Experts advise doctors on how to clear patients for space travel
2012-12-14
Can I take a space flight? Considerations for doctors
With the prospect of space travel for tourists looming, clinicians could soon be asked to advise on medical clearance for their patients, says a paper published in the BMJ Christmas edition and appearing online today.
Space travel opportunities are becoming increasingly available to the general public with bookings already in place.
A team of experts from North America therefore looked to provide advice to clinicians who require direction when advising patients on space travel.
The Aerospace Medical Association ...
McMaster researchers find age not factor in immunity to viruses
2012-12-14
Hamilton, Ont. (Dec. 13, 2012) — Our immune system does not shut down with age, says a new study led by McMaster University researchers.
A study published in PLOS Pathogens today shows a specialized class of immune cells, known as T cells, can respond to virus infections in an older person with the same vigour as T cells from a young person.
"For a long time, it was thought the elderly were at a higher risk of infections because they lacked these immune cells, but that simply isn't the case," said Jonathan Bramson, the study's principal investigator. "The elderly are ...
Cancer scientists identify a new layer of complexity within human colon cancer
2012-12-14
(TORONTO, Canada – Dec. 13, 2012 ) – Cancer scientists led by Dr. John Dick at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre have found a way to follow single tumour cells and observe their growth over time. By using special immune-deficient mice to propagate human colorectal cancer, they found that genetic mutations, regarded by many as the chief suspect driving cancer growth, are only one piece of the puzzle. The team discovered that biological factors and cell behaviour – not only genes – drive tumour growth, contributing to therapy failure and relapse.
The findings, published ...
No more lying about your age: Scientists can now gauge skin's true age with new laser technique
2012-12-14
Wrinkles, dryness, and a translucent and fragile appearance are hallmarks of old skin, caused by the natural aging of skin cells. But while most of us can recognize the signs of lost youth when we peer into the mirror each morning, scientists do not have a standardized way to measure the extent of age damage in skin. Now a group of Taiwanese researchers has used a specialized microscope to peer harmlessly beneath the skin surface to measure natural age-related changes in the sizes of skin cells. The results, which are published in the Optical Society's (OSA) open-access ...
Berkeley Lab research finds the insurance industry paying increasing attention to climate change
2012-12-14
The insurance industry, the world's largest business with $4.6 trillion in revenues, is making larger efforts to manage climate change-related risks, according to a new study published today in the journal Science.
"Weather- and climate-related insurance losses today average $50 billion a year. These losses have more than doubled each decade since the 1980s, adjusted for inflation," says the study's author Evan Mills, a scientist in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab)'s Environmental Energy Technologies Division. "Insurers have become quite adept at quantifying ...
Researchers find new culprit in castration-resistant prostate cancer
2012-12-14
BOSTON—Scientists at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have discovered a molecular switch that enables advanced prostate cancers to spread without stimulation by male hormones, which normally are needed to spur the cancer's growth. They say the finding could lead to a new treatment for prostate cancers that are no longer controlled by hormone-blocking drugs.
The researchers report in the Dec. 14 issue of Science that the molecular switch occurs in a protein, EZH2, which is increased in these tumors, termed castration-resistant prostate cancers (CRPC).
EZH2 is part of a ...
Who are sports gamers?
2012-12-14
Montreal, December 13, 2012 – From Gran Turismo to WWE Smackdown, sports-based video games represent a wide variety of pursuits. When it comes to the people who actually play those games, however, little is known. How do sports video game players fit their games into a larger sports-related context? How does their video game play inform their media usage and general sports fandom?
That's what Concordia University communications professor Mia Consalvo sought to discover when she embarked on a large-scale study of video game players, the results of which were recently published ...
'Two-faced' cells discovered in colon cancer
2012-12-14
CHICAGO -- Northwestern Medicine researchers have discovered a "two-faced" group of cells at work in human colon cancer, with opposing functions that can suppress or promote tumor growth. These cells are a subset of T-regulatory (Treg) cells, known to suppress immune responses in healthy individuals
In this previously unknown Treg subset, the presence of the protein RORγt has been shown to differentiate between cancer-protecting and cancer-promoting properties.
The Northwestern team, led by Khashayarsha Khazaie, research associate professor at the Robert H. ...
Bubble study could improve industrial splash control
2012-12-14
ARGONNE, Ill. – For the first time, scientists witnessed the details of the full, ultrafast process of liquid droplets evolving into a bubble when they strike a surface. Their research determined that surface wetness affects the bubble's fate.
This research could one day help eliminate bubbles formed during spray coating, metal casting and ink-jet printing. It also could impact studies on fuel efficiency and engine life by understanding the splashing caused by fuel hitting engine walls.
"How liquid coalesces into a drop or breaks up into a splash when hitting something ...
Despite hype, costly prostate cancer treatment offers little relief from side effects
2012-12-14
Prostate cancer patients receiving the costly treatment known as proton radiotherapy experienced minimal relief from side effects such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction, compared to patients undergoing a standard radiation treatment called intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), Yale School of Medicine researchers report in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Standard treatments for men with prostate cancer, such as radical prostatectomy and IMRT, are known for causing adverse side effects such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Proponents of ...
Tracing humanity's African ancestry may mean rewriting 'out of Africa' dates
2012-12-14
New research by a University of Alberta archeologist may lead to a rethinking of how, when and from where our ancestors left Africa.
U of A researcher and anthropology chair Pamela Willoughby's explorations in the Iringa region of southern Tanzania yielded fossils and other evidence that records the beginnings of our own species, Homo sapiens. Her research, recently published in the journal Quaternary International, may be key to answering questions about early human occupation and the migration out of Africa about 60,000 to 50,000 years ago, which led to modern humans ...
Better tools for saving water and keeping peaches healthy
2012-12-14
Peach growers in California may soon have better tools for saving water because of work by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists in Parlier, Calif.
Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientist Dong Wang is evaluating whether infrared sensors and thermal technology can help peach growers decide precisely when to irrigate in California's San Joaquin Valley. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and the research supports the USDA priority of promoting international food security.
Irrigation is the primary source of water for agriculture ...
Dark Ages scourge enlightens modern struggle between man and microbes
2012-12-14
The plague-causing bacteria Yersinia pestis evades detection and establishes a stronghold without setting off the body's early alarms.
New discoveries reported this week help explain how the stealthy agent of Black Death avoids tripping a self-destruct mechanism inside germ-destroying cells.
The authors of the study, appearing in the Dec. 13 issue of Cell Host & Microbe, are Dr. Christopher N. LaRock of the University of Washington Department of Microbiology and Dr. Brad Cookson, UW professor of microbiology and laboratory medicine.
Normally, certain defender cells ...
3 new species of venomous primate identified by MU researcher
2012-12-14
A venomous primate with two tongues would seem safe from the pet trade, but the big-eyed, teddy-bear face of the slow loris (Nycticebus sp.) has made them a target for illegal pet poachers throughout the animal's range in southeastern Asia and nearby islands. A University of Missouri doctoral student and her colleagues recently identified three new species of slow loris. The primates had originally been grouped with another species. Dividing the species into four distinct classes means the risk of extinction is greater than previously believed for the animals but could ...
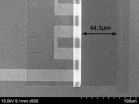
Engineers roll up their sleeves -- and then do same with inductors
2012-12-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — On the road to smaller, high-performance electronics, University of Illinois researchers have smoothed one speed bump by shrinking a key, yet notoriously large element of integrated circuits.
Three-dimensional rolled-up inductors have a footprint more than 100 times smaller without sacrificing performance. The researchers published their new design paradigm in the journal Nano Letters.
"It's a new concept for old technology," said team leader Xiuling Li, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Illinois.
Inductors, ...
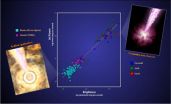
Study reveals a remarkable symmetry in black hole jets
2012-12-14
Black holes range from modest objects formed when individual stars end their lives to behemoths billions of times more massive that rule the centers of galaxies. A new study using data from NASA's Swift satellite and Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope shows that high-speed jets launched from active black holes possess fundamental similarities regardless of mass, age or environment. The result provides a tantalizing hint that common physical processes are at work.
"What we're seeing is that once any black hole produces a jet, the same fixed fraction of energy generates the ...
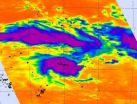
NASA sees intensifying tropical cyclone moving over Samoan Islands
2012-12-14
VIDEO:
NASA's TRMM satellite passed above an intensifying Tropical Cyclone Evan on Dec. 11 at 1759 UTC (12:59 p.m. EST/U.S.) and saw the tallest thunderstorms around Evan's center of circulation reached...
Click here for more information.
NASA satellites have been monitoring Tropical Cyclone Evan and providing data to forecasters who expected the storm to intensify. On Dec. 13, Evan had grown from a tropical storm into a cyclone as NASA satellites observed cloud formation, ...
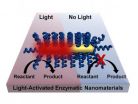
Rice uses light to remotely trigger biochemical reactions
2012-12-14
HOUSTON – (Dec. 13, 2012) – Since Edison's first bulb, heat has been a mostly undesirable byproduct of light. Now researchers at Rice University are turning light into heat at the point of need, on the nanoscale, to trigger biochemical reactions remotely on demand.
The method created by the Rice labs of Michael Wong, Ramon Gonzalez and Naomi Halas and reported today in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano makes use of materials derived from unique microbes – thermophiles – that thrive at high temperatures but shut down at room temperature.
The Rice project ...
Team solves mystery associated with DNA repair
2012-12-14
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — Every time a human or bacterial cell divides it first must copy its DNA. Specialized proteins unzip the intertwined DNA strands while others follow and build new strands, using the originals as templates. Whenever these proteins encounter a break – and there are many – they stop and retreat, allowing a new cast of molecular players to enter the scene.
Scientists have long sought to understand how one of these players, a repair protein known as RecA in bacterial cells, helps broken DNA find a way to bridge the gap. They knew that RecA guided a broken ...
More signs of the benefits of marriage?
2012-12-14
TORONTO, Dec. 13, 2012—There's new evidence about the benefits of marriage.
Women who are married suffer less partner abuse, substance abuse or post-partum depression around the time of pregnancy than women who are cohabitating or do not have a partner, a new study has found.
Unmarried women who lived with their partners for less than two years were more likely to experience at least one of the three problems. However, these problems became less frequent the longer the couple lived together.
The problems were most common among women who were separated or divorced, especially ...
Top officials meet at ONR as Arctic changes quicken
2012-12-14
ARLINGTON, Va.—The Navy's chief of naval research, Rear Adm. Matthew Klunder, met this week with leaders from U.S. and Canadian government agencies to address research efforts in the Arctic, in response to dramatic and accelerating changes in summer sea ice coverage.
"Our Sailors and Marines need to have a full understanding of the dynamic Arctic environment, which will be critical to protecting and maintaining our national, economic and security interests," said Klunder. "Our research will allow us to know what's happening, to predict what is likely to come for the region, ...
Louisiana Child Custody, How Do Courts Decide?
2012-12-14
Louisiana child custody, how do courts decide?
Divorce creates many life changes for divorcing spouses and their children. Louisiana couples going through divorce have many things to think about. Child custody is likely at the front of their minds. There are many factors that go into a child custody decision, but the process can be challenging and complex. That's why it's helpful to have an experienced family law attorney to offer guidance through the process.
What types of child custody exist in Louisiana?
When courts make a child custody determination they look ...
OSHA Campaigns For The Prevention Of Falls On Construction Sites
2012-12-14
OSHA campaigns for the prevention of falls on construction sites
Workplace accidents are always a serious matter -- especially for those who work in the construction industry. And the most serious accidents that you will find in the construction business are caused by falls.
In fact, according to research conducted by U.S. Department of Labor Statistics, in 2010, 249 construction fatalities were the result of falls -- as well as another 10,000 workplace injuries. In order to help prevent these accidents, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration and the National ...
Massachusetts Divorce Affects Insurance and Social Security Benefits
2012-12-14
Massachusetts Divorce Affects Insurance and Social Security Benefits
Divorce has far-reaching effects on many parts of people's lives, including emotional, social and financial aspects. People may not realize all of the changes that result because of a divorce, such as insurance and Social Security benefits. People should understand how divorce in Massachusetts impacts health insurance, life insurance and Social Security benefits so they are not later caught unaware.
Health Insurance
Massachusetts law allows an ex-spouse to remain on an insured spouse's private ...
Are Homeowners Responsible For Injuries That Occur On Their Properties?
2012-12-14
Are homeowners responsible for injuries that occur on their properties?
When accidents occur on private, public or commercial property, the owners and occupants of that property can be held liable for any injuries that occur under certain circumstances. This type of responsibility is called premises liability.
How premises liability works
To be held liable for injuries that occur on their properties, owners must have known or should have known of a dangerous condition on their properties that caused the injuries. Property owners have to take reasonable care that ...
[1] ... [5492]
[5493]
[5494]
[5495]
[5496]
[5497]
[5498]
[5499]
5500
[5501]
[5502]
[5503]
[5504]
[5505]
[5506]
[5507]
[5508]
... [8830]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.