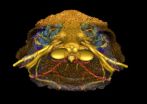
(Press-News.org) Scientists have demonstrated how new satellite technology can be used to count whales, and ultimately estimate their population size. Using Very High Resolution (VHR) satellite imagery, alongside image processing software, they were able to automatically detect and count whales breeding in part of the Golfo Nuevo, Peninsula Valdes in Argentina.
The new method, published this week in the journal PLoS ONE, could revolutionise how whale population size is estimated. Marine mammals are extremely difficult to count on a large scale and traditional methods, such as counting from platforms or land, can be costly and inefficient.
Lead author Peter Fretwell from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), which is funded by the UK's Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), explains;
"This is a proof of concept study that proves whales can be identified and counted by satellite. Whale populations have always been difficult to assess; traditional means of counting them are localized, expensive and lack accuracy. The ability to count whales automatically, over large areas in a cost effective way will be of great benefit to conservation efforts for this and potentially other whale species."
Previously, satellites have provided limited success in counting whales but their accuracy has improved in recent years.
The BAS team used a single WorldView2 satellite image of a bay where southern right whales gather to calve and mate. Driven to near extinction, these whales have made a limited recovery following the end of whaling. In recent years, however, many deaths have been seen on their nursery grounds at Peninsula Valdes. Their population size is now unknown but with this sharp increase in calf mortality, estimates are needed.
The enclosed bays in this region contain calm, shallow waters which increase the chance of spotting the whales from space. Three main criteria were used to identify whales: objects visible in the image should be the right size and shape; they should be in the right place (where whales would be expected to be) and there should be no (or few) other types of objects that could be mistaken as whales.
Whales in the image were manually identified and counted, finding 55 probable whales, 23 possible whales and 13 sub-surface features. Several automated methods where then tested against these numbers. A 'thresholding' of the Coastal Band of the WorldView2 image gave the greatest accuracy. This part of the image uses light from the far blue end of the spectrum which penetrates the water column deeper and allows us to see more whales. This technique found 89% of probable whales identified in the manual count. This is a semi automated technique that needs some user input to identify the best threshold.
Future satellite platforms will provide even high quality imagery and Worldview3 is planned to be launched this year. This will allow for greater confidence in identifying whales and differentiating mother and calf pairs. Such technological advancements may also allow scientists to apply this method to other whale species.
INFORMATION:
Issued by the British Antarctic Survey Press Office.
Contact: Rachel Law, Tel: +44 (0)1223 221437; email: raclaw@bas.ac.uk
Satellite images and photos of whales are available from the BAS Press Office.
Peter Fretwell, British Antarctic Survey, Tel: +44 (0) 1223 22145; mobile: +44 (0) 7903 208132 email: ptf@bas.ac.uk
Notes for editors
The paper: Whales from space: counting southern right whales by satellite by Peter T Fretwell, Iain J Staniland and Jaume Forcada is published in PLOS ONE on Wednesday 12 February 2014. View the paper at http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088655
Images are available on request.
Southern right whales
The southern right whale (Eubalaena australis) is a baleen whale with a circumpolar distribution in the Southern Hemisphere. An adult female can reach a maximum size of 15m and can weigh up to 47 tonnes. Southern right whales were hunted extensively from the 17th through to the 20th century, causing their numbers to drop from an estimated 55,000-70,000 to around 300 by the 1920s. The population appears to have grown strongly since the cessation of whaling but is still below 15% of historical estimates.
http://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/worldview-2.html
British Antarctic Survey (BAS), an institute of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), delivers and enables world-leading interdisciplinary research in the Polar Regions. Its skilled science and support staff based in Cambridge, Antarctica and the Arctic, work together to deliver research that uses the Polar Regions to advance our understanding of Earth as a sustainable planet. Through its extensive logistic capability and know-how BAS facilitates access for the British and international science community to the UK polar research operation. Numerous national and international collaborations, combined with an excellent infrastructure help sustain a world leading position for the UK in Antarctic affairs. For more information visit http://www.antarctica.ac.uk.
Satellites help spot whales
Scientists using satellites to identify whales
2014-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain process takes paper shape
2014-02-13
A paper-based device that mimics the electrochemical signalling in the human brain has been created by a group of researchers from China.
The thin-film transistor (TFT) has been designed to replicate the junction between two neurons, known as a biological synapse, and could become a key component in the development of artificial neural networks, which could be utilised in a range of fields from robotics to computer processing.
The TFT, which has been presented today, 13 February, in IOP Publishing's journal Nanotechnology, is the latest device to be fabricated on paper, ...
Doctors are missing chance to diagnose COPD in up to 85 percent of cases, study finds
2014-02-13
A retrospective, 20-year study led by researchers at Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry shows that in up to 85 per cent of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) the underlying disease was being overlooked. Missed opportunities occur commonly in both primary and secondary care. The paper demonstrates the pointers to help GP to come to a earlier diagnosis. The findings are published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine today, Thursday 13th February 2014.
The study encompassed almost 39,000 patients and showed that, in the ...
Cancer researchers discover pre-leukemic stem cell at root of AML, relapse
2014-02-13
(TORONTO, Canada – Feb. 12, 2014) – Cancer researchers led by stem cell scientist Dr. John Dick have discovered a pre-leukemic stem cell that may be the first step in initiating disease and also the culprit that evades therapy and triggers relapse in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The research, published online today in Nature is a significant leap in understanding the steps that a normal cell has to go through as it turns into AML, says Dr. Dick, and sets the stage to advance personalized cancer medicine by potentially identifying individuals who might benefit ...
Jaw dropping: scientists reveal how vertebrates came to have a face
2014-02-13
A team of French and Swedish researchers have presented new fossil evidence for the origin of one of the most important and emotionally significant parts of our anatomy: the face. Using micron resolution X-ray imaging, they show how a series of fossils, with a 410 million year old armoured fish called Romundina at its centre, documents the step-by-step assembly of the face during the evolutionary transition from jawless to jawed vertebrates. The research is published in Nature on 12 February 2014.
Vertebrates, or backboned animals, come in two basic models: jawless and ...
Advanced techniques yield new insights into ribosome self-assembly
2014-02-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Ribosomes, the cellular machines that build proteins, are themselves made up of dozens of proteins and a few looping strands of RNA. A new study, reported in the journal Nature, offers new clues about how the ribosome, the master assembler of proteins, also assembles itself.
"The ribosome has more than 50 different parts – it has the complexity of a sewing machine in terms of the number of parts," said University of Illinois physics professor Taekjip Ha, who led the research with U. of I. chemistry professor Zaida Luthey-Schulten and Johns Hopkins University ...
Teledermatology app system offers efficiencies, reliably prioritizes inpatient consults
2014-02-13
PHILADELPHIA - A new Penn Medicine study shows that remote consultations from dermatologists using a secure smart phone app are reliable at prioritizing care for hospitalized patients with skin conditions. Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania report in JAMA Dermatology that this teledermatology process is reliable and can help deliver care more efficiently in busy academic hospitals and potentially in community hospital settings.
A national shortage and uneven distribution of dermatologists in the United States has caused scheduling ...
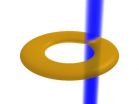
Stirring-up atomtronics in a quantum circuit
2014-02-13
VIDEO:
This is an animation showing a laser beam stirring a ring shaped quantum gas.
Click here for more information.
Atomtronics is an emerging technology whereby physicists use ensembles of atoms to build analogs to electronic circuit elements. Modern electronics relies on utilizing the charge properties of the electron. Using lasers and magnetic fields, atomic systems can be engineered to have behavior analogous to that of electrons, making them an exciting platform for studying ...
Ancient settlements and modern cities follow same rules of development, says CU-Boulder
2014-02-13
Recently derived equations that describe development patterns in modern urban areas appear to work equally well to describe ancient cities settled thousands of years ago, according to a new study led by a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder.
"This study suggests that there is a level at which every human society is actually very similar," said Scott Ortman, assistant professor of anthropology at CU-Boulder and lead author of the study published in the journal PLOS ONE. "This awareness helps break down the barriers between the past and present and allows us ...
America's only Clovis skeleton had its genome mapped
2014-02-13
They lived in America about 13,000 years ago where they hunted mammoth, mastodons and giant bison with big spears. The Clovis people were not the first humans in America, but they represent the first humans with a wide expansion on the North American continent – until the culture mysteriously disappeared only a few hundred years after its origin. Who the Clovis people were and which present day humans they are related to has been discussed intensely and the issue has a key role in the discussion about how the Americas were peopled. Today there exists only one human skeleton ...
New target for psoriasis treatment discovered
2014-02-13
Researchers at King's College London have identified a new gene (PIM1), which could be an effective target for innovative treatments and therapies for the human autoimmune disease, psoriasis.
Psoriasis affects around 2 per cent of people in the UK and causes dry, red lesions on the skin which can become sore or itchy and can have significant impact on the sufferer's quality of life.
It is thought that psoriasis is caused by a problem with the body's immune system in which new skin cells are created too rapidly, causing a build up of flaky patches on the skin's surface. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Satellites help spot whalesScientists using satellites to identify whales