For mitochondria, bigger may not be better
2012-08-23
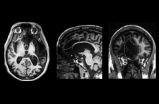
Goldilocks was on to something when she preferred everything "just right." Harvard Medical School researchers have found that when it comes to the length of mitochondria, the power-producing organelles, applying the fairy tale's mantra is crucial to the health of a cell. More specifically, abnormalities in mitochondrial length promote the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
"There had been a fair amount of interest in mitochondria in Alzheimer's and tau-related diseases, but causality was unknown," said Brian DuBoff, first author of the study ...
August 2012 tips from the journals of the American Society for Microbiology
2012-08-23
Boost for Efforts to Prevent Microbial Stowaways on Interplanetary Spacecraft
Efforts to expunge micro-organisms from spacecraft assembly cleanrooms, and the spacecraft themselves, inadvertently select for the organisms that are often the most fit to survive long journeys in space. This has the risk of thwarting the goal of avoiding contaminating other celestial bodies, as well as samples brought back to earth, according to Myron La Duc of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), California Institute of Technology, and his collaborators. Their research is published in the ...
Cancer survival in Germany after the fall of the Iron Curtain
2012-08-23
Data from the 1970s and 1980s show that people affected by cancer survived significantly longer in West Germany than cancer patients behind the Iron Curtain. Looking at a diagnosis period from 1984 to 1985 in the former German Democratic Republic, 28 percent of colorectal cancer patients, 46 percent of prostate cancer patients, and 52 percent of breast cancer patients survived the first five years after diagnosis. By contrast, 5-year survival rates for people in West Germany affected by these types of cancer were 44 percent, 68 percent, and 68 percent in the years from ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Isaac bring heavy rains to Eastern Caribbean
2012-08-23
VIDEO:
An animation of satellite observations from Aug. 20-23, 2012, shows Tropical Storm Isaac moving through the eastern Caribbean Sea. This visualization was created by the NASA GOES Project at NASA's...
Click here for more information.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite captured rainfall data from Tropical Storm Isaac as it continues moving through the Caribbean Sea.
After a quiet July, the Atlantic has seen a sharp increase in tropical activity. ...
Past tropical climate change linked to ocean circulation, says Texas A&M team
2012-08-23
A new record of past temperature change in the tropical Atlantic Ocean's subsurface provides clues as to why the Earth's climate is so sensitive to ocean circulation patterns, according to climate scientists at Texas A&M University.
Geological oceanographer Matthew Schmidt and two of his graduate students teamed up with Ping Chang, a physical oceanographer and climate modeler, to help uncover an important climate connection between the tropics and the high latitude North Atlantic. Their new findings are in the current issue of PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy ...
IBC 2012: New standard HEVC encodes films more efficiently
2012-08-23
The opening ceremonies for the Olympic Games captivated countless viewers all over the world in front of their televisions, astounding them with a gigantic show. Relatively few people were able to have a live experience of the spectacle at the London stadium. Still, some of the fans watching the show felt as if they were there live, even though they were only sitting in front of a large cinema screen. That's because a few movie theaters showed the opening ceremonies in 8K-resolution, which corresponds to 33 megapixels.
The resolution on home televisions will soon be enhanced ...
IBC 2012: Mini-camera with maxi-brainpower
2012-08-23
Just a few more meters to the finish line. The mountain biker jumps over the last hill and takes the final curve, with the rest of the competition close at his heels. At such moments, you do not want to just watch, you would really love to put yourself in the same shoes as the athlete. How does he push the pace on the final stretch? How fast is his pulse racing? What does he feel like? Viewers will soon be able to obtain this information in real time, directly with the images. Because the INCA intelligent camera, engineered by Fraunhofer researchers in Erlangen, makes completely ...
AGU: Link found between cold European winters and solar activity
2012-08-23
WASHINGTON – Scientists have long suspected that the Sun's 11-year cycle influences climate of certain regions on Earth. Yet records of average, seasonal temperatures do not date back far enough to confirm any patterns. Now, armed with a unique proxy, an international team of researchers show that unusually cold winters in Central Europe are related to low solar activity – when sunspot numbers are minimal. The freezing of Germany's largest river, the Rhine, is the key.
Although the Earth's surface overall continues to warm, the new analysis has revealed a correlation ...
Advantage flu virus
2012-08-23
When you are hit with the flu, you know it immediately -- fever, chills, sore throat, aching muscles, fatigue. This is your body mounting an immune response to the invading virus. But less is known about what is happening on the molecular level.
Now Northwestern University scientists have discovered one of the ways the influenza virus disarms our natural defense system. The virus decreases the production of key immune system-regulating proteins in human cells that help fight the invader. The virus does this by turning on the microRNAs -- little snippets of RNA -- that ...
Cameleon Software Announces Gold Sponsorship of Dreamforce 2012.
2012-08-23
Cameleon Software (www.cameleon-software.com), today announced it will be a Gold sponsor of salesforce.com's Dreamforce 2012 conference (www.dreamforce.com). The conference will be held September 18-21, 2012, at the Moscone Center in San Francisco. Cameleon Software provides a multichannel, multi-device CPQ (configure, price, quote) and eCommerce software that tightly integrates with Salesforce CRM. Cameleon CPQ enables sales and marketing teams to quickly design, configure and price offers, and generate accurate quotes and proposals on every sales channel, including tablets ...
New device monitors schoolroom air for carbon dioxide levels that may make kids drowsy
2012-08-23
PHILADELPHIA, Aug. 22, 2012 — With nearly 55 million students, teachers and school staff about to return to elementary and secondary school classrooms, scientists today described a new hand-held sensor ― practical enough for wide use ― that could keep classroom air fresher and kids more alert for learning.
They reported on the device at the 244th National Meeting & Exposition of the American
Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society, being held here this week. The sensor detects the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in classroom air. The average ...
Biorefinery makes use of every bit of a soybean
2012-08-23
PHILADELPHIA, Aug. 22, 2012 — The corn industry produces almost 4,000 products from every bushel. Oil refineries produce fuels and ingredients for an estimated 6,000 products with a thoroughness that actually squeezes 44 gallons of products from every 42-gallon barrel of crude.
Scientists today unveiled new technology intended to move soybeans, second only to corn as the top food crop in the U.S., along that same use-to-all path as a raw material for a wider portfolio of products. They described it ― a new integrated soybean biorefinery ― at the 244th National ...
Toward medicines that recruit the body's natural disease-fighting proteins
2012-08-23
PHILADELPHIA, Aug. 22, 2012 — Like recruiters pitching military service to a throng of people, scientists are developing drugs to recruit disease-fighting proteins present naturally in everyone's blood in medicine's war on infections, cancer and a range of other diseases. They reported on the latest advances in this new approach here today at the 244th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society.
David Spiegel, M.D., Ph.D., who heads one of the major research teams developing "antibody-recruiting molecules" (or ...
Archived Guthrie cards find a new purpose
2012-08-23
August 23, 2012 – Over the last 50 years, the spotting of newborn's blood onto filter paper for disease screening, called Guthrie cards, has become so routine that since 2000, more than 90% of newborns in the United States have had Guthrie cards created. In a study published online in Genome Research, researchers have shown that epigenetic information stored on archived Guthrie cards provides a retrospective view of the epigenome at birth, a powerful new application for the card that could help understand disease and predict future health.
DNA methylation, an epigenetic ...
NIH researchers find possible cause of immune deficiency cases in Asia
2012-08-23
A clinical study led by National Institutes of Health investigators has identified an antibody that compromises the immune systems of HIV-negative people, making them susceptible to infections with opportunistic microbes such as nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). In this study conducted at hospitals in Thailand and Taiwan, the researchers found that the majority of study participants with opportunistic infections made an antibody against interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), a cell-signaling molecule thought to play a major role in clearing harmful infections. The study findings ...
Self-awareness in humans is more complex, diffuse than previously thought
2012-08-23
Ancient Greek philosophers considered the ability to "know thyself" as the pinnacle of humanity. Now, thousands of years later, neuroscientists are trying to decipher precisely how the human brain constructs our sense of self.
Self-awareness is defined as being aware of oneself, including one's traits, feelings, and behaviors. Neuroscientists have believed that three brain regions are critical for self-awareness: the insular cortex, the anterior cingulate cortex, and the medial prefrontal cortex. However, a research team led by the University of Iowa has challenged this ...
Experts say ethical dilemmas contribute to 'critical weaknesses' in FDA postmarket oversight
2012-08-23
Ethical challenges are central to persistent "critical weaknesses" in the national system for ensuring drug safety, according to a commentary by former Institute of Medicine (IOM) committee members published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
With a caution against "reactive policymaking," committee co-chairs Ruth Faden, Ph.D., M.P.H., and Steven Goodman, M.D., M.H.S., Ph.D., with fellow committee member Michelle Mello, J.D., Ph.D., revisit the controversy over the antidiabetic drug Avandia that led to the formation of their IOM committee on monitoring drug ...
NIH uses genome sequencing to help quell bacterial outbreak in Clinical Center
2012-08-23
For six months last year, a deadly outbreak of antibiotic-resistant bacteria kept infection-control specialists at the National Institutes of Health's (NIH) Clinical Center in a state of high alert. A New York City patient carrying a multi-drug resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae, a microbe frequently associated with hospital-borne infections, introduced the dangerous bacteria into the 243-bed research hospital while participating in a clinical study in the summer of 2011.
Despite enhanced infection-control practices, including patient isolation, the K. pneumoniae ...
Study suggests early exposure to antibiotics may impact development, obesity
2012-08-23
NEW YORK, August 22, 2012 – Researchers at NYU School of Medicine have made a novel discovery that could have widespread clinical implications, potentially affecting everything from nutrient metabolism to obesity in children.
Since the 1950's, low dose antibiotics have been widely used as growth promoters in the agricultural industry. For decades, livestock growers have employed subtherapeutic antibiotic therapy (STAT), not to fight infection or disease, but to increase weight gain in cattle, swine, sheep, chickens and turkey, among other farm animals.
First author ...
Sky-high methane mystery closer to being solved, UCI researchers say
2012-08-23
Irvine, Calif. – Increased capture of natural gas from oil fields probably accounts for up to 70 percent of the dramatic leveling off seen in atmospheric methane at the end of the 20th century, according to new UC Irvine research being published Thursday, Aug. 23, in the journal Nature.
"We can now say with confidence that, based on our data, the trend is largely a result of changes in fossil fuel use," said chemistry professor Donald Blake, senior author on the paper.
Methane has 20 times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide, although CO2 is filling the ...
Low-dose sedative alleviates autistic-like behavior in mice with Dravet syndrome mutation
2012-08-23
A low dose of the sedative clonazepam alleviated autistic-like behavior in mice with a mutation that causes Dravet syndrome in humans, University of Washington researchers have shown.
Dravet syndrome is an infant seizure disorder accompanied by developmental delays and behavioral symptoms that include autistic features. It usually originates spontaneously from a gene mutation in an affected child not found in either parent.
Studies of mice with a similar gene mutation are revealing the overly excited brain circuits behind the autistic traits and cognitive impairments ...
Scientists reveal how river blindness worm thrives
2012-08-23
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have found that the worm which causes River Blindness survives by using a bacterium to provide energy, as well as help 'trick' the body's immune system into thinking it is fighting a different kind of infection.
River Blindness affects 37 million people, mainly in sub-Saharan Africa, causing intense itching of the skin, visual impairment and in severe cases, irreversible blindness. It is caused by a parasitic worm that is transmitted by blood-feeding blackflies, which breed in fast-flowing rivers.
The team at Liverpool investigated ...
New climate history adds to understanding of recent Antarctic Peninsula warming
2012-08-23
Results published this week by a team of polar scientists from Britain, Australia and France adds a new dimension to our understanding of Antarctic Peninsula climate change and the likely causes of the break-up of its ice shelves.
The first comprehensive reconstruction of a 15,000 year climate history from an ice core collected from James Ross Island in the Antarctic Peninsula region is reported this week in the journal Nature. The scientists reveal that the rapid warming of this region over the last 100 -years has been unprecedented and came on top of a slower natural ...
Future memory
2012-08-23
A new class of organic materials developed at Northwestern University boasts a very attractive but elusive property: ferroelectricity. The crystalline materials also have a great memory, which could be very useful in computer and cellphone memory applications, including cloud computing.
A team of organic chemists discovered they could create very long crystals with desirable properties using just two small organic molecules that are extremely attracted to each other. The attraction between the two molecules causes them to self assemble into an ordered network -- order ...
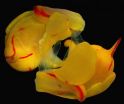
Traumatic mating may offer fitness benefits for female sea slugs
2012-08-23
Female sea slugs mate more frequently than required to produce offspring, despite the highly traumatic and biologically costly nature of their copulation, as reported Aug. 22 in the open access journal PLOS ONE.
The authors of the study, led by Rolanda Lange of the University of Tuebingen in Germany, investigated the mating behavior of a simultaneously hermaphroditic species of sea slug that mates via an extravagant ritual that involves a syringe-like penile appendage that stabs the partner to inject prostate fluids and sperm.
Surprisingly, the researchers found that ...
[1] ... [6085]
[6086]
[6087]
[6088]
[6089]
[6090]
[6091]
[6092]
6093
[6094]
[6095]
[6096]
[6097]
[6098]
[6099]
[6100]
[6101]
... [8803]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.