Can a drug-free nasal spray protect against deadly respiratory infections?
2024-09-25
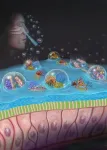
New research published in Advanced Materials reports a novel nasal spray for preventing respiratory infections. The spray works by forming a protective coating on the nasal cavity, which captures airborne respiratory droplets and acts as a physical barrier against viruses and bacteria, while effectively neutralizing them.
In studies conducted on mice, the Pathogen Capture and Neutralizing Spray (PCANS) demonstrated up to 8 hours of nasal retention. In a severe Influenza A model, a single pre-exposure dose of PCANS resulted in a greater than 99.99% reduction ...
Do natural disasters jeopardize women’s reproductive health?
2024-09-25
In research published in Brain and Behavior, investigators found increased rates of menstrual irregularities in women living in areas affected by the 2023 earthquake in Turkey.
In the study, 309 women of reproductive age living in regions declared as disaster areas completed online forms 9 months after the earthquake. Responses revealed an increase of menstrual irregularities from 14.3% before the earthquake to 44.8% after the earthquake. Risk factors for menstrual irregularities included post-traumatic stress symptoms, chronic diseases, and smoking.
The findings reveal that reproductive health ...
Can cosmic radiation in outer space affect astronauts’ long-term cognition?
2024-09-25
During missions into outer space, galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) will penetrate current spacecraft shielding and thus pose a significant risk to human health. Previous studies have shown that GCR can cause short-term cognitive deficits in male rodents. Now a study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry reveals that GCR exposure can also cause long-lasting learning deficits in female rodents.
The impact of GCR on cognition was lessened when mice were fed an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound called CDDO-EA.
Beyond ...
Do preventive health technologies promote or harm consumers’ wellbeing?
2024-09-25
Preventive health technologies—such as wrist-worn activity trackers or health and fitness apps—are popular tools for promoting wellbeing, but new research published in the Journal of Consumer Affairs reveals that consumer engagement with these technologies can be considered a double-edged sword.
The study, which involved 30 in-depth interviews with users, found that consumers engage with preventive health technologies based on a variety of health goals—for example, to lose weight, improve performance, monitor data of an enjoyable activity, or acquire a healthy routine.
These diverse goals led users ...
Preclinical studies suggest a drug-free nasal spray could ward off respiratory infections
2024-09-25
Researchers from the Brigham detail how the spray they created may offer broad-spectrum protection from respiratory infections by COVID-19, influenza, everyday cold viruses, and pneumonia-causing bacteria
A new study details how a nasal spray formulated by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, may work to protect against viral and bacterial respiratory infections. Based on their preclinical studies, the researchers say the broad-spectrum nasal spray is long-lasting, safe, and, if validated in humans, could play a key role in reducing respiratory diseases ...
Campylobacter jejuni-specific antibody gives hope to vaccine development
2024-09-25
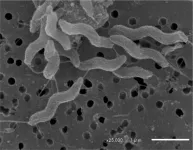
Bacterial infections resulting in enteritis, sometimes extra-intestinal infections such as sepsis, continue to be a global health concern. A leading cause of diarrheal and extra-intestinal infectious mortality among children under 5 and elderly persons is infection with Campylobacter bacteria, against which there is no effective vaccine or medication. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has recently uncovered what could be an important step toward preventing, diagnosing, and treating a species of Campylobacter bacteria.
Researchers including Professor Shinji Yamasaki and Associate Professor Noritoshi Hatanaka of the Graduate School ...
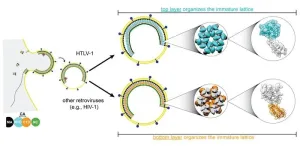
A viral close-up of HTLV-1
2024-09-25
Martin Obr is on edge, anxiously waiting for his train to the airport. A storm called “Sabine” is brewing, shutting down all public transport. He catches his flight from Frankfurt to Vienna just in time.
Obr spent the last days in Germany meticulously analyzing what he calls the “perfect sample”. This sample helped him and Florian Schur from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) decode the structure of a virus called HTLV-1 (Human T-cell Leukemia Virus Type 1).
In collaboration with the University of Minnesota and Cornell University, ...
Virtual reality can help pedestrians and cyclists swerve harmful pollutants – study
2024-09-25
Physics-informed virtual reality could be key to reducing the exposure of pedestrians and cyclists to harmful, non-exhaust vehicle emissions, according to a study published today (25 Sep) in the Royal Society Open Science journal.
The research lead by the University of Birmingham (supported by Rosetrees Trust and Research England QR Funding), targets the issue of major health risks and chronic diseases caused by exposure to unregulated particle pollutants from road, tyre and brake sources by providing easy, accessible guidance to the public, policy makers, and city planners, through immersive VR experiences.
Detailed ...
Neuroscience luminary Hermona Soreq sheds light on the roles of RNA regulators in neurodegenerative diseases
2024-09-25
In a compelling Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on September 25, 2024, Professor Hermona Soreq of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel unveils the profound implications of her groundbreaking research on the cholinergic system and small RNA regulators in brain-body communication.
Prof. Soreq, holder of the Endowed Slesinger Professorship of Molecular Neuroscience, has dedicated her career to unraveling the complexities of the parasympathetic nervous system, with a particular focus on acetylcholine's role in stress responses and neurodegenerative diseases. Her work has revolutionized our understanding of how the brain ...
Ancient reef-builders dodged extinction — at least temporarily
2024-09-25
Will modern coral reefs go extinct? The answer is uncertain, but some of their ancient counterparts managed to dodge a bullet — for a while, at least.
Scientists from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered that ancient reef-building organisms called stromatoporoids survived the Late Devonian mass extinction event and continued to thrive as major reef-builders long after their presumed extinction. These findings shed light on how life on Earth has responded to past environmental changes, offering ...
Citizen scientists help discover microplastics along the entire German coastline
2024-09-25
The global production of plastics and the resulting plastic waste has increased to such an extent that plastics have become ubiquitous in our environment. Plastics of various sizes are also found along the German North Sea and Baltic coasts. Previous studies of microplastic pollution on German beaches have often been limited to a few locations. In the citizen science project “Microplastic Detectives”, researchers from the Alfred Wegener Institute, together with citizens, have now collected samples from beaches along the entire German coast to be analyzed for microplastics. The resulting dataset is the first to be large enough to ...
Rising waters, waning forests: How scientists are using tree rings to study how rising sea levels affect coastal forests
2024-09-25
Sunlight filters through the canopy of pines, holly, sweet gum, and red maple while bird calls echo in the distance. These coastal forests may seem like others in the Mid-Atlantic, but a hidden challenge looms. Standing tall next to their salt marsh neighbors, where the wind carries the sharp scent of sulfidic seawater, these trees are more than just part of the landscape—they are living monuments to a rapidly changing environment. As sea levels rise, the future of these forests is uncertain. While the adjacent salt marshes can adapt to encroaching waters, the trees, vulnerable to the increasing frequency ...
Night-time noise linked to restless nights for airport neighbours
2024-09-25
Noise from aircraft at night is linked with disturbed sleep quality and sleep-wake cycle, a new study using movement trackers has shown.
Environmental health experts at the University of Leicester combined measurements from activity monitors and self-reported sleep information for the first time to put together a more detailed picture of how aircraft noise impacts sleep, in the largest such study to date.
The results, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, show that people exposed to higher levels of night-time aircraft noise experienced more restlessness during sleep and disruption in daily sleep rhythm, even if they had a full night’s sleep.
The team was led from the ...
Fossils from the Adriatic Sea show a recent and worrying reversal of fortunes
2024-09-25
If you’d stopped monitoring the Adriatic Sea’s marine life in the mid-20th century, the outlook would have been promising. Snails and the clams they hunt for food increased in abundance for several decades during the late 1800s and early 1900s, evidence of a vibrant and healthy ecosystem.
Then, a threshold was crossed. Populations of both predator and prey abruptly plummeted and in some cases disappeared entirely. They were replaced by the common corbulid clam (Varicorbula gibba), which has the ability to slow down its metabolism in unfavorable conditions. Whenever paleontologists find an abundance of this species in the marine fossil record, it often means ...
With curtailed carbon emissions, corals can survive climate change
2024-09-25
KANEOHE, HI (Sept 24, 2024 1:05 p.m. HST)- In a study published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, researchers at the UH Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) Toonen- Bowen “ToBo” Lab have identified scenarios under which eight of the most common species of coral found in Hawaiʻi can adapt to and survive ocean warming and acidification. The corals in the study are prevalent throughout the Indo-Pacific, a region that comprises more than two-thirds of the coral reefs on planet Earth, and were found to be capable of surviving a “low ...
Global prevalence of short-sightedness in children and teens set to top 740 million cases by 2050
2024-09-24
Around 1 in 3 children and teens around the world is short (near)-sighted, with the global prevalence of myopia set to top 740 million cases by 2050 in this age group, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology.
Female sex, East Asian or urban area residence, and educational level all seem to be key factors influencing prevalence, the findings indicate.
Short (near)-sightedness (myopia), which describes difficulty seeing objects at a distance, typically starts in early childhood and tends to worsen with age, explain the researchers. It has emerged ...
Urgent rethink of bottled water’s huge and growing toll on human and planetary health
2024-09-24
The huge and growing toll bottled water is taking on human and planetary health warrants an urgent rethink of its use as 1 million bottles are bought every minute around the globe, with that figure set to rise further still amid escalating demand, warn population health experts in a commentary published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
Some 2 billion people around the world with limited or no access to safe drinking water rely on bottled water. But for the rest of us, it’s largely a matter of convenience and the unshaken belief—aided and abetted by industry marketing—that bottled water is safer and often healthier than tap ...
Women still missing out on treatment for their No 1 killer—cardiovascular disease
2024-09-24
Women in the UK, and elsewhere, are still missing out on vital treatment for their No 1 killer—cardiovascular disease—despite significant progress in the medical management of heart disease and stroke, concludes a consensus statement published online in the journal Heart.
They continue to be underdiagnosed, undertreated, and underrepresented in clinical trials in all areas of cardiovascular disease, says the statement. Among other things, it calls for dedicated women’s heart champions and heart hubs, plus a women’s ...
Palestinian education ‘under attack’, leaving a generation close to losing hope, study warns
2024-09-24
The ongoing war in Gaza will set children and young people’s education back by up to five years and risks creating a lost generation of permanently traumatised Palestinian youth, a new study warns.
The report, by a team of academics working in partnership with the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA), is the first to comprehensively quantify the war’s toll on learning since it began in October 2023. It also details the devastating impact on children, young people and teachers, supported by new accounts from frontline staff and ...
Semaglutide improves outcomes for obese patients with common skin condition, new study shows
2024-09-24
(Wednesday, 25 September 2024, Amsterdam, Netherlands) A pioneering study, presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2024, demonstrates the significant potential of semaglutide in treating hidradenitis suppurative (HS), a common and chronic skin condition, in people with obesity.1
This is the first study to explore the use of semaglutide for HS, marking a critical milestone in the search for effective treatments for this painful and debilitating condition.
HS is currently estimated to affect approximately 1 in 100 people, with obesity being a significant risk factor. The condition is characterised ...
Could GLP1RA drugs lower high iron levels?
2024-09-24
GLP1RA agonists have been increasing in popularity for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes.
With this novel treatment proving to be very effective, researchers are curious to know more about what other potential treatments it could also hold.
Researchers at the University of Michigan investigated another potential way GLP1RA drugs can be useful in treating type two diabetes associated with a genetic condition that causes high levels of iron, called hereditary hemochromatosis.
High iron levels with hereditary hemochromatosis can cause predisposition to liver disease ...
C-Path’s PKD outcomes consortium receives BAA Award for project to advance drug development tools for autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease
2024-09-24
TUCSON, Ariz., Sept. 19, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is thrilled to announce its Polycystic Kidney Disease Outcomes Consortium (PKDOC) has been awarded an Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease (ADTKD) focused Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The overarching objective of the work supported by the BAA award is to leverage collaboration with the Wake Forest Rare Inherited Kidney Disease team and its ADTKD registry, to analyze clinical and laboratory data that will help evaluate prognosis in ADTKD and help set the stage for future clinical trials.
ADTKD only affects ...
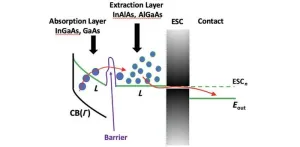
New insights into hot carrier solar cells: Increasing generation and extraction
2024-09-24
Hot carrier solar cells, a concept introduced several decades ago, have long been seen as a potential breakthrough in solar energy technology. These cells could surpass the Shockley–Queisser efficiency limit, which is a theoretical maximum efficiency for single-junction solar cells. Despite their promise, practical implementation has faced significant challenges, particularly in managing the rapid extraction of hot electrons across material interfaces.
Recent research has focused on using satellite valleys in the conduction band to temporarily store hot electrons before collection. However, ...
Clinical trial results show low-intensity therapy can achieve positive outcomes for certain pediatric leukemia subtypes
2024-09-24
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – Sept. 24, 2024) – Clinical trial results from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital demonstrate benefits to using genomics and early treatment response to guide risk classification of children with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Traditionally, the intensity of a patient’s chemotherapy regime is guided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) risk classification, which is largely determined by clinical characteristics such as age and white blood cell count at presentation. Through the flagship St. Jude ...
How emotion boosts memory for context
2024-09-24
Researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology demonstrated that emotion enhances memory for contextual details, challenging the view that emotion impairs the ability to remember such information.
The report was led by doctoral student Paul Bogdan, currently a postdoc at Duke University, and Florin and Sanda Dolcos, professors of psychology and neuroscience at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
Their research appears in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: ...
[1] ... [921]
[922]
[923]
[924]
[925]
[926]
[927]
[928]
929
[930]
[931]
[932]
[933]
[934]
[935]
[936]
[937]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.