(Press-News.org) Slight modifications in their genome sequences play a crucial role in the conversion of pluripotent stem cells into various differentiated cell types. A team at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich has now identified the factor responsible for one class of modification.
Every cell contains stored hereditary information, encoded in the sequence of nucleobases that make up its DNA. However, in any given cell type, only a fraction of this information is actually used. Which genes are activated and which are turned off is in part determined by a second tier of information which is superimposed on the nucleotide sequences that provide the blueprints for protein synthesis. This so-called epigenetic level of control is based on the localized, and in principle reversible, attachment of simple chemical tags to specific nucleotides in the genome. This system plays a major role in the regulation of gene activity, and enables the selective expression of different functions in differentiated cell types.
This explains why such DNA modifications play a major role in the differentiation of stem cells. "Several unusual nucleobases have been found in the genomes of stem cells, which are produced by targeted chemical modification of the known building blocks of DNA. These 'atypical' bases are thought to be important in determining what types of differentiated cells can be derived from a given stem cell line," says Professor Thomas Carell from the Department of Chemistry at LMU. All of the unconventional bases so far discovered are derived from the same standard base – cytosine. Furthermore, Carell and his team have shown in earlier work that so-called Tet enzymes are always involved in their synthesis.
Base oxidation regulates gene activity
In cooperation with colleagues at LMU, as well as researchers based in Berlin, Basel and Utrecht, Carell and his group have now shown, for the first time, that a standard base other than cytosine is also modified in embryonic stem cells of mice. Moreover, Tet is at work here too. "During the development of specialized tissues from stem cells, enzymes belonging to the Tet family also oxidize the thymidine base, as we have now shown with the aid of highly sensitive analytical methods based on mass spectrometry. The product of the reaction, hydroxymethyluracil, was previously – and as it now turns out, erroneously – thought to be synthesized by a different pathway," Carell explains.
The precise function of hydroxymethyluracil remains unclear. However, using an innovative method for the identification of factors capable of binding to and "reading" the chemical tags that characterize unconventional DNA bases, Carell and colleagues have shown that stem cells contain specific proteins that recognize hydroxymethyluracil, and could therefore contribute to the regulation of gene activity in these cells. "We hope that these new insights will make it possible to modulate the differentiation of stem cells – causing them to generate cells of a particular type," says Carell. "It would be wonderful if we were one day able to generate whole organs starting from differentiated cells produced, on demand, by stem cell populations."
INFORMATION: END
Stem-cell research: A new genetic switching element
2014-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low-carb vegan diet may reduce heart disease risk and weight
2014-05-22
TORONTO, May 22, 2014 -- Researchers at St. Michael's Hospital have shown for the first time that, in addition to weight loss, a specific low-carbohydrate diet may also reduce the risk of heart disease by 10 per cent over 10 years.
The diet, often called Eco-Atkins, is a low-carbohydrate vegan diet. Many low-carbohydrate diets have been proven to improve weight loss but most emphasize eating animal proteins and fats, which may raise cholesterol. Diets that are high in vegetable proteins and oils may reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering "bad cholesterol."
"We ...
Medical students may benefit from social media guidance
2014-05-22
Medical students use social media extensively, but medical schools may need to offer more guidance in potential pitfalls, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers.
"We assessed how medical students engage with social media platforms like Facebook and found that they have a pretty sophisticated understanding of its risks and benefits," said Daniel R. George, assistant professor of humanities. He and Dr. Michael J. Green, professor of humanities, conducted two studies that report findings from a survey of 2,109 medical students nationwide.
In the first ...
Screening for autism: There's an app for that
2014-05-22
DURHAM, N.C. -- Most schools across the United States provide simple vision tests to their students--not to prescribe glasses, but to identify potential problems and recommend a trip to the optometrist. Researchers are now on the cusp of providing the same kind of service for autism.
Researchers at Duke University have developed software that tracks and records infants' activity during videotaped autism screening tests. Their results show that the program is as good at spotting behavioral markers of autism as experts giving the test themselves, and better than non-expert ...
How the gut feeling shapes fear
2014-05-22
An unlit, deserted car park at night, footsteps in the gloom. The heart beats faster and the stomach ties itself in knots. We often feel threatening situations in our stomachs. While the brain has long been viewed as the centre of all emotions, researchers are increasingly trying to get to the bottom of this proverbial gut instinct.
It is not only the brain that controls processes in our abdominal cavity; our stomach also sends signals back to the brain. At the heart of this dialogue between the brain and abdomen is the vagus nerve, which transmits signals in both directions ...
Radiofrequency ablation and complete endoscopic resection equally effective for dysplastic Barrett's esophagus
2014-05-22
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. – May 21, 2014 – According to a new systematic review article, radiofrequency ablation and complete endoscopic resection are equally effective in the short-term treatment of dysplastic Barrett's esophagus, but adverse event rates are higher with complete endoscopic resection. The article comparing the two treatments appears in the May issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus ...
Molecule acts as umpire to make tough life-or-death calls
2014-05-22
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 20, 2014) Researchers have demonstrated that an enzyme required for animal survival after birth functions like an umpire, making the tough calls required for a balanced response to signals that determine if cells live or die. St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists led the study, which was published online and appears in the May 22 edition of the scientific journal Cell.
The work involved the enzyme receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1). While RIPK1 is known to be involved in many vital cell processes, this study shows that its pivotal ...
Aggressive behavior observed after alcohol-related priming
2014-05-22
May 22, 2014-- Researchers from California State University, Long Beach, the University of Kent and the University of Missouri collaborated on a study to test whether briefly exposing participants to alcohol-related terms increases aggressive behavior. It has been well documented by previous research that the consumption of alcohol is directly linked to an increase in aggression and other behavioral extremes. But can simply seeing alcohol-related words have a similar effect on aggressive behavior?
Designing the experiment
The study, published in the journal Personality ...
First broadband wireless connection ... to the moon?!
2014-05-22
WASHINGTON, May 22, 2014—If future generations were to live and work on the moon or on a distant asteroid, they would probably want a broadband connection to communicate with home bases back on Earth. They may even want to watch their favorite Earth-based TV show. That may now be possible thanks to a team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory who, working with NASA last fall, demonstrated for the first time that a data communication technology exists that can provide space dwellers with the connectivity we all enjoy here ...
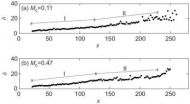
On quantification of the growth of compressible mixing layer
2014-05-22
CML has been a research topic for more than five decades, due to its wide applications in propulsion design. Mixing in CML is controlled by the compressibility effects of velocity and density variations over the mixing layer, and quantified by the growth rate of CML. However, the lack of understanding of various definitions of mixing thicknesses has yielded scatter in analyzing experimental data. Prof. SHE ZhenSu and his colleagues at the State Key Laboratory for Turbulence and Complex Systems, Peking University investigated the growth of compressible mixing layer by introducing ...
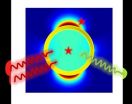
Nanoshell-emitters hybrid nanoobject was proposed as promising 2-photon fluorescence probe
2014-05-22
Two-photon excitation fluorescence is growing in popularity in the bioimaging field but is limited by fluorophores' extremely low two-photon absorption cross-section. The researcher Dr. Guowei Lu and co-workers from State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Department of Physics, Peking University, are endeavoring to develop efficient fluorescent probes with improved two-photon fluorescence (TPF) performance. They theoretically present a promising bright probe using gold nanoshell to improve the TPF performances of fluorescent emitters. Their work, entitled "Plasmonic-Enhanced ...