Hunting neuron killers in Alzheimer's and TBI
2012-11-09
Dying neurons lead to cognitive impairment and memory loss in patients with neurodegenerative disorders–conditions like Alzheimer's disease and traumatic brain injury. To better diagnose and treat these neurological conditions, scientists first need to better understand the underlying causes of neuronal death.
Enter Huaxi Xu, Ph.D., professor in Sanford-Burnham's Del E. Webb Neuroscience, Aging, and Stem Cell Research Center. He and his team have been studying the protein appoptosin and its role in neurodegenerative disorders for the past several years. Appoptosin levels ...
How infection can trigger autoimmune disease
2012-11-09
Australian scientists have confirmed a 'weak link' in the immune system – identifying the exact conditions under which an infection can trigger an autoantibody response, a process not clearly understood until now.
We have known for many years that autoimmune diseases such as rheumatic fever and Guillain-Barré syndrome (where the body makes antibodies that attack the heart and peripheral nerves respectively) can occur after the body makes immune responses against certain infectious micro-organisms.
We have not been able to explain exactly how such examples of infection-driven ...
High capacity vehicles the future?
2012-11-09
AWARD-winning research by a transport and logistics expert at the University of Huddersfield has shown that there would be economic and environmental benefits to individual companies and the country if the UK changed the rules to allow high capacity vehicles (HCVs) on to its roads.
At 25.25 metres, they would be around a third as long again as the largest lorries currently permitted in Britain. But they would NOT carry heavier loads. They would be used for larger quantities of lightweight goods, therefore cutting down the number of vehicle journeys made, leading to ...
A new way of making glass
2012-11-09
When cooling a liquid below its melting temperature it either crystallizes or transforms into a glass. Glass is a peculiar state of matter: it has the mechanical properties of a solid but an amorphous structure like a liquid.
As long ago as 1952, Sir Charles Frank at the University of Bristol argued that the structure of glasses should not be entirely disordered like a liquid but rather that it should be filled with polyhedra like the bicapped square antiprism.
Although such motifs have very recently been found in experiments and computer simulations on glassy materials, ...
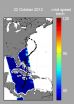
Super storm tracked by European Space Agency water mission
2012-11-09
When millions of people are bracing themselves for the onslaught of extreme weather, as much information as possible is needed to predict the strength of the impending storm. ESA's SMOS mission again showed its versatility by capturing unique measurements of Hurricane Sandy.
As its name suggests, the Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) satellite was designed to measure how much moisture is held in soil and how much salt is held in the surface waters of the oceans.
This information is helping to improve our understanding of the water cycle – an essential component ...
A scientific explanation to why people perform better after receiving a compliment
2012-11-09
A team of Japanese scientists have found scientific proof that people doing exercises appear to perform better when another person compliments them. The research was carried out by a group lead by National Institute for Physiological Sciences Professor Norihiro Sadato, Graduate University for Advanced Studies graduate student Sho Sugawara, Nagoya Institute of Technology Tenure-Track Associate Professor Satoshi Tanaka, and in collaboration with Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology Associate Professor Katsumi Watanabe. The team had previously discovered that ...
Understanding antibiotic resistance using crystallography and computation
2012-11-09
Increasingly, bacteria such as E. coli are resisting the action of carbapenems by producing enzymes (carbapenemases) that break a specific chemical bond in the antibiotic, destroying its antimicrobial activity.
Carbapenemases are members of the group of enzymes called beta-lactamases that break down penicillins and related antibiotics, but it has not been clear why carbapenemases can destroy carbapenems while other beta-lactamases cannot.
Using molecular dynamics simulations, Professor Adrian Mulholland in the School of Chemistry and Dr Jim Spencer in the School of ...
ADHD medicine affects the brain's reward system
2012-11-09
A group of scientists from the University of Copenhagen has created a model that shows how some types of ADHD medicine influence the brain's reward system. The model makes it possible to understand the effect of the medicine and perhaps in the longer term to improve the development of medicine and dose determination. The new research results have been published in the Journal of Neurophysiology.
In Denmark approximately 2-3 per cent of school-age children satisfy diagnostic criteria for ADHD, and therefore it is crucial to know how the medicine works. With a new mathematical ...
New mechanism of action for PARP inhibitors discovered
2012-11-09
PHILADELPHIA — New understanding of how drugs called PARP inhibitors, which have already shown promise for the treatment of women with familial breast and ovarian cancers linked to BRCA mutations, exert their anticancer effects has led to the identification of ways in which the patient population that might benefit from PARP inhibitors could be expanded.
Yves Pommier, M.D., Ph.D., chief of the Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology at the National Cancer Institute's Center for Cancer Research in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues reported these data in Cancer Research, a journal ...
Link found between child prodigies and autism
2012-11-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study of eight child prodigies suggests a possible link between these children's special skills and autism.
Of the eight prodigies studied, three had a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. As a group, the prodigies also tended to have slightly elevated scores on a test of autistic traits, when compared to a control group.
In addition, half of the prodigies had a family member or a first- or second-degree relative with an autism diagnosis.
The fact that half of the families and three of the prodigies themselves were affected by autism is surprising ...
Study questions the relevance of SCIP benchmarks among CABG patients
2012-11-09
(Boston) – Cardiothoracic surgeons and endocrinologists from Boston Medical Center (BMC) have found that among patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, achieving Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) benchmarks for glycemic control may be irrelevant when perioperative continuous insulin infusion protocols are implemented. These findings appear on-line in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.
Currently, 40 percent of all patients undergoing CABG suffer from diabetes, and this number is quickly rising. Traditionally these patients ...
Belatacept after a kidney transplant: Minor added benefit for certain patients
2012-11-09
Belatacept (trade name Nulojix®) has been approved since June 2011 to prevent a rejection reaction of the body to the donor organ (transplant) in adults who have received a kidney transplant. The Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the "Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products" (AMNOG).
The assessment showed an indication of a minor added benefit of belatacept in adults with transplants from donors who had been selected according to the so-called standard criteria. Serious side ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers identify novel metabolic programs driving aggressive brain tumors
2012-11-09
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center have identified metabolic signatures that may pave the way for personalized therapy in glioma, a type of tumor that starts in the brain.
The study appears online in the October issue of Cancer Research, a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research.
According to the authors, little has been known about the underlying metabolic alterations that may drive the growth of the most aggressive type of glioma, termed glioblastoma.
"For the first time, we have described global metabolomic signatures in glioma," said study ...
Considerable added benefit of ipilimumab in advanced melanoma
2012-11-09
The humanized antibody ipilimumab (trade name Yervoy®) has been approved since August 2011 for the treatment of adult patients with advanced melanoma (black skin cancer) who have already been treated. The term "advanced" means that the melanoma can no longer be removed by an operation or that metastases have formed. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG). According to the findings, the drug offers major advantages with ...
University of Huddersfield physicist investigates the Big Bang particle
2012-11-09
Scientists at the University of Huddersfield are collaborating with experts at some of the world's leading research institutes in an attempt to unravel the mysteries of a particle that played a role in the creation of the universe.
The existence of neutrinos and anti-neutrinos – particles that are almost massless and which travel at light speed from one side of the earth to the other – was confirmed more than 50 years ago. Scientists believe that they were created at the Big Bang and might hold the key to the nature of the universe.
But they are light particles that ...
Vandetanib in thyroid cancer: No proof of added benefit
2012-11-09
Vandetanib (trade name Caprelsa®) has been approved in Germany since February 2012 for adult patients suffering from a particular form of aggressive thyroid cancer. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has now examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG). According to the findings, there is no proof of added benefit, because no data on patient-relevant outcomes for those patients for whom the drug is approved were presented by the drug manufacturer in its dossier. ...
UGR and Michael J. Fox Foundation take a step forward in the study of Parkinson's disease
2012-11-09
This press release is available in Spanish.
During the past year, the research group TIC 218 at the Department of Signal Theory, Telematics and Communications attached to the University of Granada and the Andalusian Information Technology and Communications Center (CITIC) has implemented the methods for the detection and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, within the PPMI initiative of the Michael J. Fox foundation for the study of Parkinson's disease. In addition, other databases were used such as that of the Virgen de la Victoria Hospital, Málaga, Spain, and Virgen de ...
CHOP experts describe research in pediatric heart disease
2012-11-09
Physician-researchers from the Cardiac Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia presented new findings on pediatric cardiovascular disease at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2012 in Los Angeles. They described racial disparities in risk factors for sudden cardiac death, imaging modalities and novel approaches to assessing cardiac anomalies, ventricular assist device use, special considerations in syndromes in adult congenital heart disease, changes in immunosuppressive drugs after pediatric heart transplant, and many other topics.
Children's ...
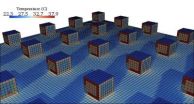
Cool pavements, warm buildings, rising electricity bills
2012-11-09
A push to replace old, heat-trapping paving materials with new, cooler materials could actually lead to higher electricity bills for surrounding buildings, engineers at the University of California, San Diego, have found. Researchers published their findings Oct. 29 in the new Journal of Urban Climate.
The new paving materials are designed to lower the overall temperature of the areas where they are used—something that the study, which was focused on local solar radiation and energy consumption, was not designed to measure.
The study sounds a note of caution at a time ...
Stem cell scientists discover potential way to expand cells for use with patients
2012-11-09
(TORONTO, Canada – Nov. 8, 2012) – Canadian and Italian stem cell researchers have discovered a new "master control gene" for human blood stem cells and found that manipulating its levels could potentially create a way to expand these cells for clinical use.
The findings, published today online ahead of print in Cell Stem Cell, usher in a new paradigm for the regulation of human blood stem cells, says co-principal investigator Dr. John Dick, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Stem Cell Biology and is a Senior Scientist at University Health Network's McEwen Centre for ...
Intensive farming with a climate-friendly touch: Farming/woodland mix increases yields
2012-11-09
This press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese.
Each year, huge carbon stores are lost as a result of deforestation. In South America, around four million hectares of forest are cut down every year. As a result, international climate protection programs are planning to financially compensate farmers who preserve forests or plant new trees. Demand for land is rising, however. And growing need for food and energy crops will inevitably lead to conflicts of interest over fertile land in countries such as Brazil and Ecuador.
Thomas Knoke and Michael Weber at Technische ...
Sweet new approach discovered to help produce metal casting parts, reduce toxicity
2012-11-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Based on a new discovery by researchers at Oregon State University, the world's multi-billion dollar foundry industry may soon develop a sweet tooth.
This industry, that produces metal castings used in everything from water pumps and jet engines to railroad and automobile parts, dates back thousands of years to before Greek and Roman times. It was important in the advance of human civilization, but still continues to evolve.
Some modern technologies use various types of "binders" to essentially glue together sands and other materials to form sophisticated ...
Preschoolers' counting abilities relate to future math performance, researcher says
2012-11-09
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Along with reciting the days of the week and the alphabet, adults often practice reciting numbers with young children. Now, new research from the University of Missouri suggests reciting numbers is not enough to prepare children for math success in elementary school. The research indicates that counting, which requires assigning numerical values to objects in chronological order, is more important for helping preschoolers acquire math skills.
"Reciting means saying the numbers from memory in chronological order, whereas counting involves understanding ...
Ovarian cancer patients have lower mortality rates when treated at high-volume hospitals
2012-11-09
New York, NY (Nov. 8, 2012) – A study by researchers at the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center (HICCC) at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center, recently e-published ahead of print by the Journal of Clinical Oncology, suggests that women who have surgery for ovarian cancer at high-volume hospitals have superior outcomes than similar patients at low-volume hospitals.
The improved survival rate is not dependent on a lower rate of complications following surgery, but on the treatment of the complications. In fact, patients with a complication after ...
Study shows young adults with addiction benefit from active 12 step group participation
2012-11-09
CENTER CITY, Minn. (November 8, 2012) – Young adults undergoing addiction treatment benefit from regular participation in Twelve Step-based self-help groups after discharge, according to a naturalistic study published electronically and in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence. The study was conducted collaboratively by the Center for Addiction Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School and the Butler Center for Research at Hazelden.
"Very little is known about the effects of Twelve Step attendance and involvement on outcomes for young adults. ...
[1] ... [5658]
[5659]
[5660]
[5661]
[5662]
[5663]
[5664]
[5665]
5666
[5667]
[5668]
[5669]
[5670]
[5671]
[5672]
[5673]
[5674]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.