Subrata Roy Talks About India's Economic Growth and the Necessity of Good Talent to Achieve the Target
2014-02-18
India is trying to raise 500 million skilled people by the end of 2022. How can companies help to make this dream comes true?
I think the human resource development is the best part of Indian corporate, working as the biggest platform of trained people. Thereby, they should try hard to get this target. It is also important to develop the entrepreneurial skills. The corporate sector should come forward to increase the job opportunities and take the employment as investment to boost up the economical condition of the country.
In such a doubtful economic condition, ...
Ten Pretty Good Reasons to Hire Boston and Rhode Island (RI) Wedding DJs Ra-Mu and The Crew for your 2014-2015 Boston-Providence-Newport Reception
2014-02-18
Ten Pretty Good Reasons to Hire Boston and Rhode Island (RI) Wedding DJs Ra-Mu and The Crew for your 2014-2015 Boston-Providence-Newport Reception
10. Ra-Mu and the Crew are CONSISTENT, DOMINANT, AND CLUTCH in getting your guests on the dance floor.
9. Ra-Mu and the Crew have the most number of positive reviews than any other DJ company in Rhode Island.
8. Ra-Mu and the Crew have ample video footage online(youtube and vimeo) to showcase talent before potential clients sign a contract.
7. Ra-Mu and the Crew is excited about your wedding. We are PASSIONATE about ...
Visix Takes Home Bronze Content Award at Digital Signage Expo
2014-02-18
Visix is honored to receive a Bronze DSE Content Award for their Western Iowa Tech Community College (WITCC) digital signage design. Robert Brown, Creative Content Artist for Visix, won the award for his custom interactive wayfinding and traditional digital signage for the school.
"Each year at DSE, they award the best in ground-breaking creative projects, and I'm honored to have been recognized," says Brown. "We always aim to bring a unique design approach to each project that not only meets the customer's technical and branding requirements, but will ...
OPTEX and Mobile Pro Systems Create a Rapid-Deployment Security Solution
2014-02-18
Optex Redscan laser detectors provide rugged and reliable detection in an innovative pole-mounted, short-term, mobile surveillance system capable of wireless communication, perimeter detection, lighting and remote monitoring. The security system is being used by Cove Properties, one of Alberta Canada's premier luxury condo builders, to secure construction sites from theft and vandalism in the harsh elements of northern Canada.
Cove Properties worked with 2020 DSS, a leading-edge digital security system company in Edmonton, Alberta, who created a unique solution based ...
RealeyeZ Takes 3D Animation to the Next Level with RealHDTM MooV
2014-02-18
Online shoppers are accustomed to viewing consumer products in 360 degrees. Now RealeyeZ3D is taking the power of RealHDTM to the next level. Their new product, RealHDTM MooV, offers moving features that are not available elsewhere in video or 3D marketing and merchandising.
"RealHDTM Moov uses the MPEG-4 movie format," says company founder and CEO, Ofer Rubin. "It is compatible with Apple and all other platforms and responsive to all screen sizes. Together with its new scalability. It will look like retailers spent tens of thousands of dollars on high-end ...
Sharon Kenig Named Associate Vice President of Credit & Syndication for AmeriQuest Transportation Services
2014-02-18
Sharon Kenig has been appointed to the position of Associate Vice President of Credit & Syndication for AmeriQuest Transportation Services, a leading provider of comprehensive fleet management services, financial solutions, and operational support services.
Kenig joined AmeriQuest in 2011 and is responsible for closing all syndication transactions ranging from $100K to $22M. In addition, she provides all credit analyses and ultimate underwriting decisions in support of all sales and syndication efforts, and conducts pricing analyses and economic summaries for funding ...
Cyclomundo, the Premier Cyclotourism Agency in France, Suggests Tips for Saving on Bicycle Trips Without Skimping on the Experience
2014-02-18
With spring fast approaching, Cyclomundo (http://www.cyclomundo.com/) believes there's no better time than now to consider planning a cycling tour of one of France's many wine-growing regions, the Swiss Alps, the breathtaking Mediterranean coast, or sensuous and historic Tuscany. The French cyclotourism agency prides itself on offering intimate, memorable bike tours at competitive prices. Now, the agency is suggesting even more ways for tourists to save their hard-earned money.
Most tours with Cyclomundo are self-guided, which has a couple of distinct advantages. Self-guided ...
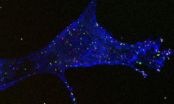
Mechanism of dengue virus entry into cells
2014-02-18
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 17, 2014 -- Dengue fever, an infectious tropical disease caused by a mosquito-borne virus, afflicts millions of people each year, causing fever, headache, muscle and joint pains and a characteristic skin rash. In some people the disease progresses to a severe, often fatal, form known as dengue hemorrhagic fever. Despite its heavy toll, the prevention and clinical treatment of dengue infection has been a "dramatic failure in public health compared to other infectious diseases like HIV," said Ping Liu of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. ...
It's alive! Bacteria-filled liquid crystals could improve biosensing
2014-02-18
VIDEO:
Enabled by the birefringence of liquid crystal, motion of 24nm thick bacteria flagella now is easily visible using a simple polarizing microscope.
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 17, 2014 -- Plop living, swimming bacteria into a novel water-based, nontoxic liquid crystal and a new physics takes over. The dynamic interaction of the bacteria with the liquid crystal creates a novel form of soft matter: living liquid crystal.
The new type of active ...
Finding ways to detect and treat Alzheimer's disease
2014-02-18
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 17, 2014 -- Alzheimer's disease has long been marked by progress -- but not the kind of progress the medical community seeks. It is the most common form of dementia among older Americans, and its risk increases with increasing age; for those living with the disease, its ravages get worse over time; and as we move into the 21st century, it will place a greater and greater burden on society. The number of Americans living with Alzheimer's has doubled since 1980 and is expected to triple again by 2050.
Sadly, Alzheimer's disease has been the least prone ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Feb. 18, 2014
2014-02-18
1. Aortic valve replacement improves function but may not improve quality of life
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) improves functional status but may not improve overall quality of life, according to an article being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Aortic stenosis (AS) is the most common valvular heart disease in developing countries and it affects up to 3 percent of adults older than 75. In recent years, TAVR has emerged as an alternative treatment to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) for high-risk or inoperable patients with symptomatic ...
Stress hormones in traders may trigger 'risk aversion' and contribute to market crises
2014-02-18
High levels of the stress hormone cortisol may contribute to the risk aversion and 'irrational pessimism' found among bankers and fund managers during financial crises, according to a new study.
The study's authors say that risk takers in the financial world exhibit risk averse behaviour during periods of extreme market volatility – just when a crashing market most needs them to take risks – and that this change in their appetite for risk may be "physiologically-driven", specifically by the body's response to cortisol. They suggest that stress could be an "under-appreciated" ...
How well do football helmets protect players from concussions?
2014-02-18
PHILADELPHIA – A new study finds that football helmets currently used on the field may do little to protect against hits to the side of the head, or rotational force, an often dangerous source of brain injury and encephalopathy. The study released today will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014.
"Protection against concussion and complications of brain injury is especially important for young players, including elementary and middle school, high school and college athletes, whose still-developing ...
How evolution shapes the geometries of life
2014-02-18
Why does a mouse's heart beat about the same number of times in its lifetime as an elephant's, although the mouse lives about a year, while an elephant sees 70 winters come and go? Why do small plants and animals mature faster than large ones? Why has nature chosen such radically different forms as the loose-limbed beauty of a flowering tree and the fearful symmetry of a tiger?
These questions have puzzled life scientists since ancient times. Now an interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Maryland and the University of Padua in Italy propose a thought-provoking ...
Theory on origin of animals challenged: Animals needs only extremely little oxygen
2014-02-18
One of science's strongest dogmas is that complex life on Earth could only evolve when oxygen levels in the atmosphere rose to close to modern levels. But now studies of a small sea sponge fished out of a Danish fjord shows that complex life does not need high levels of oxygen in order to live and grow.
The origin of complex life is one of science's greatest mysteries. How could the first small primitive cells evolve into the diversity of advanced life forms that exists on Earth today? The explanation in all textbooks is: Oxygen. Complex life evolved because the atmospheric ...
Researchers warn against abrupt stop to geoengineering method
2014-02-18
As a range of climate change mitigation scenarios are discussed, University of Washington researchers have found that the injection of sulfate particles into the atmosphere to reflect sunlight and curb the effects of global warming could pose a severe threat if not maintained indefinitely and supported by strict reductions in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
The new study, published today, 18 February, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental Research Letters, has highlighted the risks of large and spatially expansive temperature increases if solar radiation management ...
First biological marker for major depression could enable better diagnosis and treatment
2014-02-18
Teenage boys who show a combination of depressive symptoms and elevated levels of the 'stress hormone' cortisol are up to fourteen times more likely to develop major depression than those who show neither trait, according to research funded by the Wellcome Trust.
In a study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the University of Cambridge have identified the first biomarker – a biological signpost – for major, or clinical, depression. They argue that this could help identify those boys in particular at greatest risk ...
Why tackling appetite could hold the key to preventing childhood obesity
2014-02-18
A heartier appetite is linked to more rapid infant growth and to genetic predisposition to obesity, according to two papers published in JAMA Pediatrics today (Monday).
The studies investigated how weight gain is linked to two key aspects of appetite, namely lower satiety responsiveness (a reduced urge to eat in response to internal 'fullness' signals) and higher food responsiveness (an increased urge to eat in response to the sight or smell of nice food).
The first paper reveals that infants with a heartier appetite grew more rapidly up to age 15 months, potentially ...
Ancient herring catch nets fisheries weakness
2014-02-18
Archaeological data indicate modern herring management needs to take a longer look into the past to manage fisheries for the future says a new study involving Simon Fraser University researchers.
That is one of the key findings in the study, just published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). SFU researchers Iain McKechnie, Dana Lepofsky and Ken Lertzman, and scientists in Ontario, Alberta and the United States are its co-authors.
The study is one of many initiatives of the SFU-based Herring School, a group of researchers that investigates ...
'It takes a village' -- Community-based methods for improving maternal and newborn health
2014-02-18
A series of studies are published in a special supplement that presents results of the Maternal and Newborn Health in Ethiopia Partnership—a three-year pilot program funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation with the goal of improving the health of Ethiopian mothers and their newborns. This special issue of the Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health is published by Wiley on behalf of the American College of Nurse-Midwives.
High mortality rates for pregnant women and newborns continue to be a major health concern in Africa, with Ethiopia being one of the most affected ...
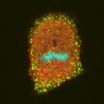
Mitosis mystery solved as role of key protein is confirmed
2014-02-18
Researchers from Warwick Medical School have discovered the key role of a protein in shutting down endocytosis during mitosis, answering a question that has evaded scientists for half a century.
The study, published today in the journal eLife, is the first to outline the role of actin, a protein, in shutting down clathrin-dependent endocytosis during mitosis.
Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb molecules that are too large to pass through the plasma membrane, such as proteins. Clathrin-dependent endocytosis is the most common route for this. Clathrin, a ...
Learning to see better in life and baseball
2014-02-17
With a little practice on a computer or iPad—25 minutes a day, 4 days a week, for 2 months—our brains can learn to see better, according to a study of University of California, Riverside baseball players reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on February 17. The new evidence also shows that a visual training program can sometimes make the difference between winning and losing.
The study is the first, as far as the researchers know, to show that perceptual learning can produce improvements in vision in normally seeing individuals.
"The demonstration that ...
Outsmarting nature during disasters
2014-02-17
The dramatic images of natural disasters in recent years, including hurricanes Katrina and Sandy and the Tohoku, Japan, earthquake and tsunami, show that nature, not the people preparing for hazards, often wins the high-stakes game of chance.
"We're playing a high-stakes game against nature without thinking about what we're doing," geophysicist Seth Stein of Northwestern University said. "We're mostly winging it instead of carefully thinking through the costs and benefits of different strategies. Sometimes we overprepare, and sometimes we underprepare."
Stein will ...
Zoonotic diseases and global viral pandemics
2014-02-17
Emergence of new microbes
While many endemic infectious diseases of humans have been largely contained, new microbes continue to emerge to threaten human and animal health. Such emerging infectious diseases are not confined to humans and their livestock but extend to wildlife ecosystems; the finely-tuned dynamic balance of which is destabilised by human interventions. The changes in the scale and manner of livestock production and marketing, the increase of global travel and trade including the trade in domestic livestock as well as the pet animal trade, the increasing ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 17, 2014
2014-02-17
Neurotensin conjugate provides pain relief in animal models
The small peptide neurotensin is a potent regulator of dopamine signaling and can provide dramatic pain relief; however, the blood brain barrier provides a substantial challenge toward clinical use of neurotensin for analgesia. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Philippe Sarret and colleagues at Université de Sherbrooke generated a conjugate of neurotensin with a peptide able to cross the blood brain barrier and evaluated the analgesic effects of this molecule in animal models of pain. The ...
[1] ... [3978]
[3979]
[3980]
[3981]
[3982]
[3983]
[3984]
[3985]
3986
[3987]
[3988]
[3989]
[3990]
[3991]
[3992]
[3993]
[3994]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.