Laura Wellington: "The Four-Star Diet" Sells Out on Amazon Leading to Invitations From "All-Star" Talk Shows
2013-03-12
No doubt, the media tour for the author of "The Four-Star Diet: Based Upon The Wisdom Of General Colin Powell & Other Ridiculously Brilliant Leaders" has only just begun. Explosive sales on Amazon and similar retailers have made it nearly impossible to get your hands on a print version of the book. With the demand continuing to rise to an already "sell out" crowd, Author Laura J. Wellington has received invitations to appear on numerous "Celebrity, Style, and News" shows from as far away as the UAE. She will begin to make those appearances ...
Rush scientists identify buphenyl as a possible drug for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-11
(CHICAGO) – Buphenyl, an FDA-approved medication for hyperammonemia, may protect memory and prevent the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Hyperammonemia is a life-threatening condition that can affect patients at any age. It is caused by abnormal, high levels of ammonia in the blood.
Studies in mice with Alzheimer's disease (AD) have shown that sodium phenylbutyrate, known as Buphenyl, successfully increases factors for neuronal growth and protects learning and memory, according to neurological researchers at the Rush University Medical Center.
Results from ...
Shock teams and ECMO save lives in massive STEMI
2013-03-11
MINNEAPOLIS, MN - March 9, 2013 - The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), accompanied by mechanical CPR, in patients with massive myocardial infarctions can lead to unexpected survival. These study findings are being presented March 9 at the American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions.
ECMO is an advanced technology that functions as a replacement for a critically ill patient's heart and lungs. This is the first report of combined ECMO, mechanical CPR and therapeutic hypothermia (TH) use within a STEMI Network.
"For many patients who present with ...
Niacin therapy shows no benefits, has some harmful effects
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 9, 2013) — A highly anticipated study evaluating a combination of the vitamin niacin with the anti-flushing agent laropiprant finds the therapy provides no benefit to and may even be harmful for patients with vascular disease, according to research presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session. Detailed trial data is presented here for the first time.
Heart Protection Study 2-Treatment of HDL to Reduce the Incidence of Vascular Events (HPS2-THRIVE) is the largest-ever study of niacin, commonly used to raise ...
Drug protects against kidney injury from imaging dye in ACS patients
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 10, 2013) —High doses of a popular cholesterol-lowering drug significantly reduced the rate of acute kidney injury caused by dye used in imaging in acute coronary syndrome patients who underwent a coronary procedure, according to research presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session. This group of patients is at high risk for kidney damage related to contrast agents used in imaging tests.
Previous studies have demonstrated the kidney-protective value of various statins administered before patients undergo ...
Encouraging early results for redesigned Sapien valve
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 10, 2013) — The new Sapien XT aortic valve showed a non-significantly lower rate of death and strokes at 30 days than the original model, and both valves demonstrated notably better short-term outcomes than seen with the Sapien system in PARTNER I, according to the first results from the PARTNER II study presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
PARTNER II is the first randomized clinical trial involving the Sapien XT valve and the only one that compares the new device to the original FDA-approved Sapien ...
New biolimus stent equal to everolimus stent at 1 year
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 10, 2013) — In a match-up of Japan's top drug-releasing stent and a new device featuring a biodegradable coating, the newcomer delivered statistically comparable one-year results, according to data from the NEXT trial presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
Drug-eluting stents are structures placed inside narrowed coronary arteries to restore proper blood flow. A polymer coating on these devices slowly releases a drug designed to prevent restenosis—another blockage at the same site—and prevent a second ...
Fewer adverse events with 'double kissing' crush stent than culotte
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 10, 2013) — Patients with a type of coronary lesion linked with poor prognosis fared significantly better with the stent technique known as double kissing crush than with culotte stenting, according to data from the DKCRUSH-III trial presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
DKCRUSH-III is the first head-to-head comparison of double kissing (DK) crush and culotte stent techniques in coronary artery disease. The study focused on bifurcation lesions, which involve a main branch and a smaller side branch ...
Cangrelor superior to clopidogrel in CHAMPION PHOENIX trial
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO (March 10, 2013) — The experimental anti-clotting drug cangrelor solidly outperformed commonly used clopidogrel in a large global trial of patients who underwent coronary stent procedures, according to data from the phase III CHAMPION PHOENIX study presented today at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session.
Cangrelor and clopidogrel interfere with the P2Y12 receptor, a platelet-surface protein that helps regulate blood clotting. Currently approved drugs in this class are effective in cutting down ischemic events—blood-flow reductions ...
New anti-clotting drug more effective than current treatment
2013-03-11
A new and experimental anti-clotting drug, cangrelor, proved better than the commonly used clopidogrel and was significantly more effective at preventing blood clots in a large trial of patients who underwent coronary stent procedures. These data, from the phase III CHAMPION PHOENIX study, were presented at the American College of Cardiology's 62nd Annual Scientific Session and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers report that the new drug, which is administered intravenously, reduced the odds of complications from stenting procedures. ...
Magnet ingestion by young children serious and growing problem
2013-03-11
Physicians and parents must be aware of the growing danger of magnet ingestion by children because magnets can adhere to each other and cause life-threatening problems such as bowel perforations, a new case study illustrates in CMAJ.
"Modern magnet technology has transformed what was once an esoteric subtype of foreign-body ingestion into a common and lethal threat," writes Dr. Daniel Rosenfield, Department of Paediatrics, The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), with coauthors.
In the past, magnet ingestion generally could be treated with a wait-and-see approach, ...
Therapies for ALL and AML targeting MER receptor hold promise of more effect with less side-effect
2013-03-11
Two University of Colorado Cancer Center studies show that the protein receptor Mer is overexpressed in many leukemias, and that inhibition of this Mer receptor results in the death of leukemia cells – without affecting surrounding, healthy cells.
The first study, published today in the journal Oncogene, worked with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), for which current chemotherapies offer a cure rate of only about 55 percent.
"In about 2/3 of all AML patients and about 90 percent of adult AML patients, we found that the Mer receptor was upregulated. Mer receptor protein ...
EARTH: Well-healed faults produce high-frequency earthquake waves
2013-03-11
Alexandria, VA – Much like our voices create sound waves with a variety of low and high pitches, or frequencies, earthquakes produce seismic waves over a broad spectrum. The seismic waves' frequencies determine, in part, how far they travel and how damaging they are to human-made structures. However, the inaccessibility of fault zones means that very little is known about why and how earthquakes produce different frequencies. With the help of a new tabletop model, scientists have now identified how a process known as fault healing can shape seismic waves and potentially ...
BGI Tech develops novel 'Ultra-Deep de novo' assembly solution for heterozygous genomes
2013-03-11
Shenzhen, China, March 11, 2013- BGI Tech Solutions Co., Ltd., also referred to as "BGI Tech", introduced today its novel assembly solution for facilitating heterozygous genomes research. This marks another technological breakthrough for BGI in heterozygous genome assembly after the completed genome sequencing of oyster, diamondback moth and pear.
The availability of a reference genome for a species is the cornerstone for the in-depth understanding of its biological secrets and commercial values. However, a major obstacle that prevents scientists to easily crack the genome ...
Gun retailers take a hard line on illegal firearm sales, UC Davis survey finds
2013-03-11
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —A scientific survey of more than 1,600 gun retailers in the U.S. has found that gun buyers frequently try to make illegal purchases and that gun retailers take a dim view of fellow sellers who engage in illegal activity — regardless of whether they are actively breaking the law or simply looking the other way.
The survey, conducted in 2011 by Garen Wintemute, professor of emergency medicine and director of the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program, is believed to be the first scientific study of a large group of gun retailers to determine ...
An Internet for robots
2013-03-11
Researchers of five European universities have developed a cloud-computing platform for robots. The platform allows robots connected to the Internet to directly access the powerful computational, storage, and communications infrastructure of modern data centers - the giant server farms behind the likes of Google, Facebook, and Amazon - for robotics tasks and robot learning.
With the development of the RoboEarth Cloud Engine the team continues their work towards creating an Internet for robots. The new platform extends earlier work on allowing robots to share knowledge ...
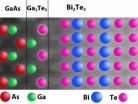
Researchers solve riddle of what has been holding 2 unlikely materials together
2013-03-11
For years, researchers have developed thin films of bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) – which converts heat into electricity or electricity to cooling – on top of gallium arsenide (GaAs) to create cooling devices for electronics. But while they knew it could be done, it was not clear how – because the atomic structures of those unlikely pair of materials do not appear to be compatible. Now researchers from North Carolina State University and RTI International have solved the mystery, opening the door to new research in the field.
"We've used state-of-the-art technology to solve ...
Amplified greenhouse effect shifts north's growing seasons
2013-03-11
Vegetation growth at Earth's northern latitudes increasingly resembles lusher latitudes to the south, according to a NASA-funded study based on a 30-year record of land surface and newly improved satellite data sets.
An international team of university and NASA scientists examined the relationship between changes in surface temperature and vegetation growth from 45 degrees north latitude to the Arctic Ocean. Results show temperature and vegetation growth at northern latitudes now resemble those found 4 degrees to 6 degrees of latitude farther south as recently as 1982.
"Higher ...
Nerve damage may underlie widespread, unexplained chronic pain in children
2013-03-11
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have described what may be a newly identified disease that appears to explain some cases of widespread chronic pain and other symptoms in children and young adults. Their report that will appear in the April issue of the journal Pediatrics, and has received early online release, finds that most of a group of young patients seen at the MGH for chronic, unexplained pain had test results indicating small-fiber polyneuropathy, a condition not previously reported in children. The MGH investigators call this new syndrome juvenile-onset ...
Study: Antibiotics are unique assassins
2013-03-11
In recent years, a body of publications in the microbiology field has challenged all previous knowledge of how antibiotics kill bacteria. "A slew of papers came out studying this phenomenon, suggesting that there is a general mechanism of killing by antibiotics," said Kim Lewis, Northeastern University Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biology and director of Northeastern's Antimicrobial Discovery Center.
The standard thinking at the time was that the three main classes of bactericidal antibiotics each had a unique way of killing ...
The household carbon emission per capita in Northwestern China is only 2.05 tons CO2 per year
2013-03-11
The current international climate policy framework is mainly based on the national and regional level of macroscopic carbon emissions data, such as the regional per capita carbon emissions are often used as the indicator to measure the fairness of carbon emission rights. However, the per capita emissions based on regional macro data can not accurately reveal the low carbon emissions of the poor within the region, and cover up the emission differences among people intra-country and intra-region, the household carbon emission data based on field surveys could compensate for ...
Why people put themselves under the knife
2013-03-11
In a long-term study, Prof. Dr. Jürgen Margraf, Alexander von Humboldt Professor for Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy at the RUB, investigated the psychological effects of plastic surgery on approximately 550 patients in cooperation with colleagues from the University of Basel. Patients demonstrated more enjoyment of life, satisfaction and self-esteem after their physical appearance had been surgically altered. The results of the world's largest ever study on this issue are reported by the researchers in the journal "Clinical Psychological Science".
The aim of the ...
Environmental change impacts on migratory shorebirds differ for males and females
2013-03-11
Extensive shell fishing and sewerage discharge in river estuaries could have serious consequences for the rare Icelandic black-tailed godwits that feed there. But it is the males that are more likely to suffer, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
Research published today in the journal Ecology and Evolution reveals very different winter feeding habits between the sexes.
Both males and females mainly consume bivalve molluscs, sea snails and marine worms, probing vigorously into soft estuary mud with their long beaks. But the study shows that ...
Coffee and tea during pregnancy affect fetal growth
2013-03-11
Drinking just two cups of coffee a day is associated with the risk of low birth weight. Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have conducted a study on 59,000 women in collaboration with the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.
Expectant mothers who consume caffeine, usually by drinking coffee, are more likely to have babies with lower birth weight than anticipated, given their gestational age. Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, conducted a study on 59,000 pregnant Norwegian women in collaboration with the Norwegian ...
Evolution in the antibody factory
2013-03-11
This press release is available in German.
Immune system B cells play a crucial role in the defence of pathogens; when they detect such an intruder, they produce antibodies that help to combat the enemy. They concurrently and continuously improve these molecules to more precisely recognize the pathogens. A team of scientists with participation of the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) has discovered that during this process the cells are able to advance their own evolution themselves by increasing the selection pressure through previously-produced antibodies. ...
[1] ... [5069]
[5070]
[5071]
[5072]
[5073]
[5074]
[5075]
[5076]
5077
[5078]
[5079]
[5080]
[5081]
[5082]
[5083]
[5084]
[5085]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.