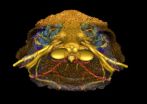
(Press-News.org) (TORONTO, Canada – Feb. 12, 2014) – Cancer researchers led by stem cell scientist Dr. John Dick have discovered a pre-leukemic stem cell that may be the first step in initiating disease and also the culprit that evades therapy and triggers relapse in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The research, published online today in Nature is a significant leap in understanding the steps that a normal cell has to go through as it turns into AML, says Dr. Dick, and sets the stage to advance personalized cancer medicine by potentially identifying individuals who might benefit from targeting the pre-leukemic stem cell. AML is an aggressive blood cancer that the new research shows starts in stem cells in the bone marrow. Dr. Dick, a Senior Scientist at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network (UHN), and Professor in the Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Toronto, pioneered the cancer stem cell field by first identifying leukemia stem cells (1994) and colon cancer stem cells (2007).
"Our discovery lays the groundwork to detect and target the pre-leukemic stem cell and thereby potentially stop the disease at a very early stage when it may be more amenable to treatment," says Dr. Dick, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Stem Cell Biology and is also Director of the Cancer Stem Cell Program at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR).
VIDEO: Dr. Dick talks about the research at: http://ow.ly/tvFL7.
"Now we have a potential tool for earlier diagnosis that may allow early intervention before the development of full AML. We can also monitor remission and initiate therapy to target the pre-leukemic stem cell to prevent relapse," he says.
The findings show that in about 25% of AML patients, a mutation in the gene DNMT3a causes pre-leukemic stem cells to develop that function like normal blood stem cells but grow abnormally. These cells survive chemotherapy and can be found in the bone marrow at remission, forming a reservoir of cells that may eventually acquire additional mutations, leading to relapse.
The discovery of pre-leukemic stem cells came out of a large Leukemia Disease Team that Dr. Dick assembled and included oncologists who collected samples for the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Biobank and genome scientists at the OICR who developed sophisticated targeted sequencing methodology. With this team, it was possible to carry out genomic analysis of more than 100 leukemia genes on many patient samples. The findings also capitalized on data from more than six years of experiments in Dr. Dick's lab involving growing human AML in special mice that do not reject human cells.
"By peering into the black box of how cancer develops during the months and years prior to when it is first diagnosed, we have demonstrated a unique finding. People tend to think relapse after remission means chemotherapy didn't kill all the cancer cells. Our study suggests that in some cases the chemotherapy does, in fact, eradicate AML; what it does not touch are the pre-leukemic stem cells that can trigger another round of AML development and ultimately disease relapse," says Dr. Dick, who anticipates the findings will spawn accelerated drug development to specifically target DNMT3a.
These findings should also provide impetus for researchers to look for pre-cancerous cells in AML patients with other mutations and even in non-blood cancers.
Dr. Dick is also renowned for isolating a human blood stem cell in its purest form (2011) – as a single stem cell capable of regenerating the entire blood system. He is a Senior Scientist at UHN's McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine and co-leader of a Cancer Stem Cell Consortium (CSCC)-funded research project HALT (Highly Active Anti-Leukemia Stem Cell Therapy), which is a partnership between CSCC and the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
For more than 20 years, Dr. Dick's research has focused on understanding the cellular processes that maintain tumour growth by investigating the complexities and interplay among genetic and non-genetic determinants of cancer. His research follows on the original 1961 discovery of the blood stem cell by Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (formerly Ontario Cancer Institute) scientists Dr. James Till and the late Dr. Ernest McCulloch, which formed the basis of all current stem cell research.
INFORMATION:
The research published today was supported by the Cancer Stem Cell Consortium (HALT Leukemia Disease Team) with funding from the Government of Canada through Genome Canada (GC) and the Ontario Genomics Institute (OGI), and through the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), CIHR, Canadian Cancer Society, Terry Fox Foundation, GC through the OGI, OICR with funding from the government of Ontario, a Canada Research Chair, the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care, and The Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation. The McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine with funding made available through the Gentle Ben Charity, CIHR's partnership with the Aplastic Anemia and Myelodysplasia Association of Canada, and the Swedish Research Council supported postdoctoral fellows on the research team.
About Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network
The Princess Margaret Cancer Centre has achieved an international reputation as a global leader in the fight against cancer and delivering personalized cancer medicine. The Princess Margaret, one of the top five international cancer research centres, is a member of the University Health Network, which also includes Toronto General Hospital, Toronto Western Hospital and Toronto Rehabilitation Institute. All are research hospitals affiliated with the University of Toronto. For more information, go to http://www.theprincessmargaret.ca or http://www.uhn.ca .
Media contact:
Jane Finlayson
Senior Public Affairs Advisor
Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
University Health Network
416-946-2846
jane.finlayson@uhn.ca
Cancer researchers discover pre-leukemic stem cell at root of AML, relapse
2014-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jaw dropping: scientists reveal how vertebrates came to have a face
2014-02-13
A team of French and Swedish researchers have presented new fossil evidence for the origin of one of the most important and emotionally significant parts of our anatomy: the face. Using micron resolution X-ray imaging, they show how a series of fossils, with a 410 million year old armoured fish called Romundina at its centre, documents the step-by-step assembly of the face during the evolutionary transition from jawless to jawed vertebrates. The research is published in Nature on 12 February 2014.
Vertebrates, or backboned animals, come in two basic models: jawless and ...
Advanced techniques yield new insights into ribosome self-assembly
2014-02-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Ribosomes, the cellular machines that build proteins, are themselves made up of dozens of proteins and a few looping strands of RNA. A new study, reported in the journal Nature, offers new clues about how the ribosome, the master assembler of proteins, also assembles itself.
"The ribosome has more than 50 different parts – it has the complexity of a sewing machine in terms of the number of parts," said University of Illinois physics professor Taekjip Ha, who led the research with U. of I. chemistry professor Zaida Luthey-Schulten and Johns Hopkins University ...
Teledermatology app system offers efficiencies, reliably prioritizes inpatient consults
2014-02-13
PHILADELPHIA - A new Penn Medicine study shows that remote consultations from dermatologists using a secure smart phone app are reliable at prioritizing care for hospitalized patients with skin conditions. Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania report in JAMA Dermatology that this teledermatology process is reliable and can help deliver care more efficiently in busy academic hospitals and potentially in community hospital settings.
A national shortage and uneven distribution of dermatologists in the United States has caused scheduling ...
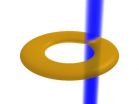
Stirring-up atomtronics in a quantum circuit
2014-02-13
VIDEO:
This is an animation showing a laser beam stirring a ring shaped quantum gas.
Click here for more information.
Atomtronics is an emerging technology whereby physicists use ensembles of atoms to build analogs to electronic circuit elements. Modern electronics relies on utilizing the charge properties of the electron. Using lasers and magnetic fields, atomic systems can be engineered to have behavior analogous to that of electrons, making them an exciting platform for studying ...
Ancient settlements and modern cities follow same rules of development, says CU-Boulder
2014-02-13
Recently derived equations that describe development patterns in modern urban areas appear to work equally well to describe ancient cities settled thousands of years ago, according to a new study led by a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder.
"This study suggests that there is a level at which every human society is actually very similar," said Scott Ortman, assistant professor of anthropology at CU-Boulder and lead author of the study published in the journal PLOS ONE. "This awareness helps break down the barriers between the past and present and allows us ...
America's only Clovis skeleton had its genome mapped
2014-02-13
They lived in America about 13,000 years ago where they hunted mammoth, mastodons and giant bison with big spears. The Clovis people were not the first humans in America, but they represent the first humans with a wide expansion on the North American continent – until the culture mysteriously disappeared only a few hundred years after its origin. Who the Clovis people were and which present day humans they are related to has been discussed intensely and the issue has a key role in the discussion about how the Americas were peopled. Today there exists only one human skeleton ...
New target for psoriasis treatment discovered
2014-02-13
Researchers at King's College London have identified a new gene (PIM1), which could be an effective target for innovative treatments and therapies for the human autoimmune disease, psoriasis.
Psoriasis affects around 2 per cent of people in the UK and causes dry, red lesions on the skin which can become sore or itchy and can have significant impact on the sufferer's quality of life.
It is thought that psoriasis is caused by a problem with the body's immune system in which new skin cells are created too rapidly, causing a build up of flaky patches on the skin's surface. ...
Two parents with Alzheimer's disease? Disease may show up decades early on brain scans
2014-02-13
MINNEAPOLIS – People who are dementia-free but have two parents with Alzheimer's disease may show signs of the disease on brain scans decades before symptoms appear, according to a new study published in the February 12, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Studies show that by the time people come in for a diagnosis, there may be a large amount of irreversible brain damage already present," said study author Lisa Mosconi, PhD, with the New York University School of Medicine in New York. "This is why it is ideal ...
Solving an evolutionary puzzle
2014-02-13
For four decades, waste from nearby manufacturing plants flowed into the waters of New Bedford Harbor—an 18,000-acre estuary and busy seaport. The harbor, which is contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and heavy metals, is one of the EPA's largest Superfund cleanup sites.
It's also the site of an evolutionary puzzle that researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and their colleagues have been working to solve.
Atlantic killifish—common estuarine fishes about three inches long—are not only tolerating the toxic conditions in the harbor, they ...
NIF experiments show initial gain in fusion fuel
2014-02-13
LIVERMORE, Calif. – Ignition – the process of releasing fusion energy equal to or greater than the amount of energy used to confine the fuel – has long been considered the "holy grail" of inertial confinement fusion science. A key step along the path to ignition is to have "fuel gains" greater than unity, where the energy generated through fusion reactions exceeds the amount of energy deposited into the fusion fuel.
Though ignition remains the ultimate goal, the milestone of achieving fuel gains greater than 1 has been reached for the first time ever on any facility. ...