DASCOM Americas Announces Continued Global Expansion with Company Incorporation in Brazil
2012-05-24
DASCOM Americas, a recognized leader in complete business printing solutions and marketer of Tally(R) , TallyDascom(R) and TallyGenicom(R) products formerly marketed by TallyGenicom Corporation, is pleased to announce its continuing global expansion with the incorporation of Dascom in Brazil.
DASCOM BRASIL Solucoes de Impressao e Sistemas de Iluminacao ltda received registration with the board of trade for the state of Rio de Janeiro in Brazil on May 2nd.
The move, part of the continued growth for Dascom Americas, is designed to make Dascom products more readily ...
New York Furniture Manufacturer Gothic Cabinet Craft Launches New Blog
2012-05-24
Real wood furniture manufacturer Gothic Cabinet Craft (http://www.gothiccabinetcraft.com) has recently launched a new blog full of tips and advice for furniture buying, furnishing urban apartments and home offices, bedroom and living room furniture design and much more.
The new furniture blog, which can be found at http://blog.gothiccabinetcraft.com/, is part of Gothic Cabinet Craft's commitment to becoming a more social brand. Gothic's President, Aristidis Zaharopoulos, says "When it comes to buying furniture, people are making a big investment and we want them ...
York Prep Considers the Pros and Cons of Online Classes
2012-05-24
It used to be that students obtained an education by attending class and listening to the teacher face-to-face. But now, with the emergence of modern technology, more students are turning to online classes for their education. The New York Times published a story outlining individuals' thoughts on the concept of online classes. York Prep, based in the Manhattan area of New York, understands why students are keen on online classes, but says they do have drawbacks.
In the New York Times story, Tara McLaughlin, explains that more prominent colleges, such as Harvard University ...
ILG Energy Endorses Further Exploration in Solar Power
2012-05-24
Energy production is always a hot topic in America, but there has seldom been such an influx of fuel-related news as there has been recently. Americans, growing weary of rising costs at the gasoline pump, are beginning to hear that increased oil production could get those fuel costs back down by the end of the summer. Meanwhile, natural gas supplies remain high, where prices are at historic lows. But while these two energy sources occupy much of the discussion about America's fuel industry, a company called ILG Energy is calling for more research to be done in the realm ...
SCG Business Services Limited Announces Launch of a New Website
2012-05-24
SCG Business Services Limited (www.scglimited.com), a leading hedge fund consulting firm to new and experienced fund managers, announced today the launch of their new website and the expansion of its services.
Fund Formation
SCG Business Services provides a full range of services specializing in offshore and domestic fund formation to new and experienced fund managers. "A fund document is not only a disclosure document that defines the terms of the fund and the risks to the investor, it also represents the fund and makes the first impression. SCG understands the ...
Joel Bernheim Calls for Fairness in Divorce Courts
2012-05-24
Divorce laws can vary greatly from one state to the next, but one thing that has long remained consistent is the fact that, in most divorce cases, conventional gender roles are strongly upheld, particularly when children are in the picture. Historically, it has typically been the father who ends up paying alimony and child support to the mother, who often gets custody of the children. A recent report finds that this might be changing, however. According to a new study, reported by Reuters, more women are paying child support and alimony to their ex-husbands than ever before. ...
Colorado Springs Dentist Celebrates 35 Years in Dentistry
2012-05-24
Dr. Ed Christiansen, Colorado Springs dentist, is thrilled to be celebrating his 35th year in dentistry and 28th year in Colorado Springs in May 2012.
"I am so happy to be able to say that I have been practicing dentistry for the past 35 years. Over the years, I have had the pleasure of meeting countless patients and helping them keep their teeth and gums healthy. I greatly enjoy what I do and I hope to meet many more patients in the coming years," said Dr. Christiansen, dentist in Colorado Springs.
Although Dr. Christiansen graduated from dental school ...
Tampa Divorce Lawyer Wins Very Complex Divorce Case
2012-05-24
Tampa Divorce Lawyer Christian Denmon of Denmon & Denmon Trial Lawyers recently handled one of his most complex divorce cases yet. The case dealt with alimony, child support, back child support and the distribution of seven marital houses.
A couple in Tampa recently went to trial on a complex divorce matter, and the wife sought Christian Denmon's representation to make sure she got a fair settlement.
In this particular scenario, the husband packed up his bags and left the house, leaving his stay-at-home wife of 17 years at home to care for their four minor children. ...
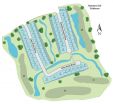
Taylor Morrison Developing Gated Golf Course Enclave in Houston, TX: Estates at Fairway Crossing in Fall Creek Skirts Redstone Golf Course
2012-05-24
Taylor Morrison is developing a gated golf course enclave called Estates at Fairway Crossing in Fall Creek located in near northeast Houston. The 50 home sites in the Estates at Fairway Crossing back up to the Redstone Golf Course or a natural creek. Home prices range from the mid-$300,000s to $600,000s.
Home sites in Estates at Fairway Crossing are the largest non-custom lots on the Redstone Golf Course. Taylor Morrison is offering 13 one- and two-story plans with 3,265 to 5,491 square feet on 80-ft. home sites. The Treviso model will open during Fall Creek's Open Homes ...
Tesco Clubcard Teams Up with Viking
2012-05-24
The world's leading river cruise line, Viking River Cruises, has been approached by retail giant TESCO to offer a discount on Viking holidays in exchange for TESCO Clubcard vouchers.
TESCO Clubcard customers can now enjoy discounts for a number of picturesque holidays on rivers across Europe, Russia and Asia. The Clubcard offer is available across all of Viking routes and 31 ships; including the new revolutionary Longships which launched in March and the Douro route which launches in 2013.
Wendy Atkin-Smith, MD of Viking River Cruises UK, said, "We were delighted ...
Fishing Tourism: Discovering the Secrets and Tradition of Sicilian Fishing
2012-05-24
In front of the sea happiness is a simple idea.
--Jean-Claude Izzo, Chourmo, 1996
The aim of Fishing Tourism is to promote and increase the value of traditions relating to Sea and Fishing Culture, which are frequently abandoned and undervalued.
Some of the recreational activities include trips along the coasts, meals served on board fishing boats and the observing of fishing operations. So, the tourists is eager to discover the sea's heritage and secrets have been able to take part in, as a unique experience in contact with fishermen and their tireless profession.
Spending ...
Edinburgh Marathon Festival
2012-05-24
The Edinburgh Marathon Festival offers a great variety of races that allows the whole family to get involved in fund raising and helping good causes. The festival not only includes races but also comedy shows and other exhibitions so if you don't fancy running there'll be plenty of other things to get into.
From manageable races like the 5k to the full marathon the festival is hugely popular with locals but also all over the UK. Those looking to take part in the full marathon needed to register by May 16th but you can wait a bit longer to book your hotel in Edinburgh. ...
What Problems do Veneers Fix?
2012-05-24
Porcelain veneers improve many different kinds of cosmetic dental issues. Most of the imperfections causing embarrassment and hesitation to smile can be concealed with porcelain veneers. Generally, dental issues involving bite misalignment may not be effectively addressed with porcelain veneers.
Uses of Porcelain Veneers
Porcelain veneers can fix the majority of common cosmetic dental problems, including:
- Chipped teeth
- Crooked teeth
- Misshapen teeth
- Cracked teeth
- Worn teeth
- Stained teeth
- Gaps between teeth
Porcelain veneers address these problems ...
The Olinsky Law Group Announces Disabled Employee Partnerships
2012-05-24
The Olinsky Law Group is proud to announce a new partnership with Aurora of CNY and the New York State Commission for the Blind (CBVH) in an effort to offer employment opportunities to their clients. This partnership will allow both organizations to better serve individuals who have disabilities living in our community.
The Olinsky Law Group is a national disability law firm, based in Syracuse, NY that focuses on Social Security, Workers' Compensation, Long-Term Disability and Americans with Disability Act Discrimination. Aurora of CNY is a not-for-profit organization ...
Handling a Dispute Over Your Lottery Winnings
2012-05-24
It is no secret that coming into money may create strife in your personal life. Never is this truer than when other parties claim to be the rightful owners of your lottery jackpot. From a colleague who believes your winning ticket was part of a workplace pool to a misguided family member seeking to dip into your jackpot, a sudden stroke of good luck often brings a wide range of unwelcome interlopers. Knowing how to respond can help keep your winnings -- and your sanity -- intact.
Alternatively, in certain instances the Lottery Commissioner may deny your rightful winnings. ...
Harassed By Creditors? California and Federal Laws Have Your Back
2012-05-24
The endless phone calls; the letters piling up in your mailbox; the questions from your friends and family about who has been asking about you. When a creditor comes after you for a debt, collection efforts can run the gamut from merely annoying to a serious disruption of your day-to-day routine.
Fortunately, there are a range of legal protections at your disposal under both state and federal law -- but you may not know about them. Although a Los Angeles bankruptcy attorney may be your best resource for dealing with creditor harassment in California, even a cursory review ...
Missouri's Legislators Propose Change to Methods of Judicial Selection
2012-05-24
Missouri uses a merit-based judicial selection process called the Nonpartisan Court Plan. Over the years, the selection process has become known as the Missouri Plan. The plan was adopted in 1940 to counter widespread abuses in the judicial system by "Boss Tom" Pendergast and his political network across the state.
Since the adoption of the Missouri Plan, 34 other states have used it as a guide in crafting their own policies to fill judicial vacancies.
And yet, the state's legislature may be shaking things up again. Earlier in the year the legislature attempted ...
Speed Limiters on Semis Show Impressive Safety Benefits
2012-05-24
In late March 2012, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration, part of the U.S. Department of Transportation, announced study findings important for the future of commercial trucking safety. Extensive research showed that installing speed limiters, also called SLs or speed governors, on large commercial trucks provides a "profound safety benefit."
Profound indeed -- the study concluded that such devices reportedly reduce crash rates by half.
An SL is an electronic device that keeps a truck engine below a programmed speed limit. SLs are already voluntarily ...
When Doctors Fail to Review Hospital Test Results
2012-05-24
When you go to the hospital, you expect that medical professionals will be able to diagnose and treat any conditions you are suffering from. To do so, doctors may run a battery of tests, and sometimes perform exploratory surgery. Some tests may take days to run, so occasionally, patients may be discharged from the hospital before these tests return.
One would hope that doctors would still review these test results. Unfortunately, this sometimes doesn't happen, resulting in the potential for misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
New York Case of Delayed Diagnosis
Take ...
Bankruptcy and Personal Injury Don't Mix
2012-05-24
Despite difficult economic times, the American Bankruptcy Institute has noted the number of bankruptcy filings has dropped across the country. However, a recent opinion from the Illinois Appellate Court confirms that trial lawyers from both sides of the bar should be aware that bankruptcy filings can, and will, impact your case. In Berge, the First District found that the doctrine of judicial estoppel bars a plaintiff from proceeding with a cause of action in state court where the plaintiff fails to disclose the action as an asset in a bankruptcy petition. Berge v. Kuno ...
She Fell Off the Operating Table: Woman Sues Yale-New Haven Hospital for Malpractice
2012-05-24
The surgery went fine, but the result was not.
Florence Fiedler, now 81, of New Canaan, thought she was going to Yale-New Haven Hospital for what has become a fairly routine procedure - implantation of a pacemaker. As expected, the surgery went fine.
However, while still sedated she fell from the operating table to the floor, crashing with such force that she suffered from traumatic brain injury, a broken collar bone, broken hip and broken toe. Hitting her head caused bleeding around the lining of her brain. She also damaged her back.
Atty. James Horwitz, the lawyer ...
More Retired NFL Players Added to Lawsuit Against NFL
2012-05-24
14 additional players are joining the roster of retired football players suing the NFL for purposefully attempting to hide a well-known link between concussions and permanent brain injury.
The group filing suit now totals 46, says attorney Matthew C. Matheny of the Provost Umphrey law firm.
"These players are suffering permanent brain injury that they and their families must endure for the rest of their lives as a result of playing for the National Football League. Its time for the NFL to admit they have known for years about the connection between multiple ...
Education Management Corp. Facing Suit Over Misconduct and Violations of Federal Education Regulations
2012-05-24
Today the Oklahoma Law Enforcement Retirement System (OLERS) filed suit in the Allegheny County Court of Common Pleas against the Allegheny County-based Education Management Corp. (EDMC) and its board of directors stemming from the company's systemic misconduct and blatant violations of federal education regulations.
Read the complaint here.
Specifically, EDMC, one of the country's largest for-profit education providers, has engaged in aggressive and illegal recruiting and has compensated its recruiters based solely on the number of new student enrollments, which ...
Teens Have Unrealistic Views About Distracted Driving, Study Finds
2012-05-24
Distracted driving is a problem that affects even the most experienced drivers, so it's not surprising that newly-minted teenage drivers -- who often have trouble controlling their impulses -- are susceptible to driving while distracted.
According to AAA, the most common distractions among teenage drivers are using electronic devices (for both talking and texting), adjusting controls in the car, and eating or drinking.
Teens Don't Believe Distracted Driving Is a Problem
Despite the research that shows that teenage drivers engage in distracted driving, they believe ...
Feldman Fox And Morgado Depuy Hip Replacement Products Liability Claims
2012-05-24
If you have been implanted with a DePuy artificial hip, or have already had one replaced due to pain, discomfort or problems with the initial surgery, you should contact a lawyer to seek recovery of your damages from DePuy.
Depuy initiated a voluntary recal of several of its artificial hip implant systems. Recalls Specific to Metal-on-Metal Hip Implant Systems: DePuy ASR XL Acetabular System.
On August 24, 2010, there was a voluntary recall of the DePuy ASR total hip system because of new, unpublished data from the UK joint registry indicating the revision rates within ...
[1] ... [6449]
[6450]
[6451]
[6452]
[6453]
[6454]
[6455]
[6456]
6457
[6458]
[6459]
[6460]
[6461]
[6462]
[6463]
[6464]
[6465]
... [8800]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.