Newcastle's Got Talent: Calling All Singers and Dancers for P&O Cruises
2013-02-02
P&O Cruises is heading to Newcastle on the hunt for hot new talent to join its Headliners Theatre Company. In search of those with skill and star quality, successful candidates will get to travel worldwide performing in various productions on P&O Cruises fleet.
P&O Cruises entertainment development manager, Andrew Millar, said: "This is a fantastic opportunity and a perfect springboard for young talent. There's no better way to see the world and visit far-flung exotic destinations than by doing something you love while entertaining thousands of people ...
Blood vessel cells coax colorectal cancer cells into more dangerous state
2013-02-01
HOUSTON - Blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to tumors can also deliver something else - a signal that strengthens nearby cancer cells, making them more resistant to chemotherapy, more likely to spread to other organs and more lethal, scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report online in Cancer Cell.
Working in human colorectal cancer cell lines and tumor samples, as well as mouse models, the researchers found that endothelial cells, which line the inside of blood vessels, can trigger changes in cancer cells without even coming into ...
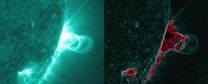
NASA's SDO provides first sightings of how a CME forms
2013-02-01
On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly ...
VISIONS: Seeing the aurora in a new light
2013-02-01
On a cold February night in Poker Flat, Alaska, a team of scientists will wait patiently for the exotic red and green glow of an aurora to illuminate the sky. Instead of simply admiring the view, this group from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center of Greenbelt, Md., and The Aerospace Corporation of El Segundo, Calif. will launch a sounding rocket up through the Northern Lights. The rocket could launch as early as the night of Feb. 2, 2013, but the team has a two-week window in order to find the perfect launch conditions.
Armed with a series of instruments developed specifically ...
NASA sees cyclone felling squeeze between Madagascar and La Reunion
2013-02-01
NASA satellite imagery ahowed Cyclone Felleng appear to squeeze between Madagascar and La Reunion island as it moves southward in the Mozambique Channel.
On Jan. 31 at 5:05 a.m. EST, The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Cyclone Felleng that showed thunderstorms continue to wrap around the center of circulation. The image also showed that Felleng's eye is now obscured by high clouds. The MODIS image showed that the western edge of the storm was brushing eastern Madagascar and eastern edge was over both ...
UCSB anthropologists study effects of modernization on physical activity and heart disease
2013-02-01
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Heart disease continues to be the leading cause of death in the United States, and a sedentary lifestyle is often cited as a major contributing factor. Among the Tsimane, an indigenous population in the lowlands of Bolivia's Amazon basin, however, indicators of heart disease are practically non-existent –– cholesterol is low, obesity is rare, and smoking is uncommon.
That's according to researchers at UC Santa Barbara and the University of New Mexico, who have been studying hunter-gatherers and forager-horticulturists to understand how their ...
Salk scientists use Amazon Cloud to view molecular machinery in remarkable detail
2013-02-01
In this week's Nature Methods, Salk researchers share a how-to secret for biologists: code for Amazon Cloud that significantly reduces the time necessary to process data-intensive microscopic images.
The method promises to speed research into the underlying causes of disease by making single-molecule microscopy of practical use for more laboratories.
"This is an extremely cost-effective way for labs to process super-resolution images," says Hu Cang, Salk assistant professor in the Waitt Advanced Biophotonics Center and coauthor of the paper. "Depending on the size of ...
A*STAR scientists solve century-old mystery by finding stable haploid strains of Candida albicans
2013-02-01
A*STAR scientists from the Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) have identified what eluded yeast scientists for the past 100 years, by constructing stable haploid strains of Candida albicans, the most prevalent human fungal pathogen. This discovery, jointly made by two teams of scientists led by Prof Wang Yue of IMCB and Prof Judith Berman of the University of Minnesota, will enable scientists to effectively target and treat infections by Candida albicans. The findings, "The 'obligate diploid' Candida albicans forms mating-competent haploids", were published ...
A gut feeling about neural stem cells
2013-02-01
Proper function of the digestive system requires coordinated contraction of the muscle in the wall of the intestinal tract, regulated by the enteric nervous system. Damage or loss of these neurons can result in intestinal motility disorders, such as Hirschsprung's disease, for which there is a dearth of effective treatments. In principle, disorders of the enteric nervous system could be treated by cell therapy, but it was previously unknown whether transplanted stem cells could migrate to the appropriate location in the gut and then become neurons that could properly innervate ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 1, 2013
2013-02-01
A gut feeling about neural stem cells
Proper function of the digestive system requires coordinated contraction of the muscle in the wall of the intestinal tract, regulated by the enteric nervous system. Damage or loss of these neurons can result in intestinal motility disorders, such as Hirschsprung's disease, for which there is a dearth of effective treatments. In principle, disorders of the enteric nervous system could be treated by cell therapy, but it was previously unknown whether transplanted stem cells could migrate to the appropriate location in the gut and then ...
Nurses at forefront of genomics in health care
2013-02-01
On April 14, 2003 a map of the human genome was completed, ushering in a new era of genetics in medicine with applications that include genetic testing; newborn screening; susceptibility to diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, or psychiatric conditions; screening, diagnosis and monitoring of disease; and treatment planning. A special Genomics Issue, including an evidence review by researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), published by Wiley in the Journal of Nursing Scholarship on behalf of the Honor Society of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau International, ...
Needless abdominal CT scans can be avoided in children, study says
2013-02-01
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) ― A study of more than 12,000 children from emergency departments throughout the country in the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) has identified seven factors that can help physicians determine the need for a computed tomography (CT) scan following blunt trauma to the abdomen. Because CT scans pose radiation hazards for youngsters, the findings may enable doctors to determine which children do not need to be exposed to such tests after a traumatic injury.
The study, titled "Identifying children at very low risk of clinically ...
Outcomes of cartilage tympanoplasty in the pediatric population
2013-02-01
Alexandria, VA — Cartilage tympanoplasty can be performed successfully in 95 percent of young children when appropriate conditions exist, according to a study in the February 2013 issue of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.
"Pediatric tympanoplasty is a frequently performed procedure with varying reported success rates ranging between 35 percent and 94 percent. In general, tympanic membrane repair success in children is often perceived as lagging behind what is typically achieved in adults having similar underlying risk factors," the authors write.
The study was ...
Genetically modified tobacco plants produce antibodies to treat rabies
2013-02-01
Bethesda, MD—Smoking tobacco might be bad for your health, but a genetically altered version of the plant might provide a relatively inexpensive cure for the deadly rabies virus. In a new research report appearing in The FASEB Journal, scientists produced a monoclonal antibody in transgenic tobacco plants that was shown to neutralize the rabies virus. This new antibody works by preventing the virus from attaching to nerve endings around the bite site and keeps the virus from traveling to the brain.
"Rabies continues to kill many thousands of people throughout the developing ...
Overdose education, bystander nasal naloxone rescue kits associated with decreased opioid overdose death
2013-02-01
(Boston) – In a study of communities in Massachusetts with high numbers of opioid overdose deaths, the implementation of overdose education and naloxone distribution (OEND) was associated with a significant reduction in opioid overdose death rates. Led by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC), Boston University Schools of Medicine (BUSM) and Public Health (BUSPH) in collaboration with the Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MDPH) and published in the British Medical Journal (BMJ), this study provides observational evidence that OEND is an effective public health ...
Novel radiation therapy method shortens prostate cancer treatment time
2013-02-01
According to a study in the January issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology, the use of volume-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) to deliver intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to prostate cancer patients results in an overall reduction in treatment time of approximately 14 percent. The study was performed at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University in Atlanta.
Treatment with IMRT is increasingly standard for prostate cancer. However, although the benefits of IMRT in the treatment of prostate cancer are ample, it remains a complex and time-consuming ...
Increases in extreme rainfall linked to global warming
2013-02-01
A worldwide review of global rainfall data led by the University of Adelaide has found that the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events is increasing across the globe as temperatures rise.
In the most comprehensive review of changes to extreme rainfall ever undertaken, researchers evaluated the association between extreme rainfall and atmospheric temperatures at more than 8000 weather gauging stations around the world.
Lead author Dr Seth Westra said, "The results are that rainfall extremes are increasing on average globally. They show that there is a 7% increase ...
New protocol recommendations for measuring soil organic carbon sequestration
2013-02-01
URBANA – Increased levels of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), have been associated with the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, cultivation of grasslands, drainage of the land, and land use changes. Concerns about long-term shifts in climate patterns have led scientists to measure soil organic carbon (SOC) in agricultural landscapes and to develop methods to evaluate how changes in tillage practices affect atmospheric carbon sequestration. University of Illinois professor of soil science Kenneth Olson has used data collected over a 20-year period ...
Gap geometry grasped
2013-02-01
Theoretical physicist Moumita Maiti and colleagues at the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research in Bangalore, India, have now implemented an algorithm for analysing void space in sphere packing, where the spheres need not all be the same size. This method, about to be published in EPJ E, could be applied to analyse the geometry of liquids present between multi-sized spheres that are akin to a model for porous material. This provides a tool for studying the flow of such fluids through porous material. More importantly, it can also be used to study the ...
How do corals survive in the hottest reefs on the planet?
2013-02-01
Coral reefs are predicted to decline under the pressure of global warming. However, a number of coral species can survive at seawater temperatures even higher than predicted for the tropics during the next century. How they survive, while most species cannot, is being investigated by researchers at the National Oceanography Centre, Southampton (NOCS) and New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD).
We tend to associate coral reefs with tropical seas of around 28 degrees, where even slight warming can have devastating effects on corals. But in the Arabian/Persian Gulf, corals ...
European investments in advanced computing systems deliver results
2013-02-01
January 31, 2013 - At the HiPEAC 2013 conference in Berlin, KALRAY demonstrated MPPA256, the world's first supercomputer-on-a-chip, consisting of 256 computing cores. This innovative processor combines the ultimate in several processor types and will enable a whole new class of embedded and industrial applications in the fields of image processing, signal processing, control, communications and data security. The MPPA256 is completely designed in Europe and is only one of the success stories resulting from the 170 million Euro investment in carefully selected European funded ...
Routes towards defect-free graphene
2013-02-01
A new way of growing graphene without the defects that weaken it and prevent electrons from flowing freely within it could open the way to large-scale manufacturing of graphene-based devices with applications in fields such as electronics, energy, and healthcare.
A team led by Oxford University scientists has overcome a key problem of growing graphene – a one atom-thick layer of carbon – when using an established technique called chemical vapour deposition, that the tiny flakes of graphene form with random orientations, leaving defects or 'seams' between flakes that ...
Study: Infection preventionists know safe care
2013-02-01
Washington, DC, February 1, 2013 – There is general agreement among hospital infection preventionists (IPs) with respect to which practices have weak or strong evidence supporting their use to prevent healthcare-associated infection, according to a new study published in the February issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Furthermore, IPs with certification in infection prevention and control (CIC®) are two to three times more likely to perceive the ...
New study sheds light on link between dairy intake and bone health
2013-02-01
Boston - A study by researchers at the Institute for Aging Research (IFAR) at Hebrew SeniorLife, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School (HMS), has found that dairy intake —specifically milk and yogurt —is associated with higher bone mineral density (BMD) in the hip, but not the spine. Cream, on the other hand, may be associated with lower BMD overall. Published today in the journal Archives of Osteoporosis, these findings suggest that not all dairy products are equally beneficial in promoting bone strength.
"Dairy foods provide several important nutrients that are beneficial ...
If you are impulsive, take modafinil and count to 10
2013-02-01
Philadelphia, PA, February 1, 2013 – Poor impulse control contributes to one's inability to control the consumption of rewarding substances, like food, alcohol, and other drugs. This can lead to the development of addiction. FDA-approved medications for alcoholism, like naltrexone (Revia) and disulfiram (Antabuse), are thought to reduce alcohol consumption by curbing cravings and creating unpleasant reactions to alcohol, effects which reduce the desire to drink alcohol.
New medications, however, might target the uncontrollable urges to consume drugs of abuse. The idea ...
[1] ... [5270]
[5271]
[5272]
[5273]
[5274]
[5275]
[5276]
[5277]
5278
[5279]
[5280]
[5281]
[5282]
[5283]
[5284]
[5285]
[5286]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.