(Press-News.org) An elusive state of matter called superconductivity could be realized in stacks of sheetlike crystals just a few atoms thick, a trio of physicists has determined.
Superconductivity, the flow of electrical current without resistance, is usually found in materials chilled to the most frigid temperatures, which is impractical for most applications. It's been observed at higher temperatures–higher being about 100 kelvin or minus 280 degrees below zero Fahrenheit–in copper oxide materials called cuprate superconductors. But those materials are brittle and unsuitable for fabricating devices like circuits.
In a paper published in Nature Communications the week of July 28, Michael Fogler and Leonid Butov, professors of physics at the University of California, San Diego, and Konstantin Novoselov, Nobel laureate in physics and professor at the University of Manchester, propose a design for an artificially structured material that should support superconductivity at temperatures rivaling those seen for cuprates.
They considered a material made by interleaving two different types of crystal, one a semiconductor compound and the other a type of insulator. Two one-atom thick layers of the semiconductor compound molybdenum disulfide would be separated by a few-atom thick spacer made of boron nitride, and surrounded by additional boron nitride cladding.
This sets up a situation in which electrons and "holes" left by a missing electrons would accumulate in separate layers of the semiconductor compound in response to an electrical field. And yet these separated electrons and holes would be bound, at a distance, in states called indirect excitons.
These indirect excitons would form a gas with vanishing viscosity. That is, below a certain temperature, the gas would become superfluid. The physicists determined that superfluidity of indirect excitons would set up countercurrents that would not dissipate, a phenomenon called counterflow superconductivity.
Superfluidity and superconductivity are macroscopic manifestations of quantum phenomena, which are usually seen at the smallest physical scales.
The proposed design is an initial blueprint, the authors write. Their analysis reveals a general principle for creating "coherent states" like superfluidity and superconductivity that would emerge in similar materials created with layers of other semiconductor compounds such as tungsten disulfide or tungsten diselenide as well.
Such van der Waals structures are the subject of many investigations; this new analysis demonstrates that they also provide a new platform for exploring fundamental quantum phenomena.
Practical uses are possible as well; these materials could be used to develop electronic and optoelectronic circuits.
INFORMATION:
The U.S. Office of Naval Research, University of California Office of the President, U.S. National Science Foundation, European Research Council and the European Commission's Future and Emerging Technologies European Graphene Flagship supported this work.
Superconductivity could form at high temperatures in layered 2-D crystals
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Autistic brain less flexible at taking on tasks, Stanford study shows
2014-07-29
The brains of children with autism are relatively inflexible at switching from rest to task performance, according to a new brain-imaging study from the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Instead of changing to accommodate a job, connectivity in key brain networks of autistic children looks similar to connectivity in the resting brain. And the greater this inflexibility, the more severe the child's manifestations of repetitive and restrictive behaviors that characterize autism, the study found.
The study, which will be published online July 29 in Cerebral Cortex, ...
Diet affects men's and women's gut microbes differently
2014-07-29
The microbes living in the guts of males and females react differently to diet, even when the diets are identical, according to a study by scientists from The University of Texas at Austin and six other institutions published this week in the journal Nature Communications. These results suggest that therapies designed to improve human health and treat diseases through nutrition might need to be tailored for each sex.
The researchers studied the gut microbes in two species of fish and in mice, and also conducted an in-depth analysis of data that other researchers collected ...
Scientists separate a particle from its properties
2014-07-29
Researchers from the Vienna University of Technology have performed the first separation of a particle from one of its properties. The study, carried out at the Institute Laue-Langevin (ILL) and published in Nature Communications, showed that in an interferometer a neutron's magnetic moment could be measured independently of the neutron itself, thereby marking the first experimental observation of a new quantum paradox known as the 'Cheshire Cat'. The new technique, which can be applied to any property of any quantum object, could be used to remove disturbance and improve ...
The quantum Cheshire cat: Scientists separate a particle from its properties
2014-07-29
The Quantum Cheshire Cat: Can a particle be separated from its properties? On July 29, the prestigious journal, Nature Communications, published the results of the first Cheshire Cat experiment, separating a neutron from its magnetic field, conducted by Chapman University in Orange, CA, and Vienna University of Technology.
Chesire Cat"Well! I've often seen a cat without a grin," thought Alice in Wonderland, "but a grin without a cat! It's the most curious thing I ever saw in my life!" Alice's surprise stems from her experience that an object and its property cannot exist ...
The quantum Cheshire cat
2014-07-29
The Cheshire Cat featured in Lewis Caroll's novel "Alice in Wonderland" is a remarkable creature: it disappears, leaving its grin behind. Can an object be separated from its properties? It is possible in the quantum world. In an experiment, neutrons travel along a different path than one of their properties – their magnetic moment. This "Quantum Cheshire Cat" could be used to make high precision measurements less sensitive to external perturbations.
At Different Places at Once
According to the law of quantum physics, particles can be in different physical states at ...
Major turtle nesting beaches protected in 1 of the UK's far flung overseas territories
2014-07-29
But on the remote UK overseas territory of Ascension Island, one of the world's largest green turtle populations is undergoing something of a renaissance.
Writing in the journal Biodiversity and Conservation, scientists from the University of Exeter and Ascension Island Government Conservation Department report that the number of green turtles nesting at the remote South Atlantic outpost has increased by more than 500 per cent since records began in the 1970s. As many as 24,000 nests are now estimated to be laid on the Island's main beaches every year, making it the second ...
Could summer camp be the key to world peace?
2014-07-29
According to findings from a new study by University of Chicago Booth School of Business Professor Jane Risen, and Chicago Booth doctoral student Juliana Schroeder, it may at least be a start.
Risen and Schroeder conducted research on Seeds of Peace, one of the largest peacebuilding programs that brings together teenagers from conflict regions, including Israelis and Palestinians, every year for three weeks in rural Maine. They tracked participants' feelings and attitudes toward the other national group for three years with three separate cohorts of campers. They found ...
Tough foam from tiny sheets
2014-07-29
HOUSTON – (July 29, 2014) – Tough, ultralight foam of atom-thick sheets can be made to any size and shape through a chemical process invented at Rice University.
In microscopic images, the foam dubbed "GO-0.5BN" looks like a nanoscale building, with floors and walls that reinforce each other. The structure consists of a pair of two-dimensional materials: floors and walls of graphene oxide that self-assemble with the assistance of hexagonal boron nitride platelets.
The researchers say the foam could find use in structural components, as supercapacitor and battery electrodes ...
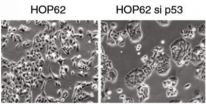
Research may explain how foremost anticancer 'guardian' protein learned to switch sides
2014-07-29
Cold Spring Harbor, NY -- Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have discovered a new function of the body's most important tumor-suppressing protein. Called p53, this protein has been called "the guardian of the genome." It normally comes to the fore when healthy cells sense damage to their DNA caused by stress, such as exposure to toxic chemicals or intense exposure to the sun's UV rays. If the damage is severe, p53 can cause a cell to commit preprogrammed cell-death, or apoptosis. Mutant versions of p53 that no longer perform this vital function, on the ...
Study: Pediatric preventive care guidelines need retooling for computerized format
2014-07-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- With the increasing use of electronic medical records and health information exchange, there is a growing demand for a computerized version of the preventive care guidelines pediatricians use across the United States. In a new study, researchers from the Indiana University School of Medicine and the Regenstrief Institute report that substantial work lies ahead to convert the American Academy of Pediatrics' Bright Future's guidelines into computerized prompts for physicians, but the payoff has the potential to significantly benefit patients from birth to ...