Patriot Taxiway Industries Receives AS9100C/ISO 9001:2008 Certification from Aviation Suppliers Association (ASA)
2013-02-18
Patriot Taxiway Industries announced today that it has been certified to AS9100C/ISO 9001:2008, based on the results of a recent assessment. AS9100C accreditation was achieved on January 15th, 2013. AS9100 is an integral part of the supplier management system of most of the world's aerospace prime manufacturers.
Steven A. Smits President of Patriot Taxiway Industries led this successful effort and stated that, "The Patriot team has embraced AS 9100 and has demonstrated a sincere commitment to the on-going journey of sustaining the principles of the AS9100 quality ...
From Bali to Brighton: Be Inspired by Next's Homeware Collections for Summer 2013
2013-02-18
Inspired by Indonesian handicrafts, ethnic influences return with embossed lanterns, carved washed wooden frames and imprinted vessels in Bali Life. Natural textures, laundered fabrics and the neutral palette of the story create a laid back feel, whilst metallic elements and highly embellished textiles add an air of luxury to the trend. In-keeping with the spiritual, carefree nature of the Balinese, patterns are mixed throughout, whilst the Buddha plays a key role within accessories and cushions, as well as lighting with the Buddha carved head lamp. Looking for larger, ...
Foresters UK Fundraising Efforts Support Disadvantaged Children
2013-02-18
Foresters - the international financial services organisation - is celebrating the success of its latest collaboration with Bauer Media's Cash for Kids (CFK) charity, aimed at helping less fortunate children aged 0-18.
The Cash for Kids Mission Christmas Appeal 2012 helped over 250,000 children to have a better Christmas and granted a record breaking GBP5.3m in cash, gifts and toys.
The Appeal, which was delivered in many major cities across the UK, was in aid of local children and young people suffering from neglect and poverty. It was the latest joint campaign ...
Sold Out on Broadway, Musical Book of Mormon Becomes London's Smash Hit, Reports LondonTown.com
2013-02-18
It's not often that a religious satire becomes a capital city's hottest in ticket in town, but the Book of Mormon has done just that. Created by South Park's Trey Parker and Matt Stone, this cheery musical about a pair of Mormon missionaries has successfully breathed a fresh breath of satirical air into London's entertainment business, creating blockbuster impact in the West End. LondonTown.com, as excited as any of the capital's entertainment hubs, advises audiences coming from outside the capital to book into London hotels early to avoid the stampede! For the show, which ...
Costa Bingo Gives Away Entertainments Prize Package in Sunny's Big Picture Game
2013-02-18
Sunny's Big Picture at Costa Bingo
Sunny's Big Picture game plays on Tuesday 26th February at 9pm and one lucky winner will walk away with a superb prize package, including an LG 55" high definition 3DTV, an LG blu-ray home cinema system and a 12 month full Sky TV subscription including Sky Entertainment, Sky Sports and Sky Movies.
Sunny's Big Picture game is a 75 ball bingo game with the winner the first player to bingo on the coverall pattern. Cards can be bought from the Diamond Store until 24th February for 10 Diamonds each and the site is also giving away ...
World's Tallest Domestic Cat, the Savannah Cat, Resembles a Leopard has the Personality of a Dog But Can Chirp Like a Bird?
2013-02-18
Residents in suburban neighborhoods are not accustom to seeing miniature "pet cheetahs" walking around. Calling the local fish and wildlife authorities thinking a bobcat might be on the prowl they are unaware the breed thrives on human interaction and behave, for the most part, like your average domestic cat breed. Michelle Mills, owner of F1Hybrids Savannahs, responded;
"Savannahs have no relation to a Bobcat, Leopard, or Ocelot, nor the body type or pattern of any of those breeds. The greatest differentiation is the temperament of a Savannah compared ...
Quantum devices: Building an innovative future for Canada
2013-02-17
February 17 – Boston, MA – Quantum information processing promises not only breakthroughs for computing, communications and cryptography, but it can also help us devise tools for navigating and controlling the nano-scale world. Sensors that operate according to quantum mechanics may achieve sensitivity, selectivity, precision and robustness far beyond their classical counterparts.
Canada Excellence Research Chair David Cory from the University of Waterloo's Institute for Quantum Computing will be in Boston for the American Association for the Advancement of Science annual ...
A new way of looking at drug discovery
2013-02-17
PHILADELPHIA - Garret FitzGerald, MD, FRS, chair of the Department of Pharmacology and Director of the Institute for Translational Medicine & Therapeutics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, has long said the current drug-development system in the United States is in need of change, "representing an unsustainable model."
Even though the number of drugs approved has risen in the last three years, overall, roughly the same number of drugs have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) each year since 1950 while the estimated cost, ...
Brown University scientists to discuss resilience of coastal communities at AAAS
2013-02-17
Hurricane Sandy was a fearsome reminder that coastal communities are highly vulnerable to extreme weather events and environmental variability, and that vulnerability is only expected to increase with climate change. Brown University scientists Heather Leslie and Leila Sievanen, members of an interdisciplinary research team focused on human-environment interactions in coastal regions, will discuss these challenges this month at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Boston.
Leslie and Sievanen will participate in a symposium ...
Rice University analysis links ozone levels, cardiac arrest
2013-02-17
BOSTON – (Feb. 17, 2013) – Researchers at Rice University in Houston have found a direct correlation between out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and levels of air pollution and ozone. Their work has prompted more CPR training in at-risk communities.
Rice statisticians Katherine Ensor and Loren Raun announced their findings today at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) conference in Boston.
Their research, based on a massive data set unique to Houston, is due to be published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
At the same AAAS ...
Briefing explores associations between air pollution and health outcomes
2013-02-17
ATLANTA- Lance Waller, PhD, chair of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics at Emory's Rollins School of Public Health, will present preliminary work that explores relationships between high-levels of air pollution exposure and health effects at a press briefing hosted by the American Association for the Advancement of Science on February 17, at 2 p.m. EST, in Boston.
During the briefing, Waller will summarize his joint work with the Southeastern Center for Air Pollution Epidemiology (SCAPE), funded by the Environmental Protection Agency. SCAPE tests air pollution levels ...
In the blink of an eye: X-ray imaging on the attosecond timescale
2013-02-17
In the blink of an eye, more attoseconds have expired than the age of Earth measured in – minutes. A lot more. To be precise, an attosecond is one billionth of a billionth of a second. The attosecond timescale is where you must go to study the electron action that is the starting point of all of chemistry. Not surprisingly, chemists are most eager to explore it with X-rays, the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can probe the core electrons of atoms, the electrons that uniquely identify atomic species.
Heralded as the science of the 21st century by Science and ...
Thirsty crops and hungry people: Symposium to examine realities of water security
2013-02-17
You may have guzzled a half-liter bottle of water at lunchtime, but your food and clothes drank a lot more. The same half-liter that quenched your thirst also produces only about one square-inch of bread or one square-inch of cotton cloth.
Agriculture is in fact one of the world's most insatiable consumers of water. And yet it's facing growing competition for water from cities, industry, and recreation at a time when demand for food is rising, and water is expected to become increasingly scarce. Take irrigation, for example, says Fred Vocasek, senior lab agronomist with ...
Get your brain fit
2013-02-17
PRESENTATION TITLE: A Vision for Excelling in Mental Health and Well-Being
We all know the importance of keeping healthy and are familiar with the refrains of 'exercise more', 'eat better' and 'get regular physicals'. But what about our mental health? Professor Barbara Sahakian, best known for her expertise on cognitive enhancers, challenges society (and government) to prioritise mental health in the same way as we do physical health.
"As a society, we take our mental health for granted," said Prof Sahakian. "But just like our bodies, it is important to keep our brains ...
Media advisory: AAAS session addresses infrastructure design in a changing climate
2013-02-17
DURHAM, N.H. – As our climate changes, the way we engineer our cities must, too. That's the message that University of New Hampshire professor Paul Kirshen, an author of a recent report that assessed Boston's vulnerability to coastal flooding, will deliver at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Annual Meeting February 14-18, 2013, in Boston.
Kirshen will speak about water infrastructure management under a changing climate at the "Effective Science for Community Adaptation to Climate Change" session Sunday morning, Feb. 17 (8:30 – 11:30 a.m., ...
Forging a new periodic table using nanostructures
2013-02-17
Northwestern University's Chad A. Mirkin, a world-renowned leader in nanotechnology research and its application, has developed a completely new set of building blocks that is based on nanoparticles and DNA. Using these tools, scientists will be able to build -- from the bottom up, just as nature does -- new and useful structures.
Mirkin will discuss his research in a session titled "Nucleic Acid-Modified Nanostructures as Programmable Atom Equivalents: Forging a New Periodic Table" at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting in Boston. ...
US science policy should focus on outcomes not efficiencies, says ASU professor
2013-02-17
BOSTON – Given the huge investment and power of science and technology in the U.S. it is surprising that more attention isn't paid to the policy decisions that drive the enterprise, said Daniel Sarewitz, co-director of the Consortium for Science, Policy and Outcomes (CSPO) at Arizona State University. What appears to be missing from the equation, he added, is a focus on outcomes.
Sarewitz was speaking at the 2013 American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting in Boston.
"Given the power of science and technology to shape and even transform ...
ASU professor sees Rachel Carson's early careers as a model for today's science journalism crisis
2013-02-17
BOSTON – It has been more than 50 years since Rachel Carson published her groundbreaking book Silent Spring. Regarded as a hero by some and a villain by others, Carson helped revolutionize the way the public views environmental science.
One area of Carson's career that is often overlooked is her time as a government employee. This is where she got her true start in journalism and it is the area G. Pascal Zachary, professor of practice with the Consortium for Science, Policy and Outcomes at Arizona State University, will be discussing at the 2013 American Association ...
Key to cleaner environment may be right beneath our feet
2013-02-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- While many people recognize that clean water and air are signs of a healthy ecosystem, most do not realize that a critical part of the environment is right beneath their feet, according to a Penn State hydrologist.
The ground plays an important role in maintaining a clean environment by serving as a natural water filtration and purification system, said Henry Lin, professor of hydropedology and soil hydrology. Understanding the components that make up this integral part of the ecosystem can lead to better groundwater management and smarter environmental ...
Evidence shows concussions require long-term follow-up for players
2013-02-17
February 17, 2013 – Boston, MA - As the National Football League braces for lawsuits by 4000 former players alleging the league failed to protect them from the long-term consequences of concussions, game-changing research by a leading Canadian researcher shows damage to the brain can persist for decades after the original head trauma.
"Even when you are symptom-free, your brain may still not be back to normal," says Dr. Maryse Lassonde, a neuropsychologist and the scientific director of the Quebec Nature and Technologies Granting Agency.
Lassonde, whose work is supported ...
ArcticNet recommends practical solutions to improve standard of living in Canada's north
2013-02-17
February 17, 2013 - Boston, MA – Northern communities are in the midst of a period of intense and rapid change brought on by modernization, industrialization and the realities of climate change. From preserving the means to hunt caribou to protecting stocks of arctic char - balancing development with a respect and preservation of traditional means of sustainability may be key to improving standards of living in the North.
With the help of the icebreaker Amundsen, Louis Fortier, Canada Research Chair on the Response of Arctic Marine Ecosystems to Climate Change and other ...
Canada's top water expert brings lessons on water resource management to AAAS
2013-02-17
February 17, 2013 — Boston, MA — With nearly 20 percent of the United States experiencing an extreme drought, the damage from Hurricane Sandy estimated at $65 billion and farmers in Canada's Prairies struggling with the effects of 2011's devastating flooding, the importance of water security in North America is impossible to overstate.
At the Global Institute for Water Security at the University of Saskatchewan, director Howard Wheater and his team use the Saskatchewan River Basin as a large-scale case study to generate the science underpinning the policies and practices ...
Brain prostheses create a sense of touch
2013-02-17
BOSTON, MA -- Rats can't usually see infrared light, but they have "touched" it in a Duke University lab.
The rats sensed the light as a sensation of touch after Duke neurobiologist Miguel Nicolelis and his team fitted the animals with an infrared detector wired to electrodes implanted in the part of the mammalian brain that processes information related to the sense of touch.
One of the main flaws of current human, brain-controlled prosthetics is that patients cannot sense the texture of what they touch, Nicolelis said. His goal is to give quadriplegics not only the ...
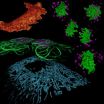
Seeing is believing: Biologists and physicists produce revealing images of cell organization, behavior
2013-02-17
BOSTON, MASS.—When difficult biological questions are tackled by creative experts in physics, what can result?
Images of great beauty, accessible for anyone to appreciate, that also offer rich information on fundamental life processes, and rewarding new paths for analysis and insight.
This leading edge of interdisciplinary collaboration in microscopy will be explored in "Innovations in Imaging: Seeing is Believing," Saturday, February 16, 1:30-4:30 PM at the AAAS Annual Meeting in Boston.
The panel will feature three physicists and three biologists, several of ...
The research is in: Physical activity enhances cognition
2013-02-17
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Exercise doesn't only strengthen your heart and muscles – it also beefs up your brain. Dozens of studies now show that aerobic exercise can increase the size of critical brain structures and improve cognition in children and older adults.
University of Illinois psychology professor Art Kramer, a nationally recognized expert on the role of physical fitness on cognition, will discuss these brain-changing outcomes at a session of the 2013 meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Boston on Feb. 16. Kramer is the director of the ...
[1] ... [5200]
[5201]
[5202]
[5203]
[5204]
[5205]
[5206]
[5207]
5208
[5209]
[5210]
[5211]
[5212]
[5213]
[5214]
[5215]
[5216]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.