Deciding to stay or go is a deep-seated brain function
2011-06-07
DURHAM, N.C. – Birds do it. Bees do it. Even little kids picking strawberries do it.
Every creature that forages for food decides at some point that the food source they're working on is no richer than the rest of the patch and that it's time to move on and find something better.
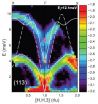
This kind of foraging decision is a fundamental problem that goes far back in evolutionary history and is dealt with by creatures that don't even have proper brains, said Michael Platt, a professor of neurobiology and director of the Center for Cognitive Neuroscience at Duke University.
Platt ...
RakeTheRake's Re-Branded Site Offers $100,000+ of Special Promotions
2011-06-07
RakeTheRake.com has re-launched its rakeback website to give online poker players new features, functionality and an improved user experience. With a simple 4 step process to sign up for rakeback and a secure, easy to use Account area, the new site offers players some key additions, namely free poker training and the new RakeTheRake forum.
Until the end of July 2011 there is also $100,000+ of special relaunch promotions running. These are bespoke promotions created by the top online poker rooms and RakeTheRake and most are open to all online poker players, whether registered ...
Neutron analysis explains dynamics behind best thermoelectric materials
2011-06-07
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., June 6, 2011 -- Neutron analysis of the atomic dynamics behind thermal conductivity is helping scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory gain a deeper understanding of how thermoelectric materials work. The analysis could spur the development of a broader range of products with the capability to transform heat to electricity.
Researchers performed experiments at both of ORNL's neutron facilities -- the Spallation Neutron Source and the High Flux Isotope Reactor -- to learn why the material lead telluride, which has a similar ...
Columbia, SC Hotel Offers Nearby Lodging to Guests Attending the Miss South Carolina Pageant
2011-06-07
The Hilton Garden Inn Hotel in Columbia SC (Northeast) offers convenient lodging to competitors and spectators attending the Miss South Carolina Pageant. The event will take place at the newly renovated Township Auditorium from June 25 - July 2, 2011. Contestants from across the state of South Carolina will compete for the crown and a $20,000 scholarship.
After begin held in Spartanburg for the past 15 years, the Miss South Carolina Pageant will take place in Columbia, South Carolina. The event will include the Miss South Carolina Finals and Miss South Carolina Teen ...
UCSB scientists discover new direction in Alzheimer's research
2011-06-07
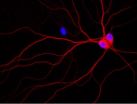
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– In what they are calling a new direction in the study of Alzheimer's disease, UC Santa Barbara scientists have made an important finding about what happens to brain cells that are destroyed in Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. The results are published in the online version of The Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Stuart Feinstein, professor of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, senior author, and co-director of UCSB's Neuroscience Research Institute, explained: "With dementia, the brain cells, or neurons, that you need for ...
Adding a Body Kit to Your Car or Truck Can Really Change It's Looks. But If You're Going to Drive it on the Street Are You Concerned About Your Safety? There Are a Few Things You Should Consider.
2011-06-07
Most people who buy a body kit for their car or truck are looking forward to making the vehicle more aggressive, a custom appearance, and completely unique. Yet the last thing that they think of when messing around with their bumpers is safety. It's kind of crazy really, some are willing to risk their safety just so they can look good.
We are proud of what we drive, but we are all unique. We like to show our style, or even enter our vehicle into some car or truck shows. One of the most drastic things that you can do to your vehicle is to add a custom body kit to it. ...
UCLA scientists identify how major biological sensor in the body works
2011-06-07
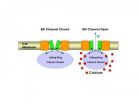
A biological sensor is a critical part of a human cell's control system that is able to trigger a number of cell activities. A type of sensor known as the "gating ring" can open a channel that allows a flow of potassium ions through the cell's wall or membrane — similar to the way a subway turnstile allows people into a station. This flow of ions, in turn, is involved in the regulation of crucial bodily activities like blood pressure, insulin secretion and brain signaling.
But the biophysical functioning of the gating ring sensor has not been clearly understood. Now, ...
New Foundation Focuses on Keeping Young People Safe Abroad
2011-06-07
A new nonprofit foundation has formed to help protect the safety of millions of young people who travel and study abroad every year. ClearCause Foundation is focused on solving problems within the US $17 billion youth-travel, exchange and study abroad industry without government regulations, including the lack of federal oversight for organizations entrusted to care for youth and students overseas.
"There are literally thousands of youth travel, study-abroad and student-exchange programs, but virtually no government oversight or federally mandated safety standards ...
Jupiter's youthful travels redefined solar system
2011-06-07
Jupiter, long settled in its position as the fifth planet from our sun, was a rolling stone in its youth. Over the eons, the giant planet roamed toward the center of the solar system and back out again, at one point moving in about as close as Mars is now. The planet's travels profoundly influenced the solar system, changing the nature of the asteroid belt and making Mars smaller than it should have been. These details are based on a new model of the early solar system developed by an international team that includes NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. ...
GO Campaign, Lemelson-MIT, and P90X Creator Tony Horton Launch Global Search for Innovators, Granting $50,000 in GO Innovation Awards to Inspire Youth to Solve Real World Problems
2011-06-07
GO Campaign, a non-profit organization supporting orphans and vulnerable children throughout the developing world, Lemelson-MIT, and P90X Creator Tony Horton are announcing the launch of GO's global search for innovators and entrepreneurs who are sharing their innovations with youth and inspiring them to create solutions for the real world community problems they face. Up to $50,000 will be granted annually to GO Innovation Award (GIA) recipients.
In addition to inviting participation in the global search, GO Campaign will call for private sector support by corporations, ...
Archive Systems Unveils OmniRIM Records Center
2011-06-07
Archive Systems, Inc., a leading provider of records and document management services, today announced the release of OmniRIM Records Center, a cloud-based solution that gives organizations the power to access, protect and control their business-critical information. It features Archive Systems' acclaimed physical records management functions, seamlessly integrated with electronic records management capabilities to provide secure lifecycle management of a company's valuable informational assets.
OmniRIM Records Center is the first SaaS-solution to unify electronic and ...
Be it numbers or words -- the structure of our language remains the same
2011-06-07
It is one of the wonders of language: We cannot possibly anticipate or memorize every potential word, phrase, or sentence. Yet we have no trouble constructing and understanding myriads of novel utterances every day. How do we do it? Linguists say we naturally and unconsciously employ abstract rules—syntax.
How abstract is language? What is the nature of these abstract representations? And do the same rules travel among realms of cognition? A new study exploring these questions—by psychologists Christoph Scheepers, Catherine J. Martin, Andriy Myachykov, Kay Teevan, and ...
Good youth programs help teens learn to think not just logically, but strategically
2011-06-07
URBANA – Teens develop strategic thinking skills in youth activities that they rarely learn in the classroom, says a new University of Illinois study of 11 high-quality urban and rural arts and leadership programs.
"In school you learn how government is supposed to work. In youth leadership programs, youth learn how government actually works. They also learn how to influence it," said Reed Larson, a professor in the U of I's Department of Human and Community Development.
Strategic thinking involves more than logic; it involves learning to anticipate the disorderly ways ...
Possible first eastern Pacific tropical depression shaping up on NASA imagery
2011-06-07
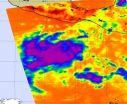
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over a low pressure system in the Eastern Pacific and captured infrared imagery that show it to be well-defined and organizing. System 91E is shaping up to likely become the Eastern Pacific's first tropical depression of the season.
Located about 425 miles south of Acapulco, Mexico, System 91E is in a good spot for development: warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear. Those are two factors needed to help a tropical cyclone develop.
Infrared imagery on June 5 at 19:47 UTC (3:47 p.m. EDT/12:47 PDT) from the AIRS instrument that flies ...
Optimalon Software Released New Excel Add-In 1DCutX for Optimal Linear Material Cutting
2011-06-07
Optimalon Software Ltd. has released 1DCutX, an Excel add-in for design engineers and operations managers that optimizes length-cutting operations for manufacturers that do a lot of linear cutting of construction materials. 1DCutX reads data directly from an open Excel spreadsheet, and instantly generates both the graphical layouts and a detailed cutting report within your Excel workbook. 1DCutX can reduce the usage of linear material by twenty to forty percent, compared to manual cutting.
In addition to minimizing raw material waste, 1DCutX saves time, minimizes production ...
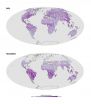
First-of-its-kind fluorescence map offers a new view of the world's land plants
2011-06-07
Scientists from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., have produced groundbreaking global maps of land plant fluorescence, a difficult-to-detect reddish glow that leaves emit as a byproduct of photosynthesis. While researchers have previously mapped how ocean-dwelling phytoplankton fluoresce, the new maps are the first to focus on land vegetation and to cover the entire globe.
To date, most satellite-derived information related to the health of vegetation has come from "greenness" indicators based on reflected rather than fluorescent light. Greenness ...
Mid America Wireless Chooses McCusker and Company for Wireless Phone Extended Warranty Program
2011-06-07
McCusker and Company, a leading nationwide developer of extended warranty protection services for the consumer electronics industry, has been selected by Mid America Wireless to setup its professional extended warranty service to the company's wireless customers.
"Mid America Wireless customers can have the peace of mind that if something goes wrong with their new wireless phone, the strength and experience of McCusker & Company's administrator and underwriting partners are there to take care of all covered claims," said McCusker & Company President ...
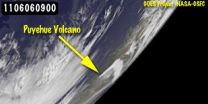
3 satellites see eruption of Puyehue-Cordón volcano from space
2011-06-07
NASA's Terra Satellite, the GOES-13 and GOES-11 satellites all captured images of the ash plume from southern Chile's Puyehue-Cordón Volcano this week. The volcano is located in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province of Chile.
The Terra satellite flew over the volcano on June 6 at 14:25 UTC (10:25 a.m. EDT). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the eruption that showed the large ash plume blowing northeast, then to the southeast and over the Atlantic Ocean. The ash plume went at least as high as ...
Joint replacement surgery riskier at hospitals with low surgical volume
2011-06-07
Patients who undergo elective total hip or total knee arthroplasty at hospitals with lower surgical volume had a higher risk of venous thromboembolism and mortality following the procedure. The complications following joint replacement surgery at low-volume sites may be reduced by modifying systems and procedures used before and after surgery according to the findings published today in Arthritis & Rheumatism, a peer-reviewed journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The ACR estimates that 27 million Americans over the age of 25 have doctor-diagnosed osteoarthritis ...
Construction industry has highest number of traumatic brain injuries in US workplace
2011-06-07
San Diego, CA, June 7, 2011 – Although traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the leading causes of death in the United States, work-related TBI has not been well documented. In a study published in the July issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers describe the epidemiology of fatal TBI in the US workplace between 2003 and 2008. This study provides the first national profile of fatal TBIs occurring in the US workplace. The construction industry had the highest number of TBIs and the agriculture, forestry, and fishing industry had the highest rates.
"While ...
Researchers find that inhibiting microRNAs may help prevent degenerative eye disorders
2011-06-07
DALLAS – June 7, 2011 – Blocking two tiny molecules of RNA – a chemical cousin of DNA – appears to suppress the abnormal growth of blood vessels that occurs in degenerative eye disorders, UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have found.
Their findings, available in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest a potential strategy to treat age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a vascular eye disorder that affects nearly 2 million Americans and is a leading cause of blindness among older people.
"MicroRNAs can affect multiple pathways involved ...
New report equates dried fruits and fresh fruits
2011-06-07
Budapest, Hungary—Internationally recognized health researchers presented their views at the 30th World Nut & Dried Fruit Congress on 21 May 2011, recommending that food policy makers consider dried fruits equivalent to fresh fruits in dietary recommendations around the world. The presentations recognize that traditional dried fruits such as dried apricots, dried apples, dates, dried figs, raisins and sultanas, and prunes should be included side by side with fresh fruit recommendations by policy makers around the world.
Organized by the International Nut and Dried Fruit ...
Excellent Casino Games at Wild Jack Casino
2011-06-07
Review Casino Games at Wild Jack Casino before Placing Bets
The Wild Jack Casino is best known for its amazing range of Blackjack games, with over 40 to choose from which include single hand Blackjack and multi-hand Blackjack, you have a fantastic choice of Blackjack casino games. Each and every one of these casino games can be reviewed online at the Wild Jack Casino website and in many cases you can also play for fun or practice before you place real money bets. As a new player to this amazing online casino you can benefit from a generous sign up bonus offer which will ...
PeerAssist Releases New Construction Safety Certification Software
2011-06-07
PeerAssist, a leading developer of tailored construction management software solutions, raises the bar for construction safety with their new application, Certification Assist. This unique construction safety certification software allows contractors to oversee and track all employees to determine who has, needs or is going to need additional safety training. Because PeerAssist tailors each application to their clients' specific needs, Certification Assist easily integrates into any accounting package, requiring very little training and eliminating the need for double entry ...
Legendary Winemaker Philippe Guigal Says Vinotech's "winesave Actually Perfect for Opened Bottles"
2011-06-07
M. Philippe GUIGAL, Directeur General and oenologue of E. GUIGAL, makers of more 100-point Robert Parker wines than any other single wine producer, has given his unqualified support to winesave (R), made by Australian company Vinotech P/L.
M. Guigal tested winesave at home at Chateau D'Ampuis during his wife Eve's pregnancy and was so impressed by it that he happily provided his quote and will have winesave on the tasting table at Chateau D'Ampuis where all Maison Guigal tastings take place. M. Guigal continues the tradition pioneered by his father Marcel of the notion ...
[1] ... [7279]
[7280]
[7281]
[7282]
[7283]
[7284]
[7285]
[7286]
7287
[7288]
[7289]
[7290]
[7291]
[7292]
[7293]
[7294]
[7295]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.