Mental health patients up to 4 times more likely to be infected with HIV, Penn study finds
2014-02-14
PHILADELPHIA— People receiving mental health care are up to four times more likely to be infected with HIV than the general population, according to a new study published Feb. 13 in the American Journal of Public Health from researchers at Penn Medicine and other institutions who tested over 1,000 patients in care in Philadelphia and Baltimore. Of that group, several new HIV cases were detected, suggesting that not all patients are getting tested in mental health care settings, despite recommendations to do so from the CDC and the Institute of Medicine.
The study is ...
Scientists reveal cosmic roadmap to galactic magnetic field
2014-02-14
DURHAM, NH –-Scientists on NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) mission, including a team leader from the University of New Hampshire, report that recent, independent measurements have validated one of the mission's signature findings—a mysterious "ribbon" of energy and particles at the edge of our solar system that appears to be a directional "roadmap in the sky" of the local interstellar magnetic field.
Unknown until now, the direction of the galactic magnetic field may be a missing key to understanding how the heliosphere—the gigantic bubble that surrounds ...
Massachusetts' fire-safe cigarette law appears to decrease likelihood of residential fires
2014-02-14
Boston, MA – A six-year-old Massachusetts law requiring that only "fire-safe" cigarettes (FSCs) be sold in the state appears to decrease the likelihood of unintentional residential fires caused by cigarettes by 28%, according to a new study by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) researchers.
The study will appear online February 13, 2014 in the American Journal of Public Health.
"This study is the first rigorous population-based study to evaluate the effectiveness of the fire-safe cigarette standards, and shows that science-based tobacco product regulation can protect ...
Efficient treatment a step closer in the fight against cancer-causing herpes
2014-02-14
Herpes virus proteins are more 'spaghetti-like' than previously thought, which provides a vital clue in the search for an efficient treatment against a type of herpes which causes a form of cancer known as Kaposi's sarcoma.
That's according to researchers from The University of Manchester who have discovered that the virus protein uses its flexible arms to pass on viral building blocks to the proteins of cells that it hijacks.
The latest part of this research is published in the February edition of PLoS Pathogens which has uncovered how the protein of cells hijacked ...
Robotic construction crew needs no foreman
2014-02-14
Cambridge, Mass. – February 13, 2014 – On the plains of Namibia, millions of tiny termites are building a mound of soil—an 8-foot-tall "lung" for their underground nest. During a year of construction, many termites will live and die, wind and rain will erode the structure, and yet the colony's life-sustaining project will continue.
Inspired by the termites' resilience and collective intelligence, a team of computer scientists and engineers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard ...
'Sexy' underwear is not the only way to feel feminine on Valentine's Day, academic says
2014-02-14
AUDIO:
This is a Podcast recording of Dr. Christiana Tsaousi explaining her research.
Click here for more information.
TV makeover shows and glossy magazines can leave women feeling guilty for not wearing "sexy" lingerie – especially on Valentine's Day.
But in fact, many different types of underwear could make them feel feminine, according to an expert on underwear consumption.
Dr Christiana Tsaousi, a lecturer in marketing and consumption at the University of Leicester's ...
Study explores link between selling and leasing market prices for cars
2014-02-14
Changes in the selling prices of cars can be used to improve calculations for how much people should be paying to lease a vehicle, according to a new study.
Researchers from Norwich Business School at the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Athens University of Economics and Business (AUEB) have for the first time modelled the relationship between variations in leasing and selling market prices, using almost 10 years of data from the US, the world's largest automobile market. They suggest that in order to determine more accurately the monthly payments agreed in leasing ...
Cancer drugs hitch a ride on 'smart' gold nanoshells
2014-02-14
Nanoparticles capable of delivering drugs to specifically targeted cancer cells have been created by a group of researchers from China.
The multifunctional 'smart' gold nanoshells could lead to more effective cancer treatments by overcoming a major limitation of modern chemotherapy techniques—the ability to target cancer cells specifically and leave healthy cells untouched.
Small peptides situated on the surface of the nanoshells are the key to the improved targeting ability, guiding the nanoshells to specific cancer cells and attaching to markers on the surface of ...
First large-scale study of stock market volatility and mental disorders
2014-02-14
Falling stock prices lead to increased hospitalisations for mental disorders, according to new research published today in the journal Health Policy and Planning.
Researchers assessed the relationship between stock price movements and mental disorders using data on daily hospitalisations for mental disorders in Taiwan over 4,000 days between 1998 and 2009. They found that a 1000-point fall in the Taiwan Stock Exchange Capitalisation Weighted Stock Index (TAIEX) coincided with a 4.71% daily increase in hospitalisations for mental disorders.
A downward daily change in ...
Crazy ants dominate fire ants by neutralizing their venom
2014-02-14
VIDEO:
In this video, a fire ant dabs venom on an attacking crazy ant. The crazy ant coats itself with formic acid to neutralize the venom, a discovery made by University...
Click here for more information.
AUSTIN, Texas — Invasive "crazy ants" are rapidly displacing fire ants in areas across the southeastern U.S. by secreting a compound that neutralizes fire ant venom, according to a University of Texas at Austin study published this week in the journal Science Express. It's ...
Cat parasite found in western Arctic Beluga deemed infectious
2014-02-14
University of British Columbia scientists have found for the first time an infectious form of
the cat parasite Toxoplasma gondii in western Arctic Beluga, prompting a health advisory to the
Inuit people who eat whale meat.
The same team also discovered a new strain of the
parasite Sarcocystis, previously sequestered in the icy north, that is responsible for killing
406 grey seals in the north Atlantic in 2012.
Presenting their findings today at the 2014
Annual Meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), Michael Grigg
and ...
NOAA researcher says Arctic marine mammals are ecosystem sentinels
2014-02-14
As the Arctic continues to see dramatic declines in seasonal sea ice, warming temperatures and increased storminess, the responses of marine mammals can provide clues to how the ecosystem is responding to these physical drivers.
Seals, walruses and polar bears rely on seasonal sea ice for habitat and must adapt to the sudden loss of ice, while migratory species such as whales appear to be finding new prey, altering migration timing and moving to new habitats.
"Marine mammals can act as ecosystem sentinels because they respond to climate change through shifts in distribution, ...
Stanford psychologist shows why talking to kids really matters
2014-02-14
Fifty years of research has revealed the sad truth that the children of lower-income,
less-educated parents typically enter school with poorer language skills than their more
privileged counterparts. By some measures, 5-year-old children of lower socioeconomic status
(SES) score two years behind on standardized language development tests by the time they enter
school.
In recent years, Anne Fernald, a psychology professor at Stanford University, has
conducted experiments revealing that the language gap between rich and poor children emerges
during infancy. ...
For understanding family structure to trauma: New technology is yielding bigger data
2014-02-14
Austin - February 13, 2014 - Social media can do more than just entertain us and keep us connected. It also can help scientists better understand human behavior and social dynamics. The volume of data created through new technology and social media such as Facebook and Twitter is lending insight into everything from mapping modern family dynamics to predicting postpartum depression.
"By analyzing different types of social media, search terms, or even blogs, we are able to capture people's thinking, communication patterns, health, beliefs, prejudices, group behaviors – ...
Genetic chip will help salmon farmers breed better fish
2014-02-14
Atlantic salmon production could be boosted by a new technology that will help select the best fish for breeding.
The development will enable salmon breeders to improve the quality of their stock and its resistance to disease.
A chip loaded with hundreds of thousands of pieces of DNA – each holding a fragment of the salmon's genetic code – will allow breeders to detect fish with the best genes.
It does so by detecting variations in the genetic code of each individual fish – known as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). These variations make it possible to identify ...
Discovery may help to explain mystery of 'missing' genetic risk
2014-02-14
A new study could help to answer an important riddle in our understanding of genetics: why research to look for the genetic causes of common diseases has failed to explain more than a fraction of the heritable risk of developing them.
Susceptibility to common diseases is believed to arise through a combination of many common genetic variants that individually slightly increase the risk of disease, plus a smaller number of rare mutations that often carry far greater risk.
However, even when their effects are added together, the genetic variants so far linked to common ...
Mixed genes
2014-02-14
This news release is available in German. When individuals from different groups interbreed, their offspring's DNA becomes a mixture of the DNA from each admixing group. Pieces of this DNA are then passed along through subsequent generations, carrying on all the way to the present day. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, Oxford University and University College London (UCL) have now produced a global map detailing the genetic histories of 95 different populations across the world, spanning the last four millennia.
The ...
Study highlights indigenous response to natural disaster
2014-02-14
DENVER (Feb. 13, 2014) – When a tsunami struck American Samoa in 2009, indigenous institutions on the islands provided effective disaster relief that could help federal emergency managers in similar communities nationwide, according to a study from the University of Colorado Denver and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
The study found that following the tsunami, residents of the remote U.S. territory in the South Pacific relied on Fa'aSamoa or The Samoan Way, an umbrella term incorporating a variety of traditional institutions governing the lives of its citizens.
"We ...
Berkeley Lab researchers at AAAS 2014
2014-02-14
Can more accurate climate models help us understand extreme weather events? Can we use
synthetic biology to create better biofuels? These questions, and the ongoing search for Dark
Matter and better photovoltaic materials, are just some of the presentations by Lawrence
Berkeley National Lab researchers at this year's AAAS meeting. Here's a quick look at Berkeley
Lab@AAAS:
Friday, Feb. 14
1:00-2:30
Opportunities for New Materials in
Photovoltaics (Toronto Room, Hyatt Regency)
Ramamoorthy Ramesh
The
Department of Energy's ...
Superconductivity in orbit: Scientists find new path to loss-free electricity
2014-02-14
UPTON, NY—Armed with just the right atomic arrangements, superconductors allow electricity to flow without loss and radically enhance energy generation, delivery, and storage. Scientists tweak these superconductor recipes by swapping out elements or manipulating the valence electrons in an atom's outermost orbital shell to strike the perfect conductive balance. Most high-temperature superconductors contain atoms with only one orbital impacting performance—but what about mixing those elements with more complex configurations?
Now, researchers at the U.S. Department of ...
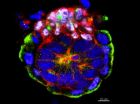
Rewriting the text books: Scientists crack open 'black box' of development
2014-02-14
We know much about how embryos develop, but one key stage – implantation – has remained a
mystery. Now, scientists from Cambridge have discovered a way to study and film this 'black box'
of development. Their results – which will lead to the rewriting of biology text books worldwide
– are published in the journal Cell. Embryo development in mammals occurs in two phases.
During the first phase, pre-implantation, the embryo is a small, free-floating ball of cells
called a blastocyst. In the second, post-implantation, phase the blastocyst embeds itself in the
mother's ...
A role of glucose tolerance could make the adaptor protein p66Shc a new target for cancer and diabetes
2014-02-14
[TORONTO,Canada, Feb 18, 2014] – A protein that has been known until recently as part of a complex communications network within the cell also plays a direct role in regulating sugar metabolism, according to a new study published on-line in the journal Science Signaling (February 18, 2014).
Cell growth and metabolism are tightly controlled processes in our cells. When these functions are disturbed, diseases such as cancer and diabetes occur. Mohamed Soliman, a PhD candidate at the Lunenfeld Tanenbaum Research Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital, found a unique role for ...
IBEX research shows influence of galactic magnetic field extends beyond our solar system
2014-02-14
In a report published today, new research suggests the enigmatic "ribbon" of energetic
particles discovered at the edge of our solar system by NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX)
may be only a small sign of the vast influence of the galactic magnetic field.
IBEX researchers have sought answers about the ribbon since its discovery in 2009. Comprising
primarily space physicists, the IBEX team realized that the galactic magnetic field wrapped around
our heliosphere — the giant "bubble" that envelops and protects our solar system — appears to
determine the orientation ...
Rebuilding the brain after stroke
2014-02-14
DETROIT – Enhancing the brain's inherent ability to rebuild itself after a stroke with molecular
components of stem cells holds enormous promise for treating the leading cause of long-term
disability in adults.
Michael Chopp, Ph.D., Scientific Director of the Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute, will present
this approach to treating neurological diseases Thursday, Feb. 13, at the American Heart
Association's International Stroke Conference in San Diego.
Although most stroke victims recover some ability to voluntarily use their hands and other body
parts, half are ...
Amidst bitter cold and rising energy costs, new concerns about energy insecurity
2014-02-14
February 13,2014 --With many regions of the country braced by an unrelenting cold snap, the problem of energy insecurity continues to go unreported despite its toll on the most vulnerable. In a new brief, researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health paint a picture of the families most impacted by this problem and suggest recommendations to alleviate its chokehold on millions of struggling Americans. The authors note that government programs to address energy insecurity are coming up short, despite rising energy costs.
Energy Insecurity (EI) is ...
[1] ... [3984]
[3985]
[3986]
[3987]
[3988]
[3989]
[3990]
[3991]
3992
[3993]
[3994]
[3995]
[3996]
[3997]
[3998]
[3999]
[4000]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.