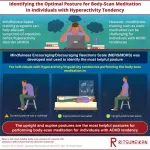
Identifying body-scan postures suitable for people with hyperactivity tendency
2024-09-17
ADHD is a developmental condition of brain with symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity or impulsivity. People with ADHD lack the ability of self-control and experience anxiety, depression, academic failure, and low self-confidence. These symptoms can be alleviated by a holistic approach such as mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. These practices encourage patients to pay attention to the present moment with purpose and without judgment. However, these practices involving meditation require sitting in certain postures which can be challenging for patients with high ADHD tendency.
To address this, ...
Indiana University selects Symplectic Elements as faculty activity reporting system
2024-09-17
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Indiana University has selected Symplectic Elements as its new faculty activity management and reporting system.
This strategic decision marks a significant advancement toward the university’s goals of streamlining the management and reporting of the work and accomplishments of its faculty.
Indiana University is internationally known for outstanding research and its world-class degree programs, from business and health to STEM and the arts at its flagship campus in Bloomington, the expanding ...
Stephenson Prize for Innovation in Pancreatic Cancer Research launched with $150 million gift to City of Hope
2024-09-17
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. and ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, has received a historic $150 million gift from entrepreneurs and philanthropists A. Emmet Stephenson Jr. and his daughter Tessa Stephenson Brand to immediately fund pancreatic cancer research.
The centerpiece of this gift is the $1 million Stephenson Prize, one of the largest ...
New understanding of the limits on nano-noise
2024-09-17
Thanks to nanoscale devices as small as human cells, researchers can create groundbreaking material properties, leading to smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient electronics. However, to fully unlock the potential of nanotechnology, addressing noise is crucial. A research team at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, has taken a significant step toward unraveling fundamental constraints on noise, paving the way for future nanoelectronics.
Nanotechnology is rapidly advancing, capturing ...
Graphite oxidation experiments reveal new type of oscillating chemical reaction
2024-09-17
A reaction that puzzled scientists for 50 years has now been explained by researchers at Umeå University. Rapid structural snapshots captured how graphite transforms into graphite oxide during electrochemical oxidation, revealing intermediate structures that appear and disappear over time. The researchers describe this as a new type of oscillating reaction.
Oscillating chemical reactions are fascinating to watch and important for developing an understanding of how complex systems work, both in chemistry and in nature. Classical visual examples of such reactions show how the colors of a solution change back and forth, cycling ...
How does a tiny shrimp find its way home in a vast ocean? Study finds it’s down to their cave’s special smell
2024-09-17
Homing is an animal’s ability to navigate towards an original location, such as a breeding spot or foraging territory. Salmon and racing pigeons are famous for homing, but similar behaviors occur in groups as diverse as bees, frogs, rats, and sea turtles. There, homing individuals are known or suspected to rely on landmarks, the Earth’s magnetic field, or the sky’s pattern of polarized light to find their way back.
Another group known to display homing are cave-dwelling mysid shrimp, also known as possum shrimp for the pouches in which females carry ...
‘Marine identity’ can help restore the ocean
2024-09-17
People’s deep connection with the ocean – their “marine identity” – can help us reset society’s relationship with the seas, new research led by Dr Pamela Buchan, from the University of Exeter, suggests.
A diverse, international group of marine researchers and practitioners met to discuss marine identity – based on testimony and photos from multiple countries.
The group included Diz Glithero of the Canadian Ocean Literacy Coalition, Dr Emma McKinley of Cardiff University who helped deliver the workshop, and others from across Europe, Africa, Indonesia, North America, and Australasia.
They found many common themes, including traditions ...
Evidence shows that estrogen blocker treatment does not increase the risk of coronary heart disease in breast cancer patients
2024-09-17
New evidence shows that extended estrogen suppression treatment using an aromatase inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive postmenopausal breast cancer is safe; it does not increase the risk of coronary artery calcification, a sign of active coronary atherosclerosis, as some prior studies had indicated. An article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the findings from a retrospective, cross-sectional observational study that investigated the association between the duration of aromatase inhibitor treatment and the severity of coronary artery calcification in postoperative breast cancer patients.
Coronary ...
Survey shows 25% of adults consider weight loss drug use without prescription
2024-09-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Injectable weight loss drugs are popular right now but can be hard to get because they are in short supply or too expensive without insurance. The result is that some people are skipping the doctor’s office and reaching out to potentially unreliable sources such as unlicensed online pharmacies or telehealth sites, which could expose patients to risks.
A new national survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center reveals 1 in 4 (25%) of 1,006 adults surveyed would consider using an injectable weight loss medication without consulting their doctor. The reasons ...
New treatment extends ovarian function in older mice
2024-09-17
Medication to reduce ovarian scarring helps extends overall health of reproductive system
Freezing eggs only addresses age-related infertility, not ovarian hormone loss. New treatment would ‘fix the root of the issue’
Findings also have implications for developing treatments for ovarian cancer
CHICAGO --- A woman’s ovaries are like a factory where eggs grow and produce hormones that regulate everything from menstruation and pregnancy to bone density and mood. As she and her factory age, production dwindles, and by the time she hits menopause ...
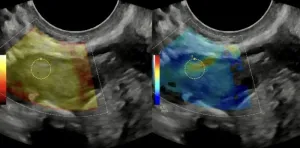
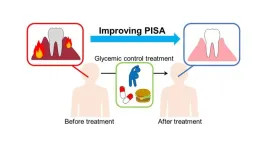
Getting to the root of the problem: Intensive diabetes treatment reduces gum disease inflammation
2024-09-17
Osaka, Japan – While the link between diabetes and periodontal disease is known, the impact of diabetes treatment on periodontal health is less well understood. Recent research published in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism demonstrates that periodontal inflammation can be positively affected just by receiving intensive diabetes treatment.
It is widely believed that there is an interrelationship between diabetes and periodontal disease. While it has been shown that treatment of periodontal disease improves blood ...
Researchers take power and efficiency of biological sensing to record level
2024-09-17
University of Arizona researchers have developed a new biological sensing method that can detect substances at the zeptomolar level – an astonishingly miniscule amount.
This level of sensing, immediately useful for drug testing and other research, has the potential to make new drug discoveries possible. Eventually, the advance could lead to portable sensors that can detect environmental toxins or chemical weapons, monitor food quality or screen for cancer.
A paper describing the results was published in the journal Nature Communications on Aug. 28.
Judith Su, associate professor of biomedical engineering and optical ...
Under-plant mirrors improve endangered plant survival and growth
2024-09-17
The most endangered plant species in the Mariana Islands, the legume tree Serianthes nelsonii, faces persistent threats in its recovery. These have been identified as a short lifespan of habitat seedlings and rapid death of saplings transplanted from conservation nurseries.
The Plant Physiology Laboratory at the University of Guam addressed this conundrum by improving growth and survival of Serianthes seedlings through strategically placed mirrors beneath deeply shaded seedlings to increase available ambient light. The resulting paper has been published ...
Widespread evidence for packaging-related chemicals in humans
2024-09-17
About this study: A new review is the first to reveal the extent of human exposure to food contact chemicals (FCC), with 3,601 chemicals used in food packaging and other food contact articles having been found in human bodies. The authors say this review also highlights significant gaps in biomonitoring and toxicity data.
---
In a new study, published in the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology, scientists describe the widespread human exposure to food contact chemicals (FCCs). The research reveals which chemicals ...
Hardship early in life can affect health and longevity – even for marmots
2024-09-16
Key takeaways
The cumulative adversity index for people quantifies numerous measures of hardship, such as poverty and stress to understand health and longevity over the individual’s lifespan.
A similar tool could help scientists who study and want to conserve animal populations by identifying the most influential stressors to mitigate.
UCLA biologists have created the first cumulative adversity index for yellow-bellied marmots. They found that as in humans, adversity early on had lifelong consequences and reduced their life expectancy.
Adversity early in life can have permanent health consequences for people — even if their circumstances improve dramatically later on. ...
Chances of successful pregnancy are the same with embryo transfer on day three or five
2024-09-16
In IVF treatment, embryos are traditionally transferred in the uterus three days after fertilization. Due to improvements in laboratory techniques, this is now also possible after five days. It was assumed that this increases the chance of a successful pregnancy. A study by Radboud university medical center and Amsterdam UMC shows that the day of transfer does not influence the success rate of the IVF trajectory.
One out of thirty children in the Netherlands is conceived via in vitro fertilization, or IVF for short. In this procedure, ...
The Lancet: More than 39 million deaths from antibiotic-resistant infections estimated between now and 2050, suggests first global analysis
2024-09-16
Embargoed access to the paper and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
The Lancet: More than 39 million deaths from antibiotic-resistant infections estimated between now and 2050, suggests first global analysis
First in-depth analysis of global health impacts of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) over time reveals trends from 1990 to 2021 and estimates potential impacts to 2050 for 204 countries and territories.
More than one million people died from AMR globally each year between 1990 and 2021. Over the period, AMR deaths among children aged under five declined by 50% while those among people aged 70 ...
Fraunhofer IAF low-noise amplifiers aboard the Arctic Weather Satellite
2024-09-16
The Arctic Weather Satellite (AWS) of the European Space Agency (ESA) was sent on its journey to a polar orbit 600 km above the Earth on August 16, 2024. On board: four low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) from the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF in Freiburg. They are essential components of the passive microwave radiometer with which the AWS measures temperature and humidity in the Arctic more precisely than ever before. This should contribute to a better understanding of both the Arctic and the climate change that is particularly visible in it. If the mission is successful, ...
Immunotherapy after surgery helps people with high-risk bladder cancer live cancer-free longer
2024-09-16
Results from a large clinical trial show that treatment with an immunotherapy drug may nearly double the length of time people with high-risk, muscle-invasive bladder cancer are cancer-free following surgical removal of the bladder. Researchers found that postsurgical treatment with pembrolizumab (Keytruda), which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating at least 18 different cancers, was superior compared with observation. The study, led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), ...
US COVID-19 rates oscillate every six months
2024-09-16
COVID-19 cases in the U.S. have shown unexpected oscillating waves every six months between the southern states and the northern states and, to a lesser degree, from east to west, according to new research published today in Scientific Reports.
Public health scientists from the University of Pittsburgh, University of Ottawa and University of Washington conducted the first detailed analysis to demonstrate and characterize the six-month oscillation of cases across space and time. It provides key information ...
Lower neighborhood opportunity may increase risk for preterm birth
2024-09-16
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, September 16, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Lower Neighborhood Opportunity May Increase Risk for Preterm Birth
A new study suggests that neighborhoods with fewer educational, health, environmental, and socioeconomic resources may increase one’s risk for preterm birth and contribute to the racial gap in preterm birth in the Commonwealth.
Preterm birth, defined as a live birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy, is the second-leading cause of infant mortality in the United States, and one that disproportionately affects Black and ...
Analysis finds cardiac devices recalled for safety reasons infrequently subjected to premarket or postmarket testing
2024-09-16
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 16 September 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Trailblazers in plasma turbulence computer simulations win 2024 James Clerk Maxwell Prize
2024-09-16
A pair of physicists with long ties to PPPL are being honored for their foundational work on turbulence in plasma. Understanding why instabilities occur and how to limit them is critical to perfecting fusion as a stable energy source for the electrical grid.
Greg Hammett, a PPPL theoretical and computational principal research physicist, and Bill Dorland, former associate laboratory director for computational sciences and current Lab adviser, have won the 2024 James Clerk Maxwell Prize for Plasma Physics. The American ...
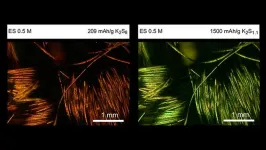
Technology could boost renewable energy storage
2024-09-16
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are critical to sustaining our planet, but they come with a big challenge: they don't always generate power when it's needed. To make the most of them, we need efficient and affordable ways to store the energy they produce, so we have power even when the wind isn't blowing or the sun isn't shining.
Columbia Engineering material scientists have been focused on developing new kinds of batteries to transform how we store renewable energy. In a new study published September 5 by Nature Communications, the team used K-Na/S batteries that combine inexpensive, readily-found elements -- ...
Introducing SandAI: A tool for scanning sand grains that opens windows into recent time and the deep past
2024-09-16
Stanford researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-based tool – dubbed SandAI – that can reveal the history of quartz sand grains going back hundreds of millions of years. With SandAI, researchers can tell with high accuracy if wind, rivers, waves, or glacial movements shaped and deposited motes of sand.
The tool gives researchers a unique window into the past for geological and archeological studies, especially for eras and environments where few other clues, such as fossils, are preserved ...
[1] ... [938]
[939]
[940]
[941]
[942]
[943]
[944]
[945]
946
[947]
[948]
[949]
[950]
[951]
[952]
[953]
[954]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.