(Press-News.org) Imagine feeling a slimy jellyfish, a prickly cactus or map directions on your iPad mini Retina display, because that's where tactile technology is headed. But you'll need more than just an index finger to feel your way around.
New research at UC Berkeley has found that people are better and faster at navigating tactile technology when using both hands and several fingers. Moreover, blind people in the study outmaneuvered their sighted counterparts – especially when using both hands and several fingers – possibly because they've developed superior cognitive strategies for finding their way around.
Bottom line: Two hands are better than one in the brave new world of tactile or "haptic" technology, and the visually impaired can lead the way.
"Most sighted people will explore these types of displays with a single finger. But our research shows that this is a bad decision. No matter what the task, people perform better using multiple fingers and hands," said Valerie Morash, a doctoral student in psychology at UC Berkeley, and lead author of the study just published in the online issue of the journal, Perception.
"We can learn from blind people how to effectively use multiple fingers, and then teach these strategies to sighted individuals who have recently lost vision or are using tactile displays in high-stakes applications like controlling surgical robots," she added.
For decades, scientists have studied how receptors on the fingertips relay information to the brain. Now, researchers at Disney and other media companies are implementing more tactile interfaces, which use vibrations, and electrostatic or magnetic feedback for users to find their way around, or experience how something feels.
In this latest study, Morash and fellow researchers at UC Berkeley and the Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute in San Francisco tested 14 blind adults and 14 blindfolded sighted adults on several tasks using a tactile map. Using various hand and finger combinations, they were tasked with such challenges as finding a landmark or figuring out if a road looped around.
Overall, both blind and sighted participants performed better when using both hands and several fingers, although blind participants were, on average, 50 percent faster at completing the tasks, and even faster when they used both hands and all their fingers.
"As we move forward with integrating tactile feedback into displays, these technologies absolutely need to support multiple fingers," Morash said. "This will promote the best tactile performance in applications such as the remote control of robotics used in space and high-risk situations, among other things."
INFORMATION:
Blind lead the way in brave new world of tactile technology
UC Berkeley study finds all hands, fingers needed to feel one's way around
2014-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Engaging parents, community to map student success in South King County
2014-07-01
If we had a road map to what parental involvement in schools should be, what would it look like? Would it be a straight line, or a complicated maze of cross streets going in every direction?
University of Washington researchers studied The Road Map Project, a collaborative effort to dramatically improve student achievement in seven school districts in South Seattle and South King County. In their report after a yearlong study of the initiative, they found that students were most successful when schools and communities found creative and culturally responsive ways of engaging ...
For cancer patients, sugar-coated cells are deadly
2014-07-01
ITHACA, N.Y. – Every living cell's surface has a protein-embedded membrane that's covered in polysaccharide chains – a literal sugar coating. A new study by a Cornell University researcher found this coating is especially thick and pronounced on cancer cells and is a crucial determinant of the cell's survival.
Consisting of long, sugar-decorated molecules called glycoproteins, the coating causes physical changes in the cell membrane that make the cell better able to thrive – leading to a more lethal cancer.
Matthew Paszek, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular ...
Clemson scientists: Kudzu can release soil carbon, accelerate global warming
2014-07-01
CLEMSON, S.C. — Clemson University scientists are shedding new light on how invasion by exotic plant species affects the ability of soil to store greenhouse gases. The research could have far-reaching implications for how we manage agricultural land and native ecosystems.
In a paper published in the scientific journal New Phytologist, plant ecologist Nishanth Tharayil and graduate student Mioko Tamura show that invasive plants can accelerate the greenhouse effect by releasing carbon stored in soil into the atmosphere.
Since soil stores more carbon than both the atmosphere ...
Cellular gates for sodium and calcium controlled by common element of ancient origin
2014-07-01
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have spotted a strong family trait in two distant relatives: The channels that permit entry of sodium and calcium ions into cells turn out to share similar means for regulating ion intake, they say. Both types of channels are critical to life. Having the right concentrations of sodium and calcium ions in cells enables healthy brain communication, heart contraction and many other processes. The new evidence is likely to aid development of drugs for channel-linked diseases ranging from epilepsy to heart ailments to muscle weakness.
"This discovery ...
Mayo Clinic: Proton therapy has advantages over IMRT for advanced head and neck cancers
2014-07-01
Rochester, Minn. -- A new study by radiation oncologists at Mayo Clinic comparing the world's literature on outcomes of proton beam therapy in the treatment of a variety of advanced head and neck cancers of the skull base compared to intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) has found that proton beam therapy significantly improved disease free survival and tumor control when compared to IMRT. The results appear in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the clinical outcomes of patients treated with proton therapy ...
Video games could provide venue for exploring sustainability concepts
2014-07-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Could playing video games help people understand and address global sustainability issues such as pollution, drought or climate change? At least two researchers believe so, outlining their argument in a concept paper published in the journal First Monday.
Video games have the potential to educate the public and encourage development of creative solutions to social, economic and environmental problems, said Oregon State University's Shawna Kelly, one of the two authors of the article.
"Video games encourage creative and strategic thinking, which could ...
Studies: Addiction starts with an overcorrection in the brain
2014-07-01
The National Institutes of Health has turned to neuroscientists at the nation's most "Stone Cold Sober" university for help finding ways to treat drug and alcohol addiction.
Brigham Young University professor Scott Steffensen and his collaborators have published three new scientific papers that detail the brain mechanisms involved with addictive substances. And the NIH thinks Steffensen's on the right track, as evidenced by a $2-million grant that will help fund projects in his BYU lab for the next five years.
"Addiction is a brain disease that could be treated like ...
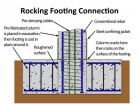
New bridge design improves earthquake resistance, reduces damage and speeds construction
2014-07-01
SEATTLE, Wash. - Researchers have developed a new design for the framework of columns and beams that support bridges, called "bents," to improve performance for better resistance to earthquakes, less damage and faster on-site construction.
The faster construction is achieved by pre-fabricating the columns and beams off-site and shipping them to the site, where they are erected and connected quickly.
"The design of reinforced concrete bridges in seismic regions has changed little since the mid-1970s," said John Stanton, a professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental ...
Chinese herbal extract may help kill off pancreatic cancer cells
2014-07-01
Bethesda, Md. (July 1, 2014) — A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer—the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the U.S.—can be devastating. Due in part to aggressive cell replication and tumor growth, pancreatic cancer progresses quickly and has a low five-year survival rate (less than 5 percent).
GRP78, a protein that protects cells from dying, is more abundant in cancer cells and tissue than in normal organs and is thought to play a role in helping pancreatic cancer cells survive and thrive. Researchers at the University of Minnesota have found triptolide, an extract ...
Tags reveal Chilean devil rays are among ocean's deepest divers
2014-07-01
Thought to dwell mostly near the ocean's surface, Chilean devil rays (Mobula tarapacana) are most often seen gliding through shallow, warm waters. But a new study by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and international colleagues reveals that these large and majestic creatures are actually among the deepest-diving ocean animals.
"So little is known about these rays," said Simon Thorrold, a biologist at WHOI and one of the authors of the paper, published July 1, 2014, in the journal Nature Communications. "We thought they probably travelled long ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Blind lead the way in brave new world of tactile technologyUC Berkeley study finds all hands, fingers needed to feel one's way around