OHL Leases 148,725 Square Foot Industrial Building from Watson Land Company
2011-04-06
Watson Land Company, one of Southern California's largest industrial real estate developers, has leased a 148,725 square foot industrial property to OHL.
Watson Land Company successfully completed more than 800,000 square feet in leases during the fourth quarter of 2010 as inbound container volume continued to increase, according to the Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach. The Port of Long Beach reported a 10.4 percent year-over-year increase in inbound loaded containers, while the Port of Los Angeles witnessed an increase of 5.6 percent during 2010.
This trend ...
How materialistic advertising messages negatively shape the female body image
2011-04-06
Sussex, UK—April 5, 2011— Psychological research has consistently shown that women feel unhappy with their body after looking at images of thin, idealized models, which are typically represented in the media. However, today's consumer culture and media promote not only the ideal of perfect beauty, but also that of the material affluent lifestyle, both of which are commonly depicted together, and highlight the benefits of beauty and of owning material goods to one's personal success and fame. A new study from the British Journal of Social Psychology is the first to examine ...
Device drops blood pressure in patients with difficult-to-treat hypertension
2011-04-06
A device designed to treat people with resistant hypertension helped lower blood pressure by 33 points, a substantial drop that would otherwise require patients to take an additional three or four drugs, on top of this subgroup's usual regimen of up to five drugs, to control their difficult-to-treat condition.
The device, called the Rheos® System, was tested in a pivotal Phase III study presented today as a late-breaking clinical trial at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Sessions. It is the first device to be tested in a large-scale clinical trial ...
Timothy's World Coffee Opens First U.S. Location at Cleveland Hopkins International Airport
2011-04-06
Timothy's World Coffee today announced expansion efforts into the U.S., with the opening of a cafe at Cleveland Hopkins International Airport. The decision comes at a time of significant growth for Vermont-based Bruegger's Enterprises Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiary Threecaf Brands, which operates Timothy's cafes.
"Bruegger's existing operating infrastructure allows us to bring this famous Canadian brand to the U.S.," said Jim Greco, CEO of Bruegger's Enterprises, Inc. "We are confident that the American consumer will appreciate the quality and variety of coffee ...
Nanopolymer shows promise for helping reduce cancer side effects
2011-04-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University biochemist has demonstrated a process using nanotechnology to better assess whether cancer drugs hit their targets, which may help reduce drug side effects.
W. Andy Tao, an associate professor of biochemistry analytical chemistry, developed a nanopolymer that can be coated with drugs, enter cells and then removed to determine which proteins in the cells the drug has entered. Since they're water-soluble, Tao believes the nanopolymers also may be a better delivery system for drugs that do not dissolve in water effectively.
"Many ...
The 'molecular octopus': A little brother of 'Schroedinger’s cat'
2011-04-06
This release is available in German.
For the first time – as presented in Nature Communications - the quantum behaviour of molecules consisting of more than 400 atoms was demonstrated by quantum physicists based at the University of Vienna in collaboration with chemists from Basel and Delaware. The international and interdisciplinary team of scientists thus sets a new record in the verification of the quantum properties of nanoparticles. In addition, an important aspect of the famous thought experiment known as 'Schroedinger's cat' is probed. However, due to the particular ...
Non-traditional learning environments need clearer definitions, MU researchers say
2011-04-06
What is the difference between e-learning, online learning and distance learning? University of Missouri researchers have found that even educators can't agree on what different forms of learning environments entail and, without some common definitions, it is difficult to study the best methods and provide students with accurate previews of courses.
Joi Moore, associate professor in the School of Information Science and Learning Technologies in the MU College of Education, along with doctoral students Camille Dickson-Deane and Krista Galyen, found several definitions ...
Santa Monica Dentist, Dr. Khoubnazar, Has a Special Offer for New Patients
2011-04-06
Santa Monica cosmetic dentist, Dr. Sanaz Khoubnazar, is offering a new special for patients that seek high quality dental care. The standard price of $185 for a dental exam and x-ray is reduced to $49. This provides a low-cost way for new patients to experience the excellent treatments and dental care provided by Dr. Khoubnazar.
Routine dental care is needed to clean the teeth and gum line professionally. Daily brushing and flossing help to reduce the buildup of bacteria and plaque, but professional dental cleanings can clean areas on the teeth and gum line that cannot ...
Migratory birds, domestic poultry and avian influenza
2011-04-06
The persistence and recurrence of H5N1 avian influenza in endemic regions can largely be blamed on movement and infection by migratory birds. Trade in poultry, poultry products and caged birds, and movement of wild birds also account for H5N1 prevalence in these areas. Several recent outbreaks of avian influenza have suggested strong evidence of migratory birds playing a role in transmitting the virus over long distances.
In a paper published last week in the SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, authors Lydia Bourouiba, Stephen A. Gourley, Rongsong Liu, and Jianhong ...
Study finds link between chronic depression and accelerated immune cell aging
2011-04-06
Certain cases of major depression are associated with premature aging of immune cells, which may make people more susceptible to other serious illness, according to findings from a new UCSF-led study.
The findings indicate that accelerated cell aging does not occur in all depressed individuals, but is dependent upon how long someone is depressed, particularly if that depression goes untreated. The study was published online in March 2011 by the journal PLoS One and is available here.
"There's a lot more to depression than feeling blue," said first author Owen Wolkowitz, ...
Films For Action Launches New Website; Features Over 700 Films Hand-Picked to Change the World
2011-04-06
After 12 months in development, Films For Action has launched its new website - a head-to-toe redesign that lays the foundation for a vibrant community-powered news site dedicated to inspiring positive social change. At the heart of the new site is a constantly growing learning library of over 200 documentaries and 500 short films that can be watched free online, daily independent news, and a practical "Take Action" section to help users find ways to make a positive impact.
"It's probably the most comprehensive collection of films dedicated to social change online," ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory: April 2011
2011-04-06
MILITARY -- H2O from diesel
Capillary action and graphite foam are being enlisted by researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to solve a logistical nightmare for the military and U.S. troops deployed around the world. While soldiers require nearly seven gallons of water a day, just getting that water to them increases troop vulnerability and limits their tactical use. Using an ORNL proprietary system, however, this problem could be greatly reduced. The system uses the pores of inorganic membranes to condense water present in a diesel's exhaust stream to produce about ...
Drought-exposed leaves adversely affect soil nutrients, study shows
2011-04-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Chemical changes in tree leaves subjected to warmer, drier conditions that could result from climate change may reduce the availability of soil nutrients, according to a Purdue University study.
Jeff Dukes, an associate professor of forestry and natural resources, found that red maple leaves accumulate about twice as much tannin when exposed to hot, droughtlike conditions. Those tannins, which defend leaves from herbivores and pathogens, were shown to interfere with the function of common enzymes in soil.
"When the leaves are particularly water-stressed ...
Happiness, comparatively speaking: How we think about life's rewards
2011-04-06
You win some, you lose some. You get the perfect job—the one your heart is set on. Or you get snubbed. You win the girl (or guy) of your dreams—or you strike out. Such are life's ups and downs.
But what if you win and lose at the same time? You land a good job—but not a great one. Or you do get a plum offer—but not the one you wanted?
A study published in an upcoming issue of Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, says you'll find a way to be happy anyway.
"Good outcomes have relative value and absolute value, and that affects ...
George Mason students highlight dangers of distracted driving
2011-04-06
The HFES George Mason University (GMU) Student Chapter was recently featured in a television news story about an interactive driving simulation video game the students developed to highlight the human factors/ergonomics science behind distracted driving. The demonstration made its first appearance at the October 2010 USA Science and Engineering Festival in Washington, DC, where the GMU students partnered with the Federation of Associations in Behavioral & Brain Sciences (FABBS). Nearly half a million visitors attended the two-day festival, and the distracted driving display ...
tokyo rag Launches Inaugural Boutique Collection of Handmade Luxury Fashion Accessories
2011-04-06
tokyo rag, a handcrafter of high end fashion accessories, unveils a new 'Tokyo-inspired' collection for this summer. Covering a wide product range in distinctive and vibrant designs, tokyo rag targets women and men with rock star attitude, who are fresh in mind, never tired to explore and interested in couture and style. No snobbishness, just high quality accessories with a creative twist. Each piece is handcrafted using luxury fabrics and ecological tanned top quality leathers from carefully selected European tanneries.
The fashion accessories are available in four ...
MU researcher says instructors can reduce cheating by being clear
2011-04-06
A new University of Missouri study says that the reasons students give for cheating are rational, and that stricter punishments won't solve the problem. Instead, teachers should communicate clear standards and provide consistent enforcement to reduce instances of cheating.
Edward Brent, associate chair of the Department of Sociology in the MU College of Arts and Science, and Curtis Atkisson, an MU anthropology student, asked students, "What circumstances, if any, could make cheating justified?"
While a majority of the students said that no circumstances can ever justify ...
Elevated levels of sodium blunt response to stress, study shows
2011-04-06
CINCINNATI—All those salty snacks available at the local tavern might be doing more than increasing your thirst: They could also play a role in suppressing social anxiety.
New research from the University of Cincinnati (UC) shows that elevated levels of sodium blunt the body's natural responses to stress by inhibiting stress hormones that would otherwise be activated in stressful situations. These hormones are located along the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls reactions to stress.
The research is reported in the April 6, 2011, issue of The Journal ...
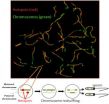
NIH, USU study maps hotspots of genetic rearrangement
2011-04-06
Researchers have zoomed in on mouse chromosomes to map hotspots of genetic recombination — sites where DNA breaks and reforms to shuffle genes. The findings of the scientists at the National Institutes of Health and Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences (USU) have the potential to improve the detection of genes linked to disease and to help understand the root causes of genetic abnormalities. The research, published online April 3 in Nature, moves scientists one step closer to understanding how mammals evolve and respond to their environments.
In this image, ...
Analysis of opioid prescription practices finds areas of concern
2011-04-06
An analysis of national prescribing patterns shows that more than half of patients who received an opioid prescription in 2009 had filled another opioid prescription within the previous 30 days. This report also suggested potential opportunities for intervention aimed at reducing abuse of prescription opioids.
Researchers from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), a component of the National Institutes of Health, will publish results of this analysis in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
"More research is needed to see if current ...
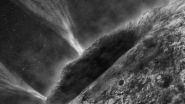
Frozen comet had a watery past, University of Arizona scientists find
2011-04-06
For the first time, scientists have found convincing evidence for the presence of liquid water in a comet, shattering the current paradigm that comets never get warm enough to melt the ice that makes up the bulk of their material.
"Current thinking suggests that it is impossible to form liquid water inside of a comet," said Dante Lauretta, an associate professor of cosmochemistry and planet formation at the UA's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. Lauretta is the principal investigator of the UA team involved in analysis of samples returned by NASA's Stardust mission.
UA ...
Using MRI, researchers may predict which adults will develop Alzheimer's
2011-04-06
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using MRI, researchers may be able to predict which adults with mild cognitive impairment are more likely to progress to Alzheimer's disease, according to the results of a study published online and in the June issue of Radiology.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an intermediate stage between the decline in mental abilities that occurs in normal aging and the more pronounced deterioration associated with dementia, a group of brain disorders that includes Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Individuals with MCI develop AD at a rate of 15 to 20 percent per ...
Marbella University Unveils an MBA Program to "Save Humanity and the Planet"
2011-04-06
Lies, cheat, deceit, distortion, hype, and a blind pursuit of profit have poisoned the business world. The price of this has been the destruction of the planet, its ecosystems and the alienation of humans from their soul and genuine inner needs.
Pollution, contamination, climate change, poverty, rising sea level, unemployment, financial crisis, social unrest, war, and a general lack of trust has taken over as a result.
The world needs new managers and CEOs; new MBAs
The state of humanity and the planet clearly shows: politics has failed, corporations have failed, ...
Study: Socioeconomics playing reduced role in autism diagnoses
2011-04-06
WASHINGTON, DC, April 4, 2011 — While there is an increasing equality in terms of the likelihood that children from communities and families across the socioeconomic spectrum will be diagnosed with autism, a new study finds that such factors still influence the chance of an autism diagnosis, though to a much lesser extent than they did at the height of rising prevalence.
"As knowledge has spread about autism, information is now more evenly distributed across different kinds of communities," said Peter S. Bearman, the Cole Professor of the Social Sciences at Columbia ...
New survey: 72 percent of Americans think health-care system needs major overhaul
2011-04-06
New York, NY, April 6, 2011—Seven of 10 adults think the U.S. health care system needs to be fundamentally changed or completely rebuilt, according to a Commonwealth Fund survey released today. The concerns reflect widespread experiences with access barriers, poorly coordinated care and growing costs. The survey also reveals strong support for more patient-centered care systems and innovative use of teams and information systems.
The new survey found that a large majority of U.S. adults have concerns about access, with 71 percent reporting problems gaining access to ...
[1] ... [7607]
[7608]
[7609]
[7610]
[7611]
[7612]
[7613]
[7614]
7615
[7616]
[7617]
[7618]
[7619]
[7620]
[7621]
[7622]
[7623]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.