feeding relationships among 700 mammal, bird, reptile, fish, insect, and plant species from a 48 million year old lake and forest ecosystem.
Their analysis of fossilized remains from the Messel deposit near Frankfurt, Germany, provides the most compelling evidence to date that ancient food webs were organized much like modern food webs. Their paper describing the research appears online and open access this week in Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
[1] ... [3829]
[3830]
[3831]
[3832]
[3833]
[3834]
[3835]
[3836]
3837
[3838]
[3839]
[3840]
[3841]
[3842]
[3843]
[3844]
[3845]
... [8814]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.