Symbols, such as traffic lights, on menus effective in educating diners
2013-03-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A little-noticed provision of the Affordable Care Act requires all chain restaurants and retail food establishments with 20 or more locations to list calorie counts on their menus. But according to research co-written by a University of Illinois agricultural economist, numeric calorie labels might not be the most effective way to influence patrons to select "healthier" (often interpreted as lower-calorie) items.
Brenna Ellison, a professor of agricultural and consumer economics, says placing a symbolic label in addition to the numeric calorie information ...
NASA sees large decrease in Cyclone Sandra's rainfall intensity
2013-03-14
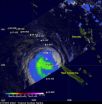
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite, also known as TRMM, flew over Cyclone Sandra twice in one day and noticed a large decrease in rainfall intensity over a nine hour period.
On March 11, 2013, NASA's TRMM satellite twice flew above weakening tropical cyclone Sandra as it was passing to the west of New Caledonia in the southern Pacific Ocean. TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) had a very good view of Sandra as it passed directly above the tropical cyclone on March 11 at 1312 UTC (9:12 a.m. EST). TRMM PR measured rainfall at the extreme rate of over 206 mm ...
Dwelling on stressful events can increase inflammation in the body, study finds
2013-03-14
ATHENS, Ohio (March 13, 2013)—Dwelling on negative events can increase levels of inflammation in the body, a new Ohio University study finds.
Researchers discovered that when study participants were asked to ruminate on a stressful incident, their levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of tissue inflammation, rose. The study is the first time to directly measure this effect in the body.
"Much of the past work has looked at this in non-experimental designs. Researchers have asked people to report their tendency to ruminate, and then looked to see if it connected to physiological ...
Scientists discover novel chemical that controls cell behavior
2013-03-14
March 12, 2013 — Albuquerque, NM (UNM Cancer Center) — It's the spread of the original cancer tumor that kills most people. That's why cancer researchers vigorously search for drugs that can prevent metastases, the spread of cancer. The research team co-led by Angela Wandinger-Ness, PhD, and Larry Sklar, PhD, at the University of New Mexico Cancer Center has found a chemical compound that appears to control cell migration and adhesion, two important characteristics of metastatic cancer cells. The team recently published a paper describing how the first-in-class compound ...
Sun spits out 2 CMEs
2013-03-14
The sun recently erupted with two coronal mass ejections (CMEs). One began at 8:36 p.m. EDT on March 12, 2013 and is directed toward three NASA spacecraft, Spitzer, Kepler and Epoxi. There is, however, no particle radiation associated with this event, which is what would normally concern operators of interplanetary spacecraft since the particles can trip computer electronics on board. A second CME began at 6:54 a.m. EDT on March 13, 2013 and its flank may pass by Earth at a speed that does not typically have a significant impact at Earth.
Experimental NASA research models, ...
Vitamin D may lower blood pressure in African-Americans
2013-03-14
Boston – High blood pressure, a risk factor for heart attacks, heart failure and stroke, is 40 percent more common in African-Americans than in other American ethnic groups. In a new study from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), along with the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Massachusetts General Hospital, researchers show that vitamin D supplementation may help African-Americans lower their blood pressure. The study publishes online in the March 13, 2013 edition of the American Heart Association journal Hypertension.
"This study may explain and help treat an important ...
US lifespans lags other high-income countries, tied to mortality rates under age 50
2013-03-14
Higher mortality rates among Americans younger than 50 are responsible for much of why life expectancy is lower in the United States than most of the world's most developed nations.
The research, by Jessica Ho, a University of Pennsylvania doctoral candidate in demography and sociology, found that excess mortality among Americans younger than 50 accounted for two-thirds of the gap in life expectancy at birth between American males and their counterparts and two-fifths between females and their counterparts in the comparison countries.
The study, "Mortality Under Age ...
Foundations of carbon-based life leave little room for error
2013-03-14
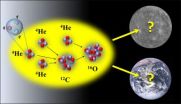
Life as we know it is based upon the elements of carbon and oxygen. Now a team of physicists, including one from North Carolina State University, is looking at the conditions necessary to the formation of those two elements in the universe. They've found that when it comes to supporting life, the universe leaves very little margin for error.
Both carbon and oxygen are produced when helium burns inside of giant red stars. Carbon-12, an essential element we're all made of, can only form when three alpha particles, or helium-4 nuclei, combine in a very specific way. The ...
UI study of Midwest finds increase in heavy rainfalls over 60 years
2013-03-14
Heavy rains have become more frequent in the upper Midwest over the past 60 years, according to a study from the University of Iowa. The trend appears to hold true even with the current drought plaguing the region, the study's main author says.
The fact that temperatures over the country's midsection are rising, too, may be more than coincidence.The hotter the surface temperature, which has been the trend in the Midwest and the rest of the world, the more water that can be absorbed by the atmosphere. And the more water available for precipitation means a greater chance ...
Video game 'exercise' for an hour a day may enhance certain cognitive skills
2013-03-14
Playing video games for an hour each day can improve subsequent performance on cognitive tasks that use similar mental processes to those involved in the game, according to research published March 13 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Adam Chie-Ming Oei and Michael Donald Patterson of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Non-gamer participants played five different games on their smartphones for an hour a day, five days of the week for one month. Each participant was assigned one game. Some played games like Bejeweled where participants matched three identical ...
Series of studies first to examine acupuncture's mechanisms of action
2013-03-14
WASHINGTON — While acupuncture is used widely to treat chronic stress, the mechanism of action leading to reported health benefits are not understood. In a series of studies at Georgetown University Medical Center (GUMC), researchers are demonstrating how acupuncture can significantly reduce the stress hormone response in an animal model of chronic stress.
The latest study was published today in the April issue of Journal of Endocrinology.
"Many practitioners of acupuncture have observed that this ancient practice can reduce stress in their patients, but there is a ...
Brain stent offers alternative to shunt for fixing potentially blinding vein narrowing
2013-03-14
A team of interventional neuroradiologists and neurosurgeons at Johns Hopkins reports wide success with a new procedure to treat pseudotumor cerebri, a rare but potentially blinding condition marked by excessive pressure inside the skull, caused by a dangerous narrowing of a vein located at the base of the brain.
The Johns Hopkins team's latest study, to be published in the Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology online March 14, is believed to be the first to show how directly lowering pressure inside the vein alleviates the condition and improves vision.
The study report on ...
Garbled text messages may be the only symptoms of stroke
2013-03-14
DETROIT – Difficulty or inability to write a coherent text message, even in patients who have no problem speaking, may become a "vital" tool in diagnosing a type of crippling stroke, according to new research at Henry Ford Hospital.
The case study focused on a 40-year-old man visiting the metro Detroit area on business who showed signs of "dystextia," a recently coined term for incoherent text messaging that can sometimes be confused with autocorrect garble. But in his case, the man saw nothing wrong with the garble.
The patient had no problem with a routine bedside ...
Rapid hearing loss may be a symptom of rare Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
2013-03-14
DETROIT – Rapid hearing loss in both ears may be a symptom of the rare but always-fatal Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and should be considered a reason for clinicians to test for the disorder.
That was the conclusion of Henry Ford Hospital researchers after encountering a 67-year-old patient who had been progressively losing hearing in both ears for two months and was eventually diagnosed with the disease.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, or CJD, is often confused with so-called "mad cow disease," and though they are in the same family of disorders, are not the same.
However, ...
Sleepwalkers sometimes remember what they've done
2013-03-14
Three myths about sleepwalking – sleepwalkers have no memory of their actions, sleepwalkers' behaviour is without motivation, and sleepwalking has no daytime impact – are dispelled in a recent study led by Antonio Zadra of the University of Montreal and its affiliated Sacré-Coeur Hospital. Working from numerous studies over the last 15 years at the hospital's Centre for Advanced Studies in Sleep Medicine at the Hôpital du Sacré-Cœur de Montréal and a thorough analysis of the literature, Zadra and his colleagues have raised the veil on sleepwalking and clarified the diagnostic ...
Texas is number one in nation for fines from illegal immigration audits
2013-03-14
Texas is number one in nation for fines from illegal immigration audits
Article provided by Goldstein & Scopellite, PC
Visit us at http://www.lawyersdallas.com
In 2011, United States Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) had its most productive year for audits conducted and fines issued in the pursuit of identifying and punishing employers who hire illegal individuals; who are classified as those who entered the country illegally; who do not have work authorization; or who arrived legally but have not fallen out of their legal status. To avoid prosecution, ...
Las Vegas Dermatology and Bagatelle Las Vegas Host "Ladies Night" on Thursday, March 14th, 2013
2013-03-14
On Thursday, March 14th, 2013 Las Vegas Dermatology and Bagatelle will host "Ladies Night". The first 100 ladies to make dinner reservations will dine free. Some lucky ladies will receive swag bags with valuable gift certificates inside from Las Vegas Dermatology. Las Vegas Dermatology is excited to provide a raffle boasting an age-defying skincare package, to include both service and product, valued at over $570.00.
Bagatelle Las Vegas redefines the Mediterranean dining experience through an exquisite seasonal menu and the untouchable beautifully designed ...
New Online Incubation Portal Rolls Out Welcome Mat for Budding Traders
2013-03-14
Armed with a growing following after its launch in November 2012, seed capital web portal RAPA Cap Intro is preparing for its first major allocation at the end of this month.
Matching trading talent with investment capital, RAPA Cap Intro serves to nurture and build budding traders through its online platform. Set to allocate $1.2 million to the top five traders on the RAPA Leaderboard, the company relies on its RAPA Score algorithm as a primary filter to screen traders presenting their performance numbers.
Michael Berman, CEO and Co-Founder of RAPA Cap Intro, says ...
Share the Vision: St. Louis Society for the Blind & Visually Impaired Hosts The Visionary Gala on April 13, 2013
2013-03-14
Join leaders in business, medicine, media, philanthropy and social work as St. Louis Society for the Blind & Visually Impaired (http://www.SLSBVI.org) hosts The Visionary Gala awards dinner on Saturday, April 13, 2013, at The Palladium Saint Louis.
The Society's Visionary Gala will feature a cocktail reception, dinner and wine service, superb desserts, and a presentation of the internationally distinguished Leslie Dana Gold Medal. Music will be provided by Silk Pajamas. Society Visionary Awards for community service also will be presented. Dr. Nicholas and Mrs. Sabra ...
Author Donates 10% of Book Sales to LGBT Youth
2013-03-14
Charitable acts don't always come easy but for Buffalo, NY author, Deanna DiLorenzo, the decision to donate 10% of the first year's book sales of her debut novel, Tell Me, to Gay & Lesbian Youth Services of WNY was simple.
"It just made sense," Deanna says. "The book is geared toward a lesbian & bisexual audience. I knew I wanted to donate some of the proceeds to a GLBT cause but I wasn't sure which one. Then I came across Gay & Lesbian Youth Services of WNY."
Gay & Lesbian Youth Services of WNY is an organization that provides ...
Las Vegas Turns up Technology Heat with Workshop for Local Young Girls
2013-03-14
Between downtown tech start-ups and the SXSW expo interest Las Vegas is becoming a mini Silicon Valley and driving the appetite for technology skills. The new tech scene has created a virtual onslaught of young girls hoping to attend the upcoming BlackGirlsCode Las Vegas "Build a Webpage in a Day" (Part two). The remix event takes place this Saturday, March 16, 2013 from 10:00 AM to 4:00 PM.
BlackGirlsCode (BGC) workshops are geared towards introducing participants to technology and encouraging them to pursue careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering ...
Excel Software Announces AppProtect 3 for Mac and Windows
2013-03-14
Excel Software announced AppProtect 3.0 to protect Mac or Windows software. AppProtect applies protection with a human controlled or automated online activation process to a compiled application in minutes without programming. It supports MAX multi-media applications or Unity games. AppProtect 3.0 works with OfficeProtect 2.0 to generate a protected application from an Excel spreadsheet.
AppProtect 3.0 is LicenseCard enabled for drag and drop activation. Protected Windows applications can now passthru command line parameters. The developer interface has enhancements ...
Kryton Celebrates 40 Years of Concrete Waterproofing
2013-03-14
Like many companies, Kryton was built to solve a problem. CanWest Waterproofing Company was a waterproofing applicator that opened its doors by the current chairman of the Kryton board, R.G. (Ron) Yuers. It was soon realized that the materials they purchased from a local supplier weren't working satisfactorily. Ron decided that if there wasn't a solution available in the market, he would create one. So, he hired a chemist. After hundreds of hours in a laboratory, Krystol technology was born and in 1973 Kryton was formed as a new company to launch it into a global market. ...
New 'My Girly Side' Subscription Service Shifts Period Prep Into Autopilot
2013-03-14
Convinced they are spot on when it comes to period preparedness, two Atlanta women have launched MYGIRLYSIDE.COM, a web-based subscription service that discreetly delivers feminine hygiene products direct to members along with a feel-good charity bonus and a subtle dose of menstrual humor.
In three simple steps, My Girly Side offers subscribers a choice of name-brand tampons to fit their cycle, a delivery schedule of every two, three or four months and participation in a charitable donation that benefits women's causes. Pricing for the service starts at $18.95 for delivery ...
Crystal Cove Alliance Hires Jackie McDougall, Experienced Nonprofit Executive, as Vice President of Development
2013-03-14
Jackie McDougall has been hired by Crystal Cove Alliance (CCA) as Vice President of Development, a new position in which McDougall will direct membership, major gifts and grants programs and the spectacular gala held each fall on the bluffs at Crystal Cove State Park.
McDougall, a longtime resident of neighboring Laguna Beach, will work closely with the CCA staff and its partners -- Crystal Cove State Park, Crystal Cove Beach Cottages and The Beachcomber Cafe.
"We are very fortunate to have attracted such an experienced development professional," said CCA ...
[1] ... [5056]
[5057]
[5058]
[5059]
[5060]
[5061]
[5062]
[5063]
5064
[5065]
[5066]
[5067]
[5068]
[5069]
[5070]
[5071]
[5072]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.