Lessons learned from the 'ethical odyssey' of an HIV trial
2012-06-15
In the battle against HIV/AIDS conditions on the frontlines are constantly in flux as treatment, research and policy evolve. The landmark HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) 052 study, which established that antiretroviral treatment in people who are HIV positive decreases the likelihood of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners, was no exception. One year after publication the study serves as a case study of ethical challenges faced at every stage of the research trial process in the new paper "Establishing HIV treatment as prevention in the HIV Prevention Trials ...
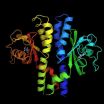
Atomic-resolution view of a receptor reveals how stomach bacterium avoids acid
2012-06-15
EUGENE, Ore. -- (June 14, 2012) -- University of Oregon scientists have discovered how the bacterium Helicobacter pylori navigates through the acidic stomach, opening up new possibilities to inactivate its disease-causing ability without using current strategies that often fail or are discontinued because of side effects.
Their report -- online ahead of regular publication July 3 in the journal Structure -- unveils the crystal structure of H. pylori's acid receptor TlpB. The receptor has an external protrusion, identified as a PAS domain, bound by a small molecule called ...
Elderly prisoners need better medical care, according to report
2012-06-15
Soaring numbers of older, sicker prisoners are causing an unprecedented health care challenge for the nation's criminal justice system, according to a new UCSF report.
As the American penal system confronts a costly demographic shift toward older prisoners, the authors call for an overhaul in health care practices for elderly inmates who disproportionately account for escalating medical expenses behind bars. The recommendations include screening for dementia among prisoners, improved palliative care, and standard policies for geriatric housing units for infirm inmates.
The ...
Stanford engineers perfecting carbon nanotubes for highly energy-efficient computing
2012-06-15
Energy efficiency is the most significant challenge standing in the way of continued miniaturization of electronic systems, and miniaturization is the principal driver of the semiconductor industry. "As we approach the ultimate limits of Moore's Law, however, silicon will have to be replaced in order to miniaturize further," said Jeffrey Bokor, deputy director for science at the Molecular Foundry at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Professor at UC-Berkeley.
To this end, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are a significant departure from traditional silicon technologies ...
Tense film scenes trigger brain activity, CCNY-led team finds
2012-06-15
Visual and auditory stimuli that elicit high levels of engagement and emotional response can be linked to reliable patterns of brain activity, a team of researchers from The City College of New York and Columbia University reports. Their findings could lead to new ways for producers of films, television programs and commercials to predict what kinds of scenes their audiences will respond to.
"Peak correlations of neural activity across viewings can occur in remarkable correspondence with arousing moments of the film," the researchers said in an article published in the ...
Environmental factors spread obesity, CCNY-led team reports
2012-06-15
An international team of researchers' study of the spatial patterns of the spread of obesity suggests America's bulging waistlines may have more to do with collective behavior than genetics or individual choices. The team, led by City College of New York physicist Hernán Makse, found correlations between the epidemic's geography and food marketing and distribution patterns.
"We found there is a relationship between the prevalence of obesity and the growth of the supermarket economy," Professor Makse said. "While we can't claim causality because we don't know whether obesity ...
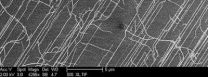
Gone fishing: Researchers' imaging technique trolls in quiet cellular seas
2012-06-15
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Experienced anglers know that choppy waters make for difficult fishing, so they try not to rock the boat. Thanks to a new microscopy technique, cell biology researchers can heed that same advice.
University of Illinois researchers developed a method they call "trolling AFM," which allows them to study soft biological samples in liquid with high resolution and high quality. Led by mechanical science and engineering professor Min-Feng Yu, the group published its findings in the journal Nanotechnology.
"We developed a highly sensitive method for high-resolution ...
Take-home methadone maintenance treatment associated with decreased hospital admissions
2012-06-15
(Boston) – A recent study conducted by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC) shows that patients receiving "take home" methadone maintenance treatment (MMT) were less likely to be admitted to the hospital as compared to those not receiving take home doses. The findings, which are published online in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, demonstrate the potential benefits of successful addiction treatment, including better overall health and decreased health care utilization.
This research was led by Alexander Walley, MD, MSc, physician in general internal medicine at ...
9 out of 10 non-elderly Californians will be covered under Affordable Care Act
2012-06-15
Nine out of 10 Californians under the age of 65 will be enrolled in health insurance programs as a result of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), according to a joint study by the UC Berkeley Center for Labor Research and Education and the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research.
Between 1.8 million and 2.7 million previously uninsured Californians will gain coverage by 2019, when the law's effect is fully realized, the researchers said.
The report, which uses a sophisticated computer simulation model to project the ACA's impact on insurance coverage, ...
How aging normal cells fuel tumor growth and metastasis
2012-06-15
PHILADELPHIA—It has long been known that cancer is a disease of aging, but a molecular link between the two has remained elusive.
Now, researchers at the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson (KCC) have shown that senescence (aging cells which lose their ability to divide) and autophagy (self-eating or self-cannibalism) in the surrounding normal cells of a tumor are essentially two sides of the same coin, acting as "food" to fuel cancer cell growth and metastasis.
Michael P. Lisanti, M.D., Ph.D., Professor and Chair of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine at Jefferson ...
Soft drink consumption not the major contributor to childhood obesity
2012-06-15
Ottawa, Ontario (June 14, 2012) – Most children and youth who consume soft drinks and other sweetened beverages, such as fruit punch and lemonade, are not at any higher risk for obesity than their peers who drink healthy beverages, says a new study published in the October issue of Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. The study examined the relationship between beverage intake patterns of Canadian children and their risk for obesity and found sweetened beverage intake to be a risk factor only in boys aged 6-11.
"We found sweetened drinks to be dominant beverages ...
Study finds predators have outsized influence over habitats
2012-06-15
A grasshopper's change in diet to high-energy carbohydrates while being hunted by spiders may affect the way soil releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, according to Yale and Hebrew University researchers in Science.
Grasshoppers like to munch on nitrogen-rich grass because it stimulates their growth and reproduction. But when spiders enter the picture, grasshoppers cope with the stress from fear of predation by shifting to carbohydrate-rich plants, setting in motion dynamic changes to the ecosystem they inhabit.
"Under stressful conditions they go to different ...
Grasshoppers 'stressed' by spiders affect the productivity of our soil
2012-06-15
Jerusalem, June 14, 2012 – How do grasshoppers who are being frightened by spiders affect our ecosystem? In no small measure, say researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and at Yale University in the US.
A grasshopper who is in fear of an attacker, such as a spider, will enter a situation of stress and will consume a greater quantity of carbohydrate-rich plants – similar to humans under stress who might eat more sweets.
This type of reaction will, in turn, cause chemical changes in the grasshopper and in its excretions, affecting the ecosystem it inhabits. ...
Virtual colonoscopy without laxative equals standard in identifying clinically significant polyps
2012-06-15
Computed tomographic colonography (CTC), also known as virtual colonoscopy, administered without laxatives is as accurate as conventional colonoscopy in detecting clinically significant, potentially cancerous polyps, according to a study performed jointly at the San Francisco VA Medical Center, the University of California, San Francisco and Massachusetts General Hospital.
"I think we have demonstrated that laxative-free CTC is a valid tool for detecting polyps that are clinically significant," said co-author and site principal investigator Judy Yee, MD, chief of radiology ...
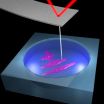
Catching some rays
2012-06-15
Drawn together by the force of nature, but pulled apart by the force of man – it sounds like the setting for a love story, but it is also a basic description of how scientists have begun to make more efficient organic solar cells.
At the atomic level, organic solar cells function like the feuding families in Romeo and Juliet. There's a strong natural attraction between the positive and negative charges that a photon generates after it strikes the cell, but in order to capture the energy, these charges need to be kept separate.
When these charges are still bound together, ...
Hidden vitamin in milk yields remarkable health benefits
2012-06-15
NEW YORK (June 14, 2012) — A novel form of vitamin B3 found in milk in small quantities produces remarkable health benefits in mice when high doses are administered, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College and the Polytechnic School in Lausanne, Switzerland.
The findings, recently reported in the June 2012 issue of the journal, Cell Metabolism, reveal that high doses of the vitamin precursor, nicotinamide riboside (NR) — a cousin of niacin — prevent obesity in mice that are fed a fatty diet, and also increase muscle performance, ...
Study suggests expanded concept of 'urban watershed'
2012-06-15
BALTIMORE, Md., June 14, 2012 – Within two decades, 60 percent of the world's population will live in cities, and coping with the resulting urban drinking water and sanitation issues will be one of the greatest challenges of this century. A U.S. Forest Service study recently published in Urban Ecosystems proposes an expanded view of the complex world of urban water.
The study presents a new conceptual framework that addresses characteristics of watersheds that are affected by urban land uses, including:
hydrologic connectivity between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems ...
Researchers outline plan to end preventable child deaths in a generation
2012-06-15
Preventable childhood deaths caused by illnesses such as pneumonia and diarrhea can be nearly eliminated in 10 years according to researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the National Institutes of Health. In a new commentary featured in the June issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers outline a strategy and benchmarks for curbing childhood preventable deaths and recommend a new common vision for a global commitment to end all preventable child deaths.
Developed in 2000 by the United Nations, eight Millennium ...
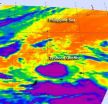
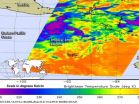
Guchol is a tiny typhoon on NASA satellite imagery
2012-06-15
Tropical Storm Guchol intensified into a typhoon and is a compact system. It appears as a strong, small typhoon in infrared NASA satellite imagery today.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Typhoon Guchol on June 13 and 14 and captured an infrared view of the storm's clouds and temperatures. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared and temperature data on Guchol. When cloud temperatures get colder, it means that clouds are getting higher. The lowest temperatures were as cold as or colder than 220 degrees Kelvin ...
NASA sees bitter cold cloud tops in newborn Tropical Storm Carlotta
2012-06-15
Bitter cold cloud tops tell forecasters that a storm has a lot of uplift, and the colder the cloud tops, the higher they are in the atmosphere, and the stronger the thunderstorms. NASA's Aqua satellite data showed that the cloud top temperatures in newborn Tropical Storm Carlotta became colder overnight and continue to grow colder as the low pressure area formely known as System 94E strengthened into a tropical storm. Carlotta is even expected to strengthen further and become a hurricane.
Because Carlotta is expected to continue strengthening, the government of Mexico ...
Chance alignment between galaxies mimics a cosmic collision
2012-06-15
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows a rare view of a pair of overlapping galaxies, called NGC 3314. The two galaxies look as if they are colliding, but they are actually separated by tens of millions of light-years, or about ten times the distance between our Milky Way and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. The chance alignment of the two galaxies, as seen from Earth, gives a unique look at the silhouetted spiral arms in the closer face-on spiral, NGC 3314A.
The motion of the two galaxies indicates that they are both relatively undisturbed and that they are moving in markedly ...
First flight instrument delivered for James Webb
2012-06-15
The first of four instruments to fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) has been delivered to NASA. The Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) will allow scientists to study cold and distant objects in greater detail than ever before.
MIRI arrived at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., May 29. It has been undergoing inspection before being integrated into Webb's science instrument payload known as the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM).
Assembled at and shipped from the Science and Technology Facilities Council's Rutherford Appleton Laboratory ...
New solar active region spitting out flares
2012-06-15
An active region on the sun, numbered AR 1504, rotated into view over the left side of the sun on June 10, 2012. The region fired off two M-class flares and two coronal mass ejections (CMEs) on June 13 and June 14, 2012. The first flare lasted for a relatively long three hours, peaking on June 13, 2012 at 9:17 AM EDT. The associated CME traveled at approximately 375 miles per second and is directed toward Earth, though due to its slow speed, the effect on Earth is expected to be minimal.
The second M-class flare was also a long-duration flare, and it peaked on June 14, ...
Unexpected discovery highlights new role for cell death regulator
2012-06-15
An unexpected discovery of how the body controls cell death has revealed a potential new therapeutic target.
A research team based at Cardiff University's School of Biosciences has already revealed the mechanism by which high alcohol intake can induce pancreatitis and its progression to pancreatic cancer. Now a new study, published in Current Biology, reveals a hitherto unknown interaction between two well known molecules, which has important implications for our understanding of inflammation and cancer in the pancreas as well as other organs.
The Cardiff team studied ...
Vitamin D with calcium shown to reduce mortality in elderly
2012-06-15
A study recently published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM) suggests that vitamin D—when taken with calcium—can reduce the rate of mortality in seniors, therefore providing a possible means of increasing life expectancy.
During the last decade, there has been increasing recognition of the potential health effects of vitamin D. It is well known that calcium with vitamin D supplements reduces the risk of fractures. The present study assessed mortality among patients randomized to either vitamin D alone or vitamin D with ...
[1] ... [6448]
[6449]
[6450]
[6451]
[6452]
[6453]
[6454]
[6455]
6456
[6457]
[6458]
[6459]
[6460]
[6461]
[6462]
[6463]
[6464]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.