(Press-News.org) For bees and the flowers they pollinate, a compatible tongue length is essential to a successful relationship. Some bees and plants are very closely matched, with bee tongue sized to the flower depth. Other bee species are generalists, flitting among flower species to drink nectar and collect pollen from a diverse variety of plants. Data on tongue lengths can help ecologists understand and predict the behavior, resilience and invasiveness of bee populations.
But bee tongues are hard to measure. The scarcity of reliable lingual datasets has held back research, so Ignasi Bartomeus of the Estación Biológica de Doñana (EBD-CSIC) in Sevilla, Spain, and his colleagues at Rutgers University (New Brunswick, N.J.) looked for a more easily measured proxy, like body size. Bee tongues are proportional to body size, but modulated by family adaptations—bee families typically have characteristic tongue shapes and proportions. The research group came up with an equation to predict tongue length from a combination of body size and taxonomic relationships.
Bartomeus will explain the equation and the usefulness of tongue length data for ecology at the 99th Annual Meeting of the Ecological Society of America in Sacramento, Cal., this August during the "Pollination I" oral session on Thursday afternoon, August 14. The meeting lasts five days and draws roughly 3,500 environmental scientists from around the world.
A bee collects pollen on its body as it laps sugar-rich nectar from within the cupped interior of the flower's petals, and carries the flower's genetic heritage away with it to fertilize the next flower of the same species that it visits. In most species, the bee's tongue is guarded by a long, two-sided, beak of a sheath, which folds under the body when the bee flies.
Perched at the mouth of a flower, the bee unfolds the beaky maxilla and extends its tongue into the corolla of the flower, dipping and retracting it to lap up the nectar. If its tongue is too short to reach the nectar, the bee has a problem. Long flowers like honeysuckle or columbine are too deep for short-tongued bees.
But longer isn't always better; long tongues are harder to wrangle into short flowers. Long-tongued bees are often specialists, favoring a few deep-throated flower species. In the bumblebee-sparse southern tip of Argentina, for example, Bombus dahlbomii, the native long-tongued giant of Patagonia, has lost ground to a new bumblebee from Europe, the short-tongued generalist Bombus terrestris, imported to help pollinate tomatoes. Although disease has likely played a role in the retreat of the long-tongued giant, B. terrestris also appears to be out-competing an earlier European immigrant, the long-tongued Bombus ruderatus.
Because specialists depend on just a few flowers, they can be more vulnerable to change. Tongue length can thus be intertwined with a species' risk of extinction, as well as specialization.
INFORMATION:
Presentation
Contributed talk 122-4 - The allometry of bee tongue length and its uses in ecology
Thursday, August 14, 2014: 2:30 PM
Room 315, Sacramento Convention Center
Speaker
Ignasi Bartomeus, Estación Biológica de Doñana (EBD-CSIC), Sevilla, Spain
nacho.bartomeus@gmail.com
Session:
Contributed talks 102: Pollination I.
Thursday, August 14, 2014: 1:30 PM-5:00 PM. Room 315.
Additional reference
Carolina L Morales, Marina P Arbetman, Sydney A Cameron, and Marcelo A Aizen (2013). Rapid ecological replacement of a native bumble bee by invasive species. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment11: 529. http://dx.doi.org/10.1890/120321
Find more bees, butterflies, birds and other pollinators at ESA's 2014 Annual Meeting, August 10-15, 2014, at the Sacramento Convention Center in Sacramento, Cal. listed on the meeting media topics page.
The Ecological Society of America is the world's largest community of professional ecologists and a trusted source of ecological knowledge. ESA is committed to advancing the understanding of life on Earth. The 10,000 member Society publishes five journals, convenes an annual scientific conference, and broadly shares ecological information through policy and media outreach and education initiatives. Visit the ESA website at http://www.esa.org.
For bees and flowers, tongue size matters
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds why some firms are 'named and shamed' by activists
2014-07-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study of the anti-sweatshop campaigns of the 1990s reveals which companies are most likely to become targets of anti-corporate activists.
Researchers found that companies tended to attract the attention of labor activists if they were large, had prominent brand images, or had good corporate reputations. When combined, these factors were especially important.
"Companies that had all of these characteristics were nearly guaranteed to be a target of activism," said Tim Bartley, lead author of the study and associate professor of sociology at The ...
Fundamental chemistry findings could help extend Moore's Law
2014-07-15
Over the years, computer chips have gotten smaller thanks to advances in materials science and manufacturing technologies. This march of progress, the doubling of transistors on a microprocessor roughly every two years, is called Moore's Law. But there's one component of the chip-making process in need of an overhaul if Moore's law is to continue: the chemical mixture called photoresist. Similar to film used in photography, photoresist, also just called resist, is used to lay down the patterns of ever-shrinking lines and features on a chip.
Now, in a bid to continue decreasing ...
Study: Body Dysmorphic Disorder patients have higher risk of personal and appearance-based rejection sensitivity
2014-07-15
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In a recent study, researchers at Rhode Island Hospital found that fear of being rejected because of one's appearance, as well as rejection sensitivity to general interpersonal situations, were significantly elevated in individuals with Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD). These fears, referred to as personal rejection sensitivity and appearance-based rejection sensitivity, can lead to diminished quality of life and poorer mental and overall health. BDD is a common, often severe, and under-recognized body image disorder that affects an estimated 1.7 to 2.4 ...
Prostate cancer in young men -- More frequent and more aggressive?
2014-07-15
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- The number of younger men diagnosed with prostate cancer has increased nearly 6-fold in the last 20 years, and the disease is more likely to be aggressive in these younger men, according to a new analysis from researchers at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Typically, prostate cancer occurs more frequently as men age into their 70s or 80s. Many prostate cancers are slow-growing and many older men diagnosed with early stage prostate cancer will end up dying from causes other than prostate cancer.
But, the researchers found, ...
Rollout strategy for diagnostic test in India may impact TB
2014-07-15
Xpert MTB/RIF, a recently implemented tuberculosis (TB) test, has the potential to control the TB epidemic in India, but only if the current, narrow, implementation strategy is replaced by a more ambitious one that is better funded, also includes the private sector, and better referral networks are developed between public and private sectors, according to new research published in this week's PLOS Medicine. The study by David Dowdy, from Johns Hopkins University, United States, and colleagues is a mathematical model that suggests alternative strategies that include engagement ...
Molecular 'eat now' signal makes cells devour dying neighbors
2014-07-15
A team of researchers has devised a Pac-Man-style power pellet that gets normally mild-mannered cells to gobble up their undesirable neighbors. The development may point the way to therapies that enlist patients' own cells to better fend off infection and even cancer, the researchers say.
A description of the work will be published July 15 in the journal Science Signaling.
"Our goal is to build artificial cells programmed to eat up dangerous junk in the body, which could be anything from bacteria to the amyloid-beta plaques that cause Alzheimer's to the body's own ...
Neurons, brain cancer cells require the same little-known protein for long-term survival
2014-07-15
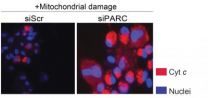
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the UNC School of Medicine have discovered that the protein PARC/CUL9 helps neurons and brain cancer cells override the biochemical mechanisms that lead to cell death in most other cells. In neurons, long-term survival allows for proper brain function as we age. In brain cancer cells, though, long-term survival contributes to tumor growth and the spread of the disease.
These results, published in the journal Science Signaling, not only identify a previously unknown mechanism used by neurons for their much-needed survival, but show that ...
Rollout strategy is key to battling India's TB epidemic, researchers find
2014-07-15
A new study led by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers suggests that getting patients in India quickly evaluated by the right doctors can be just as effective at curbing tuberculosis (TB) as a new, highly accurate screening test.
While ideally all suspected TB cases would be evaluated with the new test, it is primarily being used only on the highest-risk populations and only in public health clinics, partly because of its cost and the complexity of the nation's health care system. This slows diagnosis of a disease that must be caught early, the ...
New assay to spot fake malaria drugs could save thousands of lives
2014-07-15
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Chemists and students in science and engineering at Oregon State University have created a new type of chemical test, or assay, that's inexpensive, simple, and can tell whether or not one of the primary drugs being used to treat malaria is genuine – an enormous and deadly problem in the developing world.
The World Health Organization has estimated that about 200,000 lives a year may be lost due to the use of counterfeit anti-malarial drugs. When commercialized, the new OSU technology may be able to help address that problem by testing drugs for efficacy ...
3-D nanostructure could benefit nanoelectronics, gas storage
2014-07-15
A three-dimensional porous nanostructure would have a balance of strength, toughness and ability to transfer heat that could benefit nanoelectronics, gas storage and composite materials that perform multiple functions, according to engineers at Rice University.
The researchers made this prediction by using computer simulations to create a series of 3-D prototypes with boron nitride, a chemical compound made of boron and nitrogen atoms. Their findings were published online July 14 in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
The 3-D prototypes fuse one-dimensional boron nitride ...