Atlanta Video Production Company Optimum Productions Honored to Produce the Media for the 2012 CVC of Atlanta IMPACT Awards
2013-01-03
Atlanta video production company Optimum Productions is pleased to announce that it produced the video, photography and A/V setup for the 15th Annual Corporate Volunteer Council of Atlanta IMPACT Awards, hosted on September 20th, 2012. The team at Optimum Productions feels honored to have been a part of such a worthy cause.
The Corporate Volunteer Council (CVC) of Atlanta is a network of local businesses who are interested in giving to the community through volunteerism. Volunteering as a company helps to support the community and encourage companies to prosper through ...
Atlanta Bus Charter Company, Samson Trailways, Shares How to Go Green with Mass Transit
2013-01-03
Just as with a carpool, a bus rental in Atlanta can take cars off the congested streets. With more and more cities in the U.S. going green with public mass transit initiatives, a bus charter can provide an additional avenue to save energy.
Reasons to Turn to Green Alternatives
Transporting a bunch of people in a single car can lead to less CO2 emissions. Emissions related to transportation account for about 28 percent of greenhouse gases in the U.S. Further, transportation equates the second largest share of greenhouse gas emissions in the country. Of these, private ...
Georgia Injury Accident Lawyer, McAleer Law, Reminds Customers of Satellite Office in Mobile, Ala.
2013-01-03
Charles McAleer opened his business in 2003 to service the Atlanta metropolitan area and other regions of Georgia. Never resting on his accomplishments from this state alone, he obtained a license to practice in Alabama as well and opened a satellite office in Mobile. These accomplishments as a Georgia injury accident lawyer include the following in 2012:
- $2,000,000 for a client who was hit by a car while walking on the sidewalk
- $850,000 in workers' compensation for someone who was seriously injured in a car accident while on the way to work
- $2,000,000 in a pedestrian/car ...
Atlanta Staffing Agency TRC Staffing Services, Inc., Discusses Top Interview Mistakes to Avoid
2013-01-03
TRC Staffing Services, Inc., has been helping companies and candidates with finding ideal employment matches since 1980. In that time, the Atlanta staffing experts have seen many interview blunders, and they wish to encourage potential job candidates to avoid some of the most common interview mistakes they've seen. Here are several interview mistakes TRC recommends avoiding:
- Dressing Inappropriately
When you are trying to present yourself in a professional situation, you need to look the part. The best bet for everyone of both genders is to opt for a suit for professional ...
Orlando Bankruptcy Attorney, Clark & Washington, Discusses the Late Anna Nicole Smith's Bankruptcy Case
2013-01-03
The Background of the Case
Anna Nicole Smith was 27 years old when her 90-year-old billionaire husband, J. Howard Marshall, passed away. Upon his death, it was discovered that he left nothing to his former model wife. Smith was not in a good financial condition when her husband passed. She had next to nothing in her bank account and decided to file a lawsuit against the estate. It was her contention that her husband's son undermined an agreement to create a trust in her name. This led to a lengthy court case with the estate that cost her a great deal of money to pursue. ...
Atlanta Orthopedic Practice OrthoAtlanta Discusses Common Fall and Winter Injuries
2013-01-03
OrthoAtlanta would like to discuss the dangers of certain injuries that are more likely to occur during the fall/winter seasons and how you should go about treating them.
Fall sports, especially football, can lead to a number of painful injuries. One very common injury is a jammed finger, resulting in a fracture. Really any contact sport can lead to this condition, and though it may heal on its own, leaving a fracture alone is not the wisest idea. Oftentimes fractures will heal improperly, which can cause painful reoccurrences and spoil many fun fall games in the years ...
New Season Essentials for the 2013 Fashion Season from Next
2013-01-03
Feminine softness in the form of Poetic, offers delicate florals and tailoring in soft hues of cream, powder peach and mushroom with highlights of exotic pink. Cropped trousers are printed and worn with peplum tops and a must-have waterfall soft leather jacket adds a bit of romance.
Micro Optics take classic city tailoring but adds a little attitude. Cute and traditional boucle suits and jackets are mixed with graphic aztec prints and peg leg trousers in metallic, black, gold and lurex cream. Contrast collars and intricate cut out detail adds charm and softens making ...
In an Empty-Pocket Economy, CashbackClick.com Has a Cure
2013-01-03
Saving money by the click, diligent web surfers discover multiple Internet alcoves promoting smart spending in everyday shopping.
Working Americans are juggling the prospects for their future budgets; and although it comes as no surprise that greenback saving opportunities are out there, the sad flip-side to the coin is that maybe they're not looking in the right places. As business specialist Dr. Ivan Misner says, "It's all about your mindset". It's not just about saving on only large spending or in isolated incidences; it's about everyday saving on everything, ...
Nutrition Revolution in Wylie, Texas is Excited to Help You Take Control of Your Weight Loss Goals, Beginning With The Weight Loss Challenge of 2013 Starting Monday January 7th at 7:00 pm
2013-01-03
Co-owner of Nutrition Revolution and Wellness Coach Erin Raines, said about the Weight Loss Challenge, "There is no better feeling than helping clients reach goals you set together; goals they once thought were unattainable."
Imagine a room filled with streamers, confetti, balloons and 40 of your newest friends; friends who supported and motivated you through 8 weeks of reaching your health goals. Your wellness coaches line up to give your hugs and high fives as you jump up and make your way to the front of the room to collect your prize for winning The Weight ...
New Evangelism Website Aims to Warn the World of Mankind's Most Fatal Disease
2013-01-03
A new website, InteriorDisaster.org, has been created to raise awareness of a fatal disease that is responsible for many recent deaths. InteriorDisaster.org is currently looking for supporters to raise awareness of the disease and to help people find the cure.
Long for More Founder Spencer Longmore, a filmmaker in Los Angeles, CA, was blessed with this idea two years ago while helping to start a church plant in Pasadena. He says it was a time where he was brainstorming on incentives and things to do for the Kingdom of God.
The goal of Long for More Foundation is ...
New Male Talk Show Coming in February
2013-01-03
A new male talk show will hit the airwaves on February 9th via Regal Media Group, LLC and executive producer Todd A. Smith.
The show entitled Regal Roundtable will be a 30-minute talk show that discusses hot topics and current events similar to The View and The Talk, but from a male perspective.
The show is the brainchild of Smith, who also publishes the online men's magazine RegalMag.com.
Regal Roundtable will appeal to men of all races and ethnicities and will give men the platform to debate issues ranging from politics, religion, sports, health, relationships ...
CasinoPulp Launches All New Machine a Sous
2013-01-03
CasinoPulp recently launched live online casino for all those people who are internet casino fans. All those fans who love blackjack, or baccarat, or maybe roulette will love the format of online casino live. CasinoPulp has formatted the Casino En ligne based on the advanced and futuristic remote technology. This technology is further coupled with webcams casinos that connect the computers of players in order to recreate the feeling of direct playing. The online live casino is better than the traditional version of online casino in more than one way. The online casino live ...
RDS Investments Purchases Arlington Retail Center and Signs 7k Sq ft Leasing Tenant to High Traffic Strip Center Location
2013-01-03
Fort Worth-based commerical real estate developer RDS Real Estate (http://rdsrealestate.us) has added 25,000 sqft of prime retail space for lease at 5100 West Sublett Rd in Arlington, TX, to its more than 1,000,000 sq ft of owned real estate under management.
The newly acquired property is located right off 287 at the Kennedale Sublett Road exit on the SW corner of the intersection of 287 and Sublett Road. "This retail space is especially desirable because approximately 72,000 vehicles per day pass by it, and 100,000 people live within a five mile radius of the ...
2012 International Space Station Research and Discovery Highlights
2013-01-03
This past year has been a busy one for the International Space Station. With a variety of new investigations, facilities, researchers, data and results, the space station Program Science Office has had much to share. These investigations benefit life on Earth, inform future space exploration and advance fundamental scientific understanding.
"This has been an amazing year for the space station," said International Space Station Program Scientist Julie Robinson, Ph.D. "We have achieved and exceeded our research goals for the first year of full research ...
Concurrent Technologies Corporation Teams with InfoTech Solutions to Provide Worldwide Intelligence Analysis Services Under the Defense Intelligence Agency's $5.6 Billion SIA II Contract
2013-01-03
Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC) announced today that it will team with InfoTech Solutions for Business on a multiple award, multi-year, indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity (IDIQ) contract from the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), with a contract ceiling of $5.6 billion over a five-year period. The work will be performed worldwide to provide professional support services to the intelligence analysis mission, warfighters, defense planners, and defense and national security policymakers.
CTC was awarded the original SIA contract in 2008 and executed a variety ...
Bonobos will share with strangers before acquaintances
2013-01-03
DURHAM, N.C. -- You're standing in line somewhere and you decide to open a pack of gum. Do you share a piece with the coworker standing to one side of you, or with the stranger on the other?
Most humans would choose the person they know first, if they shared at all.
But bonobos, those notoriously frisky, ardently social great apes of the Congo, prefer to share with a stranger before sharing with an animal they know. In fact, a bonobo will invite a stranger to share a snack while leaving an acquaintance watching helplessly from behind a barrier.
"It seems kind ...
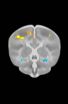
Risk genes for Alzheimer's and mental illness linked to brain changes at birth
2013-01-03
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Some brain changes that are found in adults with common gene variants linked to disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, and autism can also be seen in the brain scans of newborns.
"These results suggest that prenatal brain development may be a very important influence on psychiatric risk later in life," said Rebecca C. Knickmeyer, PhD, lead author of the study and assistant professor of psychiatry in the University of North Carolina School of Medicine. The study was published by the journal Cerebral Cortex on Jan. 3, 2013.
The study ...
Food for friendship: Bonobos share with strangers in exchange for company
2013-01-03
Bonobos voluntarily share food and will even forego their own meals for a stranger, but only if the recipient offers them social interaction, according to research published January 2 by Jingzhi Tan and Brian Hare of Duke University.
In a series of experiments, the researchers found that bonobos would voluntarily forego their food and offer it to a stranger in exchange for social interaction. The authors found that the bonobos' behavior was at least partially driven by unselfish motivations, since the animals helped strangers acquire food that was out of reach even when ...
ALMA sheds light on planet-forming gas streams
2013-01-03
Astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope have seen a key stage in the birth of giant planets for the first time. Vast streams of gas are flowing across a gap in the disc of material around a young star. These are the first direct observations of such streams, which are expected to be created by giant planets guzzling gas as they grow. The result is published on 2 January 2013 in the journal Nature.
The international team of astronomers studied the young star HD 142527, over 450 light-years from Earth, which is surrounded by a ...
Nature: Political action the biggest swing factor in meeting climate targets
2013-01-03
The new study, published today in the journal Nature, examined the probability of keeping average global temperatures from rising more than 2°C above preindustrial levels under varying levels of climate policy stringency, and thus mitigation costs. In addition, the study for the first time quantified and ranked the uncertainties associated with efforts to mitigate climate change, including questions about the climate itself, uncertainties related to future technologies and energy demand, and political uncertainties as to when action will be taken.
The climate system itself ...
Our galaxy's 'geysers' are towers of power
2013-01-03
VIDEO:
This is Ettore Carretti talking about how the telescope makes maps of the sky.
Click here for more information.
"Monster" outflows of charged particles from the centre of our Galaxy, stretching more than halfway across the sky, have been detected and mapped with CSIRO's 64-m Parkes radio telescope.
Corresponding to the "Fermi Bubbles" found in 2010, the outflows were detected by astronomers from Australia, the USA, Italy and The Netherlands. The finding is reported ...
Study refutes accepted model of memory formation
2013-01-03
A study by Johns Hopkins researchers has shown that a widely accepted model of long-term memory formation — that it hinges on a single enzyme in the brain — is flawed. The new study, published in the Jan. 2 issue of Nature, found that mice lacking the enzyme that purportedly builds memory were in fact still able to form long-term memories as well as normal mice could.
"The prevailing theory is that when you learn something, you strengthen connections between your brain cells called synapses," explains Richard Huganir, Ph.D., a professor and director of the Johns Hopkins ...
ALMA shows how young star and planets grow simultaneously
2013-01-03
Astronomers have used the ALMA telescope to get their first glimpse of a fascinating stage of star formation in which planets forming around a young star are helping the star itself continue to grow, resolving a longstanding mystery. The young system, about 450 light-years from Earth, is revealing its complex gravitational dance to the ever-sharpening vision of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), scheduled for completion this year.
As young stars gather material from their surrounding clouds of gas and dust, the incoming material forms a flat, spinning ...
Galactic geysers fuelled by star stuff
2013-01-03
Enormous outflows of charged particles from the centre of our Galaxy, stretching more than halfway across the sky and moving at supersonic speeds, have been detected and mapped with CSIRO's 64-m Parkes radio telescope.
Corresponding to the "Fermi Bubbles" found in 2010, the recent observations of the phenomenon were made by a team of astronomers from Australia, the USA, Italy and The Netherlands, with the findings reported in today's issue of Nature.
"There is an incredible amount of energy in the outflows," said co-author Professor Lister-Staveley-Smith from The University ...
The laws of global warming
2013-01-03
With policymakers and political leaders increasingly unable to combat global climate change, more scientists are considering the use of manual manipulation of the environment to slow warming's damage to the planet.
But a University of Iowa law professor believes the legal ramifications of this kind of geo-engineering need to be thought through in advance and a global governance structure put in place soon to oversee these efforts.
"Geo-engineering is a global concern that will have climate and weather impacts in all countries, and it is virtually inevitable that some ...
[1] ... [5430]
[5431]
[5432]
[5433]
[5434]
[5435]
[5436]
[5437]
5438
[5439]
[5440]
[5441]
[5442]
[5443]
[5444]
[5445]
[5446]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.