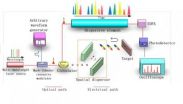
(Press-News.org) Ultrafast real-time optical imaging is an effective and important tool for studying dynamical events, such as shock waves, neural activity, laser surgery and chemical dynamics in living cells. Limited by the frame rate, conventional imaging system such as charge-coupled device (CCD) and complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) imaging device can not image fast dynamic processes. Last few years, serial time-encoded amplified microscopy (STEAM) technique based on space-frequency mapping combined with frequency-time mapping has been demonstrated as a completely new optical imaging modality. By employing a spatial disperser and a dispersive element, the spatial information is converted to a serial sequence in time and can be detected with a single-pixel photodiode and captured by a real-time oscilloscope. However, these methods need a large and high-cost pulsed laser; for this type of lasers, the spectral width is generally limited to about 10 nm which limits the measurement range. In addition, the pulse repetition rate is fixed to dozens of megahertz which in turn means that the imaging frame rate is also fixed to dozens of megahertz.
Recently, a new study entitled by "Serial time-encoded amplified microscopy for ultrafast imaging based on multi-wavelength laser" was published in the Chinese Science Bulletin. Professor LI Ming and his group from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences have figured out a STEAM system by employing a multi-wavelength laser to overcome those limitations. Based on mutually phase-uncorrelated lasing lines, the system avoids the need for a broadband coherent laser light source and the limitations of the measurement range and the imaging frame rate. Compared with a pulsed laser, the use of a multi-wavelength laser as the light source can relieve the cost of the STEAM system. The measurement range can be largely extended by simply increasing the number of wavelength. The frame rate is also reconfigurable by electrically tuning the gating rate. A frame rate up to 250 MHz is experimentally obtained in this work. With the development of photonic integrate circuits (PIC), the multi-wavelength laser source has the potential for integration on a photonic chip and thus the size and cost of the STEAM system could be largely reduced in the future.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
http://csb.scichina.com:8080/kxtbe/EN/abstract/abstract509126.shtml
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11434-014-0381-8
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 60 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.
http://www.scichina.com
Serial time-encoded amplified microscopy for ultrafast imaging based on multi-wavelength laser
2014-07-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
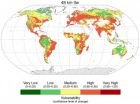
Study finds Europe's habitat and wildlife is vulnerable to climate change
2014-07-28
New research has identified areas of the Earth that are high priorities for conservation in the face of climate change.
Europe is particularly vulnerable, as it has the lowest fraction of its land area, only four per cent, of any continent in 'refugia' – areas of biological diversity that support many species where natural environmental conditions remain relatively constant during times of great environmental change. The refugia that do exist in Europe are mostly in Scandinavia and Scotland.
The biggest refugia are in the Amazon, the Congo basin, the boreal forests ...
Why do dogs smell each other's behinds? Chemical communication explained (video)
2014-07-28
WASHINGTON, July 28, 2014 — Here at Reactions, we ask the tough questions to get to the bottom of the biggest scientific quandaries. In that spirit, this week's video explains why dogs sniff each other's butts. It's a somewhat silly question with a surprisingly complex answer. This behavior is just one of many interesting forms of chemical communication in the animal kingdom. Find out more at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PZlJ8XfwiNg.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The ...
Refrigerator magnets
2014-07-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The magnets cluttering the face of your refrigerator may one day be used as cooling agents, according to a new theory formulated by MIT researchers.
The theory describes the motion of magnons — quasi-particles in magnets that are collective rotations of magnetic moments, or "spins." In addition to the magnetic moments, magnons also conduct heat; from their equations, the MIT researchers found that when exposed to a magnetic field gradient, magnons may be driven to move from one end of a magnet to another, carrying heat with them and producing a cooling ...
Children with disabilities benefit from classroom inclusion
2014-07-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The secret to boosting the language skills of preschoolers with disabilities may be to put them in classrooms with typically developing peers, a new study finds.
Researchers found that the average language skills of a child's classmates in the fall significantly predicted the child's language skills in the spring – especially for children with disabilities.
The results support inclusion policies in schools that aim to have students with disabilities in the same classrooms alongside their typically developing peers, said Laura Justice, co-author of the ...
Study shows new link between obesity in the young and the lowering of age of puberty
2014-07-28
A new link has been identified between obesity in childhood and the lowering of the age of puberty.
The research which discovered the link, carried out at Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, is published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The study focuses on a protein called sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), the regulation and role of which in children are poorly defined. SHBG binds to the sex hormones androgen and oestrogen. SHGB levels are initially high in childhood but decline significantly before puberty, in ...
Henry Ford study: Burnout impacts transplant surgeons
2014-07-28
VIDEO:
Despite saving thousands of lives yearly, nearly half of organ transplant surgeons report a low sense of personal accomplishment and 40 percent feel emotionally exhausted, according to a new national...
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – Despite saving thousands of lives yearly, nearly half of organ transplant surgeons report a low sense of personal accomplishment and 40% feel emotionally exhausted, according to a new national study on transplant surgeon burnout.
The ...
Many people never grow out of their growing pains
2014-07-28
Over the years, many adolescents have been forced to accept the diagnosis "growing pains" when they complained about pain in their knees. A new PhD study involving 3,000 adolescents has now shown that the knee pain often carries on:
"We can see from the study that one in three young people between the ages of 12 and 19 experience problems with pain in their knees. Seven percent of the adolescents experience daily knee pain in the front of the knee," says physiotherapist and PhD Michael Skovdal Rathleff from Aarhus University, and continues:
"More than half still have ...
Glow in space is evidence of a hot bubble in our galaxy
2014-07-28
VIDEO:
Dr. Massimilano Galeazzi discusses his work on a sounding rocket, sent into the atmosphere to search for answers about the universe.
Click here for more information.
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (July 27, 2014) — When we look up to the heavens on a clear night, we see an immense dark sky with uncountable stars. With a small telescope we can also see galaxies, nebulae, and the disks of planets. If you look at the sky with an X-ray detector, you would see many of these same familiar ...
Interfering with interferon
2014-07-28
Using the body's natural virus killers to prevent and treat HIV infection has been problematic until now because of the strong inflammatory response these molecules can arouse as they get rid of the invaders. Now, collaborative research conducted by scientists at the Weizmann Institute and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have demonstrated how suppressing the activity of these molecules – interferons – around the time of infection could have long-term implications for the course of the disease. Their research appeared in Nature.
Interferons, named for their ability ...
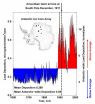
Industrial lead pollution beat explorers to the South Pole by 22 years and persists today
2014-07-28
RENO – Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen became the first man to reach the South Pole in December of 1911. More than 100 years later, an international team of scientists led by Joe McConnell of Nevada's Desert Research Institute (DRI) have proven that air pollution from industrial activities arrived long before.
Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, McConnell's team created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over the Earth's southernmost continent. ...