Like humans, artificial minds can learn by thinking
2024-09-18
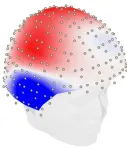
Some of the greatest discoveries don’t come merely from observations but from thinking. Einstein developed theories about relativity through thought experiments, and Galileo derived insights about gravity through mental simulations. A review published September 18 in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences shows that this process of thinking is not exclusive to humans. Artificial intelligence, too, is capable of self-correction and arriving at new conclusions through “learning by thinking.”
“There are some recent demonstrations of what looks like learning by thinking in AI, ...
Discarding the placenta after birth leads to loss of valuable information, pathologists say
2024-09-18
In an opinion article publishing September 18 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Molecular Medicine, physician-scientists argue that with most placentas discarded after birth, placental pathology is underutilized clinically, should be a routine part of obstetric and neonatal care, and also deserves more research attention.
“Placentas should not be considered a waste tissue,” says senior author Mana Parast, MD, PhD, professor of pathology at University of California San Diego School of Medicine. ...
Nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth spiked during pandemic
2024-09-18
Drug overdose mortality has risen faster among adolescents than the general population in recent years, largely due to fentanyl, a potent opioid pain medication. A new study published in JAMA sheds light on trends in nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth – an area that was not as well characterized, but key to formulating prevention strategies to save lives.
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues analyzed data using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) encounters from January 2018 to December 2022. They found that opioid overdoses in youth increased at pandemic onset and remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels. The majority ...
Characteristics and trends of prehospital encounters for opioid overdoses among US youth, 2018-2022
2024-09-18
About The Study: Prehospital encounters for youth opioid overdoses were increasing prior to the pandemic, increased with the onset, and then stabilized, remaining higher than pre-pandemic levels. Although overall patterns were largely driven by those ages 18 through 24, adolescents ages 12 through 17 were the only subgroup with an increasing number of encounters both before and during the pandemic.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jamie Lim, MD, email jlim@luriechildrens.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
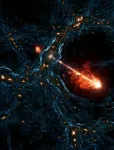
Gargantuan black hole jets are biggest seen yet
2024-09-18
** Caltech is hosting an embargoed media zoom about this result on Monday, September 16 at 10am Pacific/1pm Eastern. You can register here:
https://caltech.zoom.us/webinar/register/WN_gYEV5Tl1S0uZkZG1gDIEnQ#/registration
Astronomers have spotted the biggest pair of black hole jets ever seen, spanning 23 million light-years in total length. That's equivalent to lining up 140 Milky Way galaxies back to back.
"This pair is not just the size of a solar system, or a Milky Way; we are talking about 140 Milky Way diameters in total," says Martijn ...
An update on the survival of the first 50 face transplants worldwide
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, the overall survival of the face transplants is encouraging. These data suggest that the acceptable long-term survival of face transplants makes them a reconstructive option for extensive facial defects.
Quote from corresponding author Pauliina Homsy, MD, PhD:
“A total of 50 face transplants have been performed since 2005. Activity has been concentrated with only 18 centers in 11 countries giving this treatment. Our study demonstrates an overall 5- and 10-year survival of face transplants ...
Social determinants of health and insurance claim denials for preventive care
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1.5 million patients seeking preventive care, denials of insurance claims for preventive care were disproportionately more common among at-risk patient populations. This administrative burden potentially perpetuates inequitable access to high-value health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alex Hoagland, PhD, email alexander.hoagland@utoronto.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33316)
Editor’s ...
Patient self-guided interventions to reduce sedative use and improve sleep
2024-09-18
About The Study: The results of this randomized clinical trial showed that transitioning insomnia care for older adults away from long-term sedative use and toward cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia can be achieved using a mailed, direct-to-patient approach.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, David M. Gardner, PharmD, MSc CH&E, email david.gardner@dal.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.2731)
Editor’s ...
Brigham researchers use machine learning to improve cardiovascular risk assessment
2024-09-18
Risk calculators are used to evaluate disease risk for millions of patients, making their accuracy crucial. But when national models are adapted for local populations, they often deteriorate, losing accuracy and interpretability. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, used advanced machine learning to increase the accuracy of a national cardiovascular risk calculator while preserving its interpretability and original risk associations. Their results showed higher accuracy overall in an electronic health records cohort ...
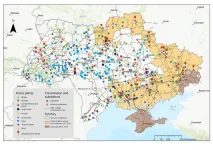
How Ukraine can rebuild its energy system
2024-09-18
One of the main targets of Russia’s ongoing attacks on Ukraine is the energy infrastructure. The extent of the destruction is enormous. “One year after the start of the war in February 2022, 76 percent of thermal power plants had been destroyed; now the figure is 95 percent,” says Ukrainian scientist Iryna Doronina. “And all the large hydroelectric power plants have also failed.” The breaching of the Kakhovka dam proved to be particularly devastating. The huge outflow of water – the reservoir ...
Research points a way to modulate scarring in spinal cord injury
2024-09-18
Media Contact: laura.kurtzman@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
After a spinal cord injury, nearby cells quickly rush to action, forming protective scar tissue around the damaged area to stabilize and protect it. But over time, too much scarring can prevent nerves from regenerating, impeding the healing process and leading to permanent nerve damage, loss of sensation or paralysis.
Now, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered how a rarely studied cell type controls the formation of scar tissue in spinal cord injuries. Activating ...
Breast and ovarian cancer newly linked to thousands of gene variants
2024-09-18
Scientists have pinpointed thousands of genetic changes in a gene that may increase a person’s risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer, paving the way for better risk assessment and more personalised care.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators focused on the ‘cancer protection’ gene RAD51C, finding over 3,000 harmful genetic changes that could potentially disrupt its function and increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and risk of aggressive subtypes of breast ...
Metal exposure can increase cardiovascular disease risk
2024-09-18
Metal exposure from environmental pollution is associated with increased calcium buildup in the coronary arteries at a level comparable to traditional risk factors like smoking and diabetes, according to a study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The findings support that metals in the body are associated with the progression of plaque buildup in the arteries and potentially provide a new strategy for managing and preventing atherosclerosis.
"Our findings highlight the importance ...
Penny for your thoughts? Master copper regulator discovery may offer Alzheimer’s clues
2024-09-18
New therapeutic opportunities often emerge from research on simple organisms. For instance, the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier, Ph.D., and Jennifer Doudna, Ph.D., for their CRISPR-based DNA editing discovery began with studies using bacteria just a decade prior. Today, CRISPR therapies are approved for several disorders, and more such treatments are in the offing.
Recognizing the translational potential of studies in simpler animal models, a team of scientists led by Randy D. Blakely, ...
Keck Hospital of USC named a 2024 top performer by Vizient, Inc.
2024-09-18
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC has been named a top performer in the 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership award by Vizient, Inc., a leading health care performance improvement company.
The top performer designation acknowledges the hospital’s excellence in delivering high-quality care as measured by the annual Vizient Quality and Accountability Study.
Keck Hospital was among 14 top performers out of 115 comprehensive academic medical centers nationally and achieved a five-star ...
NSF and Simons Foundation launch 2 AI Institutes to help astronomers understand the cosmos
2024-09-18
Note: Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. ET on Sept. 18, 2024
From the early telescopes made hundreds of years ago by Galileo to the sophisticated astronomical observatories of today, people have built increasingly innovative tools to probe and measure the cosmos. Soon, researchers at two new institutes funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the Simons Foundation will build a new breed of astronomical tools by harnessing the uniquely powerful abilities of artificial intelligence to assist and accelerate humanity's understanding of the universe.
The new National Artificial Intelligence ...
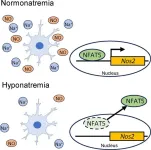
Exploring the effect of low sodium concentrations on brain microglial cells
2024-09-18
Low serum sodium concentrations in blood are called hyponatremia, a prevalent clinical electrolyte disorder. In contrast to acute hyponatremia, chronic hyponatremia has been previously considered asymptomatic because the brain can successfully adapt to hyponatremia. If not treated, chronic hyponatremia can lead to complications such as fractures, falls, memory impairment, and other mental issues. Treating the chronic condition is, however, quite tricky as it has been observed that overly rapid correction of hyponatremia ...
New Alzheimer’s studies reveal disease biology, risk for progression, and the potential for a novel blood test
2024-09-18
EMBARGOED by Alzheimer’s & Dementia until 7 a.m., ET, Sept. 18, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, Boston University, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
Contact: Andrea Zeek, IU School of Medicine, 317-671-3114, anzeek@iu.edu
(Boston)— The failure to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia in the elderly, at an early stage of molecular pathology is considered a major reason why treatments fail in clinical trials. Previous research to molecularly diagnose Alzheimer’s disease yielded "A/T/N" central biomarkers based on the measurements of proteins, β-amyloid (“A”) and tau (“T”), ...
Comorbidity and disease activity in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, a higher burden of comorbidity was associated with worse clinical outcomes in people with multiple sclerosis (MS), although comorbidity could potentially be a partial mediator of other negative prognostic factors. The findings suggest a substantial adverse association of the comorbidities investigated with MS disease activity and that prevention and management of comorbidities should be a pressing concern in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Amber Salter, PhD, email amber.salter@utsouthwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
£18 million for DARE UK to support secure research on sensitive data
2024-09-18
London, United Kingdom, 18 September 2024 – UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), the UK’s largest public funder of research, has confirmed funding for a new phase of the DARE UK (Data and Analytics Research Environments UK) programme with up to £18.2 million made available over 2.5 years.
Starting this month, Phase 2 of the DARE UK programme will bring together Trusted Research Environments (TREs) across the UK to test and build new capabilities for a connected national network of secure data ...
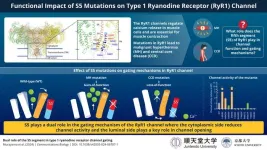
New study unveils the impact of mutations in the calcium release channel on muscle diseases
2024-09-18
The type 1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an important calcium release channel in skeletal muscles essential for muscle contraction. It mediates calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a calcium-storing organelle in muscle cells, a process vital for muscle function. Mutations in the RyR1 gene can affect the channel's function in extremely contrasting ways leading to severe muscle diseases such as malignant hyperthermia (MH) and central core disease (CCD). MH is an inherited disease that causes high fever and muscle contractures in response to inhalational anesthetics in patients with gain-of-function RyR1 variants. CCD is one ...
Scientists quantify energetic costs of the migratory lifestyle in a free flying songbird
2024-09-18
Millions of birds migrate every year to escape winter, but spending time in a warmer climate does not save them energy, according to research by the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB). Using miniaturized loggers implanted in wild blackbirds, scientists recorded detailed measurements of heart rate and body temperature from birds every 30 minutes from fall to the following spring—the first time the physiology of free flying birds has been quantified continuously at this scale over the entire wintering period. The data offer unprecedented insights into the true energetic costs of migrant and resident strategies and reveal a previously unknown mechanism used by migrants to ...
Understanding changes in pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease
2024-09-18
Amyloid-beta and tau proteins have long been associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The pathological buildup of these proteins leads to cognitive decline in people with the disease. How it does that, though, remains poorly understood.
A new study from the labs of Sylvain Baillet at The Neuro and Sylvia Villeneuve at the Douglas Research Centre provides important insight into how these proteins impact brain activity and possibly contribute to cognitive decline.
The team led by Jonathan Gallego Rudolf, a Ph.D. candidate in Baillet and Villeneuve’s ...
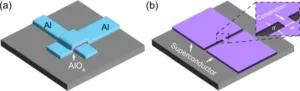
Constriction junction, do you function?
2024-09-18
UPTON, N.Y. — Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have shown that a type of qubit whose architecture is more amenable to mass production can perform comparably to qubits currently dominating the field. With a series of mathematical analyses, the scientists have provided a roadmap for simpler qubit fabrication that enables robust and reliable manufacturing of these quantum computer building blocks.
This research was conducted as part of the Co-design Center for ...
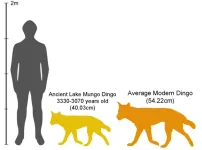
Early dingoes are related to dogs from New Guinea and East Asia
2024-09-18
New archaeological research by the University of Sydney has discovered for the first time clear links between fossils of the iconic Australian dingo, and dogs from East Asia and New Guinea.
The remarkable findings suggest that the dingo came from East Asia via Melanesia, and challenges previous claims that it derived from pariah dogs of India or Thailand.
Previous studies used traditional morphometric analysis – which looks at the size and shape of the animal using callipers – ...
[1] ... [926]
[927]
[928]
[929]
[930]
[931]
[932]
[933]
934
[935]
[936]
[937]
[938]
[939]
[940]
[941]
[942]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.