The Ocean Corporation collaborates with UTHealth Houston on Space Medicine Fellowship program
2024-09-19
UTHealth Houston and The Ocean Corporation are collaborating on UTHealth Houston’s Space Medicine Training Fellowship program, which now includes a two-week intensive training focused on hyperbaric technologies and analog environments akin to those astronauts experience during extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks.
The training will enhance the hands-on learning experience of fellows in the Space Medicine Fellowship program, giving them a deeper understanding of physiological and medical challenges encountered in extreme environments.
“Integrating ...
Mysteries of the bizarre ‘pseudogap’ in quantum physics finally untangled
2024-09-19
By cleverly applying a computational technique, scientists have made a breakthrough in understanding the ‘pseudogap,’ a long-standing puzzle in quantum physics with close ties to superconductivity. The discovery, presented in the September 20 issue of Science, will help scientists in their quest for room-temperature superconductivity, a holy grail of condensed matter physics that would enable lossless power transmission, faster MRI machines and superfast levitating trains.
Certain materials involving copper and oxygen display superconductivity (where electricity flows without resistance) at relatively high — but still frigid — temperatures below ...
Study: Proteins in tooth enamel offer window into human wellness
2024-09-19
A new way of looking at tooth enamel could give scientists a path to deeper understanding of the health of human populations, from the ancient to the modern.
The method, published this week in the Journal of Archaeological Science, examines two immune proteins found embedded in human tooth enamel: immunoglobulin G, an antibody that fights infection, and C-reactive protein, which is present during inflammation in the body.
“These proteins are present in tooth enamel, and they are something we can use to study the ...
New cancer cachexia treatment boosts weight gain and patient activity
2024-09-19
Researchers discovered a drug that safely and effectively helped cancer patients when they suffered from cachexia (ku-KEK-see-uh), a common condition related to cancer that involves weight loss and muscle wasting.
The results of the randomized phase 2 clinical trial, which included187 individuals who experienced cachexia with lung, pancreatic, or colorectal cancer, were reported in the New England Journal of Medicine on Sept. 14, 2024. Richard Dunne, MD, MS, a Wilmot Cancer Institute oncologist and cachexia expert was part of the large group of investigators ...
Rensselaer researcher receives $3 million grant to explore gut health
2024-09-19
Blanca Barquera's investigation into the energy-generating processes of Bacteroides, the most abundant member of the gut microbiome, and their impact on our well-being holds the promise of significant advancements in human health. Barquera is a professor at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in the Departments of Biological Sciences and Chemistry and Chemical Biology.
In recent years, it has become increasingly clear that an unhealthy gut is more than just a source of digestive troubles. A healthy ...
Elam named as a Fellow of the Electrochemical Society
2024-09-19
Jeffrey Elam, senior chemist, Distinguished Fellow, and founder of the atomic layer deposition (ALD) research program at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, was named as a fellow of the Electrochemical Society (ECS), which focuses on advancing theory and practice at the forefront of electrochemical and solid-state science and technology. Elam, who has been with the lab since 2002, has been a trailblazer in thin film coating science and technology for over 20 years, ...
Study reveals gaps in access to long-term contraceptive supplies
2024-09-19
Oregon Health & Science University researchers have found that despite legislation in 19 states requiring insurers to cover a 12-month supply of contraception, patients aren’t receiving a year’s worth of their prescription; most receive just three months or less.
Their study recently published in the journal JAMA Health Forum shows that policies requiring coverage of a 12-month supply of short-acting hormonal contraception — most commonly the birth control pill — have not been fully implemented, resulting in no substantial increases nationally in year-long prescription orders. This leaves many patients at an increased risk for unintended ...
Shining a light on the roots of plant “intelligence”
2024-09-19
All living organisms emit a low level of light radiation, but the origin and function of these 'biophotons' are not yet fully understood. An international team of physicists, funded by the Foundational Questions Institute, FQxI, has proposed a new approach for investigating this phenomenon based on statistical analyses of this emission. Their aim is to test whether biophotons can play a role in the transport of information within and between living organisms, and whether monitoring biophotons could contribute to the development of medical techniques for the early diagnosis of various diseases. Their analyses of the measurements of the faint glow emitted by lentil ...
Scientists identify a unique combination of bacterial strains that could treat antibiotic-resistant gut infections
2024-09-19
Antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections often occur in patients with chronic inflammatory intestinal conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, and in patients who have taken antibiotics for a long time. Gram-negative bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae are a common cause of these infections and have few treatment options. Fecal microbiota transplants have shown promise to curb some of these infections, but their composition varies between batches and they aren’t always successful.
Researchers at Keio University School of Medicine in Tokyo and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have isolated ...
Pushing kidney-stone fragments reduces stones’ recurrence
2024-09-19
Sometimes all it takes is a little push.
That is the conclusion of a recently published study in which doctors used a handheld ultrasound device to nudge patients’ kidney-stone fragments.
As many as 50% of patients who have kidney stones removed surgically still have small fragments remaining in the kidneys afterward. Of those patients, about 25% find themselves returning for another operation within five years to remove the now-larger fragments.
UW Medicine researchers found, however, that patients ...
Sweet success: genomic insights into the wax apple's flavor and fertility
2024-09-19
A recent study has successfully decoded the autotetraploid genome of the wax apple, uncovering its genetic evolution and key factors driving fruit diversity. The research highlights the fruit’s rich antioxidant profile, with promising implications for human health and breeding strategies aimed at enhancing nutritional value.
Wax apple (Syzygium samarangense), known for its crisp texture, rose-like aroma, and health benefits, faces breeding challenges due to its complex genetic diversity and limited genomic data. These obstacles have hindered efforts to improve key fruit qualities such as size and sugar ...
New study charts how Earth’s global temperature has drastically changed over the past 485 million years, driven by carbon dioxide
2024-09-19
A new study co-led by the Smithsonian and the University of Arizona offers the most detailed glimpse yet of how Earth’s surface temperature has changed over the past 485 million years. In a paper published today, Sept. 19, in the journal Science, a team of researchers, including paleobiologists Scott Wing and Brian Huber from the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History, produce a curve of global mean surface temperature (GMST) across deep time—the Earth’s ancient past stretching over many millions of years. ...
Scientists say we have enough evidence to agree global action on microplastics
2024-09-19
Science has provided more than sufficient evidence to inform a collective and global approach to tackle the continued spread of plastic pollution, according to a new report.
Writing in the journal Science, an international group of experts say the need for worldwide action to tackle all forms of plastic and microplastic debris has never been more pressing.
It is clear that existing national legislation alone is insufficient to address the challenge, they say, and the United Nations’ Plastic Pollution Treaty ...
485 million-year temperature record of Earth reveals Phanerozoic climate variability
2024-09-19
Estimating past global temperature is important for understanding the history of life on Earth and for predicting future climate. Now, a new reconstruction of Earth’s temperature history over the past 485 million years – based on a method that combines diverse physical proxy data with climate model predictions – reveals a much wider range of climate variability across the Phanerozoic eon than previously understood. The findings highlight atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) as the dominant factor controlling climate variability throughout this period, offering new ...
Atmospheric blocking slows ocean-driven glacier melt in Greenland
2024-09-19
Cooling in the subsurface waters beneath Greenland’s Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden Glacier (79NG) from 2018 to 2021 was driven by European atmospheric blocking, which forced changes in the large-scale ocean circulation of the Nordic seas, researchers report, slowing glacial melt, despite ongoing global warming trends. The findings highlight the importance of regional atmospheric dynamics in influencing glacier stability. Understanding these dynamics is key to predicting the future of glaciers like ...
Study: Over nearly half a billion years, Earth’s global temperature has changed drastically, driven by carbon dioxide
2024-09-19
Published in the journal Science, the study presents a curve of global mean surface temperature that reveals Earth's temperature has varied more than previously thought over much of the Phanerozoic Eon a period of geologic time when life diversified, populated land and endured multiple mass extinctions. The curve also confirms Earth's temperature is strongly correlated to the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The start of the Phanerozoic Eon 540 million years ago is marked by the Cambrian ...
Clinical trial could move the needle in traumatic brain injury
2024-09-19
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Subscribe to UCSF News
Department of Defense-funded study aims to end a decades-long impasse in treatment development.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) results in close to 70,000 deaths in the United States every year, and it is the cause of long-term physical, cognitive and mental disability in 5 million Americans. But despite three decades of work, treatments are sorely lacking.
Now, an innovative drug development trial will be available in emergency departments of 18 level 1 trauma sites nationwide. It is launched by UC San Francisco and the Transforming Research and Clinical Knowledge in Traumatic ...
AI model can reveal the structures of crystalline materials
2024-09-19
For more than 100 years, scientists have been using X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of crystalline materials such as metals, rocks, and ceramics.
This technique works best when the crystal is intact, but in many cases, scientists have only a powdered version of the material, which contains random fragments of the crystal. This makes it more challenging to piece together the overall structure.
MIT chemists have now come up with a new generative AI model that can make it much easier to determine the structures of these powdered crystals. The prediction model could help researchers characterize ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for September 19, 2024
2024-09-19
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
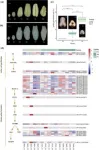
Genetic factors underscore disparities in colorectal cancer survival
Patients with colorectal cancer have varied overall survival, but it remains unclear how the frequency of certain gene mutations among different racial and ethnic groups influences outcomes. To investigate, researchers led by John Paul Shen, M.D., and ...
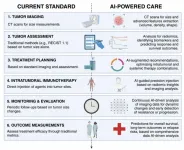
The role of artificial intelligence in advancing intratumoral immunotherapy
2024-09-19
“We explore how integrating these technologies could revolutionize personalized oncology.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 19, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 17, 2024, entitled, “The emerging role of AI in enhancing intratumoral immunotherapy care.”
As highlighted in the abstract of this editorial, the emergence of immunotherapy (IO), and more recently, intratumoral IO, offers a novel approach to cancer treatment. This method enhances immune responses, allows for combination therapies, and helps reduce systemic adverse events. These techniques aim to ...
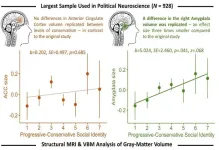
Political ideology is associated with differences in brain structure, but less than previously thought
2024-09-19
Conservative voters have slightly larger amygdalas than progressive voters—by about the size of a sesame seed. In a replication study publishing September 19 in the Cell Press journal iScience, researchers revisited the idea that progressive and conservative voters have identifiable differences in brain morphology, but with a 10x larger and more diverse sample size than the original study. Their results confirmed that the size of a person’s amygdala is associated with their political views but failed to find a consistent association between politics and the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Anatomical differences in both ...
Genetic tracing at the Huanan Seafood market further supports COVID animal origins
2024-09-19
A new international collaborative study provides a list of the wildlife species present at the market from which SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, most likely arose in late 2019. The study is based on a new analysis of metatranscriptomic data released by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The data come from more than 800 samples collected in and around the Huanan Seafood Wholesale market beginning on January 1, 2020, and from viral genomes reported from early COVID-19 patients. The research appears September 19 in the journal Cell.
“This is one of the most ...
Breastfeeding is crucial to shaping infant’s microbes and promoting lung health
2024-09-19
Human breast milk regulates a baby’s mix of microbes, or microbiome, during the infant’s first year of life. This in turn lowers the child’s risk of developing asthma, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and the University of Manitoba, the study results showed that breastfeeding beyond three months supports the gradual maturation of the microbiome in the infant’s digestive system and nasal cavity, the upper part of the respiratory tract. Conversely, stopping breastfeeding earlier than three months disrupts the paced development of the microbiome and ...
Scientists at the CNIC discover an unexpected involvement of sodium transport in mitochondrial energy generation
2024-09-19
The GENOXPHOS (Functional Genetics of the Oxidative Phosphorylation System) group at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) has discovered a crucial role of sodium in the generation of cellular energy. The study, led by GENOPHOS group leader Dr. José Antonio Enríquez, also involved the participation of scientists from the Complutense University of Madrid, the Biomedical Research Institute at Hospital Doce de Octubre, the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and the Spanish research networks on frailty and healthy aging (CIBERFES) ...
Origami paper sensors could help early detection of infectious diseases in new simple, low-cost test
2024-09-19
Researchers at Cranfield University have developed an innovative new method for identifying biomarkers in wastewater using origami-paper sensors, enabling the tracking of infectious diseases using the camera in a mobile phone. The new test device is low-cost and fast and could dramatically change how public health measures are directed in any future pandemics.
Wastewater a key way to track infections
Testing wastewater is one of the primary ways to assess the prevalence of infectious diseases in populations. Researchers take samples from various ...
[1] ... [930]
[931]
[932]
[933]
[934]
[935]
[936]
[937]
938
[939]
[940]
[941]
[942]
[943]
[944]
[945]
[946]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.