AGU: Uncovering the secret world of the Plastisphere
2014-02-24
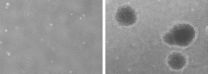
HONOLULU – Scientists are revealing how microbes living on floating pieces of plastic marine debris affect the ocean ecosystem, and the potential harm they pose to invertebrates, humans and other animals. New research being presented here today delves deeper into the largely unexplored world of the "Plastisphere" – an ecological community of microbial organisms living on ocean plastic that was first discovered last year.
When scientists initially studied the Plastisphere, they found that at least 1,000 different types of microbes thrive on these tiny plastic islands, ...
Pinwheel 'living' crystals and the origin of life
2014-02-24
ANN ARBOR—Simply making nanoparticles spin coaxes them to arrange themselves into what University of Michigan researchers call 'living rotating crystals' that could serve as a nanopump. They may also, incidentally, shed light on the origin of life itself.
The researchers refer to the crystals as 'living' because they, in a sense, take on a life of their own from very simple rules.
Sharon Glotzer, the Stuart W. Churchill Collegiate Professor of Chemical Engineering, and her team found that when they spun individual nanoparticles in a simulation—some clockwise and some ...
New study supports body shape index as predictor of mortality
2014-02-24
In 2012, Dr. Nir Krakauer, an assistant professor of civil engineering in CCNY's Grove School of Engineering, and his father, Dr. Jesse Krakauer, MD, developed a new method to quantify the risk specifically associated with abdominal obesity.
A follow-up study, published February 20 by the online journal PLOS ONE, supports their contention that the technique, known as A Body Shape Index (ABSI), is a more effective predictor of mortality than Body Mass Index (BMI), the most common measure used to define obesity.
The team analyzed data for 7,011 adults, 18+, who participated ...
Volcanoes, including Mount Hood in the US, can quickly become active
2014-02-24
New research results suggest that magma sitting 4-5 kilometers beneath the surface of Oregon's Mount Hood has been stored in near-solid conditions for thousands of years.
The time it takes to liquefy and potentially erupt, however, is surprisingly short--perhaps as little as a couple of months.
The key to an eruption, geoscientists say, is to elevate the temperature of the rock to more than 750 degrees Celsius, which can happen when hot magma from deep within the Earth's crust rises to the surface.
It was the mixing of hot liquid lava with cooler solid magma that ...
Geosphere covers Mexico, the Colorado Plateau, Russia, and offshore New Jersey
2014-02-24
Boulder, Colo., USA – New Geosphere postings cover using traditional geochemistry with novel micro-analytical techniques to understand the western Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt; an investigation of mafic rock samples from a volcanic field near Yampa, Colorado, travertine deposits in the southeastern Colorado Plateau of New Mexico and Arizona; a study "Slushball Earth" rocks from Karelia, Russia, using field and micro-analytical techniques; and an addition to the "The History and Impact of Sea-level Change Offshore New Jersey" special issue.
Abstracts for these and other ...
Building artificial cells will be a noisy business
2014-02-24
Engineers like to make things that work. And if one wants to make something work using nanoscale components—the size of proteins, antibodies, and viruses—mimicking the behavior of cells is a good place to start since cells carry an enormous amount of information in a very tiny packet. As Erik Winfree, professor of computer science, computation and neutral systems, and bioengineering, explains, "I tend to think of cells as really small robots. Biology has programmed natural cells, but now engineers are starting to think about how we can program artificial cells. We want ...
Study evaluates role of infliximab in treating Kawasaki disease
2014-02-24
Kawasaki Disease (KD) is a severe childhood disease that many parents, even some doctors, mistake for an inconsequential viral infection. If not diagnosed or treated in time, it can lead to irreversible heart damage.
Signs of KD include prolonged fever associated with rash, red eyes, mouth, lips and tongue, and swollen hands and feet with peeling skin. The disease causes damage to the coronary arteries in a quarter of untreated children and may lead to serious heart problems in early adulthood. There is no diagnostic test for Kawasaki disease, and current treatment fails ...
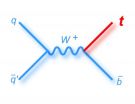
Scientists complete the top quark puzzle
2014-02-24
Scientists on the CDF and DZero experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory have announced that they have found the final predicted way of creating a top quark, completing a picture of this particle nearly 20 years in the making.
The two collaborations jointly announced on Friday, Feb. 21 that they had observed one of the rarest methods of producing the elementary particle – creating a single top quark through the weak nuclear force, in what is called the "s-channel." For this analysis, scientists from the CDF and DZero collaborations ...
As hubs for bees and pollinators, flowers may be crucial in disease transmission
2014-02-24
AMHERST, Mass. – Like a kindergarten or a busy airport where cold viruses and other germs circulate freely, flowers are common gathering places where pollinators such as bees and butterflies can pick up fungal, bacterial or viral infections that might be as benign as the sniffles or as debilitating as influenza.
But "almost nothing is known regarding how pathogens of pollinators are transmitted at flowers," postdoctoral researcher Scott McArt and Professor Lynn Adler at the University of Massachusetts Amherst write. "As major hubs of plant-animal interactions throughout ...
Mental health conditions in most suicide victims left undiagnosed at doctor visits
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
The mental health conditions of most people who commit suicide remain undiagnosed, even though many visit a primary care provider or medical specialist in the year before they die, according...
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – The mental health conditions of most people who commit suicide remain undiagnosed, even though many visit a primary care provider or medical specialist in the year before they die, according to a national study led by Henry Ford Health ...
Cancer patients turning to mass media and non-experts for info
2014-02-24
PHILADELPHIA (February 24, 2014) – The increasing use of expensive medical imaging procedures in the U.S. like positron emission tomography (PET) scans is being driven, in part, by patient decisions made after obtaining information from lay media and non-experts, and not from health care providers.
That is the result from a three-year-long analysis of survey data, and is published in the article , "Associations between Cancer-Related Information Seeking and Receiving PET Imaging for Routine Cancer Surveillance – An Analysis of Longitudinal Survey Data," appearing in ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 24, 2014
2014-02-24
PPAR-γ agonist reverses cigarette smoke induced emphysema in mice
Pulmonary emphysema results in irreversible lung damage and is most often the result of long term cigarette smoke exposure. Immune cells, such as macrophages and myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) accumulate in the lungs of smokers with emphysema and release cytokines associated with autoimmune and inflammatory responses. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation Farrah Kheradmand and colleagues at Baylor University found that peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) ...
Mdm2 suppresses tumors by pulling the plug on glycolysis
2014-02-24
Cancer cells have long been known to have higher rates of the energy-generating metabolic pathway known as glycolysis. This enhanced glycolysis, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect, is thought to allow cancer cells to survive the oxygen-deficient conditions they experience in the center of solid tumors. A study in The Journal of Cell Biology reveals how damaged cells normally switch off glycolysis as they shut down and shows that defects in this process may contribute to the early stages of tumor development.
Various stresses can cause cells to cease proliferating ...
Two-pronged approach successfully targets DNA synthesis in leukemic cells
2014-02-24
A novel two-pronged strategy targeting DNA synthesis can treat leukemia in mice, according to a study in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Current treatments for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), an aggressive form of blood cancer, include conventional chemotherapy drugs that inhibit DNA synthesis. These drugs are effective but have serious side effects on normal dividing tissues.
In order to replicate, cells must make copies of their DNA, which is made up of building blocks called deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs). Cells can either make dNTPs from scratch ...
Blocking autophagy with malaria drug may help overcome resistance to melanoma BRAF drugs
2014-02-24
PHILADELPHIA— Half of melanoma patients with the BRAF mutation have a positive response to treatment with BRAF inhibitors, but nearly all of those patients develop resistance to the drugs and experience disease progression.
Now, a new preclinical study published online ahead of print in the Journal of Clinical Investigation from Penn Medicine researchers found that in many cases the root of the resistance may lie in a never-before-seen autophagy mechanism induced by the BRAF inhibitors vermurafenib and dabrafenib. Autophagy is a process by which cancer cells recycle ...
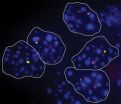
Like mom or dad? Some cells randomly express one parent's version of a gene over the other
2014-02-24
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – We are a product of our parents. Maybe you have your mother's large, dark eyes, and you inherited your father's infectious smile. Both parents contribute one copy, or allele, of each gene to their offspring, so that we have two copies of every gene for a given trait – one from mom, the other from dad. In general, both copies of a gene are switched on or off as an embryo develops into an adult. The "switching on" of a gene begins the process of gene expression that ultimately results in the production of a protein.
Occasionally, a cell will arbitrarily ...
Caring for patients with multiple chronic conditions -- New research and future challenges
2014-02-24
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2014) – The millions of Americans living with more than one chronic disease are at high risk of poor health outcomes, and account for a disproportionate share of health care costs. A special March supplement to Medical Care presents updates from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality's (AHRQ) Multiple Chronic Conditions (MCC) Research Network, formed to address knowledge gaps and research challenges in meeting the complex health care needs of this growing population. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part ...
Nearly half of uninsured children live in immigrant families, reports study in Medical Care
2014-02-24
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2014) – Children from immigrant families now account for 42 percent of uninsured children in the United States, reports a study in the March issue of Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
More than two-thirds of uninsured children with immigrant parents are US citizens, according to an analysis of nationwide survey data by Eric E. Seiber, PhD, of The Ohio State University College of Public Health, Columbus. He writes, "Initiatives to expand coverage or increase Medicaid ...
Preventing suicide should start in a general medical setting
2014-02-24
The mental health conditions of most people who commit suicide remain undiagnosed, even though most visit a primary care provider or medical specialist in the year before they die. To help prevent suicides, health care providers should therefore become more attuned to their patients' mental health state and possible suicide ideation. These are the findings of Brian Ahmedani from the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, Michigan, in a new study¹ documenting the type and timing of health services sought by Americans who commit suicide. The study is the largest geographically ...
Did you hear the one about the doctor?
2014-02-24
LEBANON, NH (Feb. 24, 2014) – In a study that demonstrates the potential of using social networking sites for research on health and medicine, Dartmouth researchers studied jokes made about doctors posted on Facebook.
"Social networking sites, such as Facebook, have become immensely popular in recent years and present a unique opportunity for researchers to eavesdrop on the collective conversation of current societal issues," said Matthew Davis of The Dartmouth Institute of Health Policy & Clinical Practice.
In one of the first studies of social networking site conversations ...
Exclusive David Gancberg article in Human Gene Therapy
2014-02-24
New Rochelle, NY, February 24, 2014—Over the past three funding stages, the European Commission has invested nearly $475 million in 100 projects in the gene transfer and gene therapy field. David Gancberg, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, European Commission (Brussels), describes the substantial opportunities for funding to support basic and clinical research in gene and cell therapy to find new treatments for chronic and rare diseases and novel regenerative medicine approaches in a Commentary article in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary ...
Volcanoes contribute to recent warming 'hiatus'
2014-02-24
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Volcanic eruptions in the early part of the 21st century have cooled the planet, according to a study led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. This cooling partly offset the warming produced by greenhouse gases.
Despite continuing increases in atmospheric levels of greenhouse gases, and in the total heat content of the ocean, global-mean temperatures at the surface of the planet and in the troposphere (the lowest portion of the Earth's atmosphere) have shown relatively little warming since 1998. This so-called 'slow-down' or 'hiatus' has received ...
Personalized medicine best way to treat cancer, study argues
2014-02-24
If a driver is traveling to New York City, I-95 might be their route of choice. But they could also take I-78, I-87 or any number of alternate routes. Most cancers begin similarly, with many possible routes to the same disease. A new study found evidence that assessing the route to cancer on a case-by-case basis might make more sense than basing a patient's cancer treatment on commonly disrupted genes and pathways.
The study found little or no overlap in the most prominent genetic malfunction associated with each individual patient's disease compared to malfunctions ...
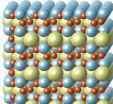
On the road to Mottronics
2014-02-24
"Mottronics" is a term seemingly destined to become familiar to aficionados of electronic gadgets. Named for the Nobel laureate Nevill Francis Mott, Mottronics involve materials – mostly metal oxides - that can be induced to transition between electrically conductive and insulating phases. If these phase transitions can be controlled, Mott materials hold great promise for future transistors and memories that feature higher energy efficiencies and faster switching speeds than today's devices. A team of researchers working at Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source (ALS) have ...
New ideas change your brain cells: UBC research
2014-02-24
A new University of British Columbia study identifies an important molecular change that occurs in the brain when we learn and remember.
Published this month in Nature Neuroscience, the research shows that learning stimulates our brain cells in a manner that causes a small fatty acid to attach to delta-catenin, a protein in the brain. This biochemical modification is essential in producing the changes in brain cell connectivity associated with learning, the study finds.
In animal models, the scientists found almost twice the amount of modified delta-catenin in the brain ...
[1] ... [3975]
[3976]
[3977]
[3978]
[3979]
[3980]
[3981]
[3982]
3983
[3984]
[3985]
[3986]
[3987]
[3988]
[3989]
[3990]
[3991]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.