ATS publishes clinical practice guidelines on interpretation of FENO levels
2011-09-02
The American Thoracic Society has issued the first-ever guidelines on the use of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) that address when to use FENO and how to interpret FENO levels in different clinical settings. The guidelines, which appear in the September 1 American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, are graded based on the available evidence in the literature.
"There are existing guidelines to measure FENO but none to interpret the results," noted Raed A. Dweik, MD, chair of the guideline writing committee and professor of medicine and director ...
New map shows where tastes are coded in the brain
2011-09-02
Each taste, from sweet to salty, is sensed by a unique set of neurons in the brains of mice, new research reveals. The findings demonstrate that neurons that respond to specific tastes are arranged discretely in what the scientists call a "gustotopic map." This is the first map that shows how taste is represented in the mammalian brain.
There's no mistaking the sweetness of a ripe peach for the saltiness of a potato chip – in part due to highly specialized, selectively-tuned cells in the tongue that detect each unique taste. Now, Howard Hughes Medical Institute and NIH ...
Ben-Gurion U. researchers identify gene that leads to myopia (nearsightedness)
2011-09-02
BEER-SHEVA, ISRAEL, September 1, 2011— A Ben-Gurion University of the Negev research group led by Prof. Ohad Birk has identified a gene whose defect specifically causes myopia or nearsightedness.
In an article appearing online in the American Journal of Human Genetics today, Birk and his team reveal that a mutation in LEPREL1 has been shown to cause myopia.
"We are finally beginning to understand at a molecular level why nearsightedness occurs," Prof. Birk says. The discovery was a group effort at BGU's Morris Kahn Laboratory of Human Genetics at the National Institute ...
2 brain halves, 1 perception
2011-09-02
Our brain is divided into two hemispheres, which are linked through only a few connections. However, we do not seem to have a problem to create a coherent image of our environment – our perception is not "split" in two halves. For the seamless unity of our subjective experience, information from both hemispheres needs to be efficiently integrated. The corpus callosum, the largest fibre bundle connecting the left and right side of our brain, plays a major role in this process. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in Frankfurt investigated whether ...
Faster progress through puberty linked to behavior problems
2011-09-02
Children who go through puberty at a faster rate are more likely to act out and to suffer from anxiety and depression, according to a study by researchers at Penn State, Duke University and the University of California, Davis. The results suggest that primary care providers, teachers and parents should look not only at the timing of puberty in relation to kids' behavior problems, but also at the tempo of puberty -- how fast or slow kids go through puberty.
"Past work has examined the timing of puberty and shown the negative consequences of entering puberty at an early ...
Sex hormones impact career choices
2011-09-02
Teacher, pilot, nurse or engineer? Sex hormones strongly influence people's interests, which affect the kinds of occupations they choose, according to psychologists.
"Our results provide strong support for hormonal influences on interest in occupations characterized by working with things versus people," said Adriene M. Beltz, graduate student in psychology, working with Sheri A. Berenbaum, professor of psychology and pediatrics, Penn State.
Berenbaum and her team looked at people's interest in occupations that exhibit sex differences in the general population and ...
First long-term study of WTC workers shows widespread health problems 10 years after Sept. 11
2011-09-02
In the first long-term study of the health impacts of the World Trade Center (WTC) collapse on September 11, 2001, researchers at The Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York have found substantial and persistent mental and physical health problems among 9/11 first responders and recovery workers. The data are published this week in a special 9/11 issue of the medical journal Lancet.
The Mount Sinai World Trade Center Clinical Center of Excellence and Data Center evaluated more than 27,000 police officers, construction workers, firefighters, and municipal workers over the ...
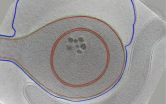
Caltech team says sporulation may have given rise to the bacterial outer membrane
2011-09-02
VIDEO:
This video uses animation to piece together cryotomograms of Acetonema longum cells at different stages of the sporulation process. Cryotomograms appear in black and white. Inner membranes are shown in...
Click here for more information.
PASADENA, Calif.—Bacteria can generally be divided into two classes: those with just one membrane and those with two. Now researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have used a powerful imaging technique to find ...
Digital quantum simulator realized
2011-09-02
Almost two years ago Rainer Blatt's and Christan Roos' research groups from the University of Innsbruck recreated the properties of a particle moving close to speed of light in a quantum system. They encoded the state of the particle into a highly cooled calcium atom and used lasers to manipulate it according to equations proposed by the famous quantum physicist Paul Dirac. Thereby, the scientists were able to simulate so called Zitterbewegung (quivering motion) of relativistic particles, which had never been observed directly in nature before. In the current work, the ...
New Free Spins Game at Casino-Mate
2011-09-02
Casino-Mate has stepped up to the demand for a highly popular game to stand as the Welcoming Free Spins game for new players. This Australian Casino has nominated ThunderStruck 2 as the first stop for new players at the casino.
The induction of ThunderStruck 2 Video Slot game as the introductory game for new players at the casino is set to show players the quality of games that they will be experiencing at the casino. All the games are powered by Microgaming , an online gaming creator and provider. There are, in total, over 550 games available at the online casino, ...
Online activity grows in a similar pattern to those of real-life networks
2011-09-02
The activity of online communities does not grow in line with the number of users, according to a model recently published in the European Physical Journal B.
The Internet has given rise to its own sorting devices. Among these, tagging consists of assigning user-chosen keywords to a piece of information (such as a digital image) to facilitate searches. Lingfei Wu, a researcher at the City University of Hong Kong's Department of Media and Communication, used the tagging behaviour of social media application users to study the growth of online communities' activity.
Wu ...
Fibrous stroma associated with poor prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
2011-09-02
The nature of the connective tissue surrounding lung cancer nests can help predict the aggressiveness of squamous cell carcinoma, according to research published in the September issue of the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC).
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the major cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide; its two major subtypes are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC). Although many reports have described the prognostic markers for adenocarcinoma, less research ...
Wrong Site Surgeries a Troubling Problem for Patients in North Carolina
2011-09-02
Operating on the wrong side of a patient's body is a horrible mistake that should never happen. Unfortunately, it occurs more often than you think. Based on data submitted to the Joint Commission Center for Transforming Healthcare, wrong site surgeries and procedures occur nearly 40 times per week across the U.S.
The aftermath of wrong site and wrong side surgeries are devastating. In addition to the pain of additional surgery and a lifetime of disfigurement, these mistakes can leave lasting emotional scars. Victims of this type of error may have grounds for a surgery ...
Insect gut microbe with a molecular iron reservoir
2011-09-02
Microbes are omnipresent on earth. They are found as free-living microorganisms as well as in communities with other higher organisms. Thanks to modern biological techniques we are now able to address the complex communities and study the role of individual microorganisms and enzymes in more detail.
Microbacterium arborescens is a bacterium, which can be found in the guts of herbivorous caterpillars. The Department of Bioorganic Chemistry at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology studies interactions between insects and microorganisms which live in their digestive ...
Defense of Drug Possession and Drug Distribution Cases
2011-09-02
Under Virginia law prosecutors bear the burden to prove each and every element of a crime beyond a reasonable doubt. In short, that means they bear the burden of excluding every reasonable hypothesis of innocence.
In drug cases there are generally three prevailing defenses. Each defense is fact driven so although a defense may work in one case it may not actually work on all. The three prevailing defenses in drug cases are (1) search and seizure issues (2) possession issues and (3) whether the commonwealth can prove that the substance found is illegal.
All searches ...
Perception of facial expressions differs across cultures
2011-09-02
WASHINGTON — Facial expressions have been called the "universal language of emotion," but people from different cultures perceive happy, sad or angry facial expressions in unique ways, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"By conducting this study, we hoped to show that people from different cultures think about facial expressions in different ways," said lead researcher Rachael E. Jack, PhD, of the University of Glasgow. "East Asians and Western Caucasians differ in terms of the features they think constitute an angry face ...
Missouri Lawmakers Consider Comprehensive Driver Texting Ban
2011-09-02
Distracted driving takes a horrible toll on innocent Missouri drivers every year. It does not matter whether the distraction comes from applying makeup, checking a map, talking to a passenger or changing a radio station; a moment's negligence, even at moderate speeds, is enough for a car or truck to miss a stop sign or veer into an opposing lane and cause a serious or fatal auto accident. Missouri personal injury attorneys are all too familiar with the horrific harm that such accidents can cause to injury victims and surviving family members.
Personal electronic devices ...
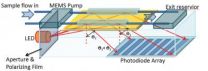
Faster diagnostics through cheap, ultra-portable blood testing
2011-09-02
WASHINGTON, Sept. 1—Blood tests are important diagnostic tools. They accurately tease-out vanishingly small concentrations of proteins and other molecules that help give a picture of overall health or signal the presence of specific diseases. Current testing procedures, however, are expensive and time-consuming, while sophisticated test equipment is bulky and difficult to transport.
Now, a team of researchers from the University of Toledo in Ohio has addressed all these drawbacks by developing a low-cost, portable technique that is able to quickly and reliably detect ...
Dangers on Missouri Highways: Unsecured Truck Loads
2011-09-02
It might seem like an accident that could only happen in a horror movie, but the reality of unsecured cargo is much more serious and more prevalent than most people assume. AAA reported that around 25,000 vehicle accidents and 80-90 deaths occur as a direct result of unsecured cargo per year. Unsecured cargo is essentially insufficient stability of the materials a trucker is transporting.
Typically, materials transported by 18-wheelers include steel coils, lumber, auto parts and various construction supplies, but the list can also extends to liquid or hazardous materials ...
Getting the Lead Out: Protecting Children From Dangerous Toys
2011-09-02
How do you protect your child's safety when there are 30,000 tons of potentially dangerous toys pouring into the United States from foreign countries every year? These boatloads of foreign toys account for 95 percent of the toys sold in the U.S. every year -- and many of them cause serious injuries to children.
Of course, American-made toys can cause children's injuries too. Regardless of their origin, toys should not put children at undue risk of injury.
Trouble in Toyland Report
That's why a leading consumer advocacy group, U.S. PIRG, tries to educate the public ...
Lung cancer ALK rearrangement may predict pemetrexed efficacy, study shows
2011-09-02
Patients with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) responded significantly better to pemetrexed (brand name: Alimta) than patients whose cancer did not show ALK translocation, according to research published in the September issue of the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC).
Lung adenocarcinoma can display genetic mutations, including anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Knowing whether the tumor displays ...
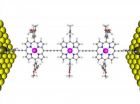
The quantum tunneling effect leads electron transport in porphyrins
2011-09-02
Porphyrins are organic molecules that appear in the central region of
macromolecules such as chlorophyll and hemoglobin, and have a metal atom
at their center that determines their specific function. The importance of these molecules
in the field of molecular electronics lies in their "ease of transfer
electrons from one region to another" explains the responsible of the work at the Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Center (a joint research center of the CSIC, the University of Oviedo and the Government of the Principality of Asturias) Víctor Manuel García. ...
Federal Study Determines Causes of Trucking Accidents
2011-09-02
Commercial tractor-trailers are involved in an increasing number of serious, and often fatal, accidents. To learn why, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) conducted the Large Truck Crash Causation Study (LTCCS). This study provided vital information, including the reasons behind serious crashes involving large trucks.
Researchers reviewed 120,000 crashes that occurred between April 2001 and December 2003 and selected a nationally representative sample of 963 accidents. These accidents, ...
Decrease in smoking reduces death rates within months
2011-09-02
A study by the University of Liverpool has found that a decrease in smoking rapidly reduces mortality rates in individuals and entire populations within six months.
Research by Professor Simon Capewell and Dr Martin O'Flaherty at the Institute of Psychology, Health and Well-being, examined evidence from clinical trials and natural experiments. They found that a reduction in smoking has a positive impact on mortality rates in both individuals and populations within six months. Likewise, dietary improvements get very positive results within one to three years.
Professor ...
Sight fails when defective eye cells cripple renewal
2011-09-02
In a rare eye disease, the retina degenerates because light-receiving cells fail to regenerate, research led by a student at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine shows.
The researchers include Dr. Samuel G. Jacobson's group at the University of Pennsylvania and Dr. Andreas Engel's group at University of Basel, Switzerland. They found that when the natural renewal process fails, metabolites are locked in, build up and turn toxic, killing cells over time in Enhanced S-Cone Syndrome.
A description of their work is online and will be published in print in ...
[1] ... [6984]
[6985]
[6986]
[6987]
[6988]
[6989]
[6990]
[6991]
6992
[6993]
[6994]
[6995]
[6996]
[6997]
[6998]
[6999]
[7000]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.