Researchers uncover how 'love hormone' regulates sexual behavior
2014-10-09
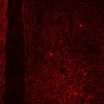
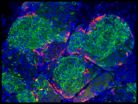
(Press-News.org) Oxytocin has been called the "love hormone" because it plays an important role in social behaviors, such as maternal care and pair bonding. In a study published by Cell Press on October 9th in the journal Cell, researchers uncover oxytocin-responsive brain cells that are necessary for female social interest in male mice during estrus—the sexually receptive phase of their cycle. These neurons, found in the prefrontal cortex, may play a role in other oxytocin-related social behaviors such as intimacy, love, or mother-child bonding.
"Our findings suggest that social interactions that stimulate oxytocin production will recruit this newly identified circuit to help coordinate the complex behavioral responses elicited by changing social situations in all mammals, including humans," says senior study author Nathaniel Heintz of The Rockefeller University. "Future investigation of the exact mechanisms responsible for activation of this interesting circuit may provide insights into autism spectrum disorder and other social behavioral disorders."
Oxytocin-responsive neurons are found in many brain structures, highlighting the importance of the hormone for a variety of social behaviors. But it is not clear which cells are targeted by oxytocin, or how the hormone affects neural circuits. One potential clue came when lead study author Miho Nakajima of The Rockefeller University discovered a population of neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex that express the oxytocin receptor. When the researchers disrupted the activity of these neurons, female mice lost interest in male mice during estrus and spent about the same amount of time with them as with a plastic Lego block. By contrast, these females retained a normal level of social interest in other females during estrus, and in male mice when not in estrus. Moreover, the social behavior of male mice was unaffected by the silencing of these neurons.
Taken together, the findings show that the new class of oxytocin-responsive neurons regulates an important aspect of female social behavior in mice. "Our work highlights the importance of the prefrontal cortex in social and sexual behaviors and suggests that this critical cell population may mediate other aspects of behavior in response to the elevated oxytocin levels that occur in a variety of different contexts," Heintz says.
INFORMATION:
Cell, Nakajima et al.: "Oxytocin modulates female sociosexual behavior through a specific class of prefrontal cortical interneurons."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-09
Oxytocin, the body's natural love potion, helps couples fall in love, makes mothers bond with their babies, and encourages teams to work together. Now new research at Rockefeller University reveals a mechanism by which this prosocial hormone has its effect on interactions between the sexes, at least in certain situations. The key, it turns out, is a newly discovered class of brain cells.
"By identifying a new population of neurons activated by oxytocin, we have uncovered one way this chemical signal influences interactions between male and female mice," says Nathaniel ...
2014-10-09
Researchers at Yale School of Medicine have uncovered a molecular process in the brain known to control eating that transforms white fat into brown fat. This process impacts how much energy we burn and how much weight we can lose. The results are published in the Oct. 9 issue of the journal Cell.
Obesity is a rising global epidemic. Excess fatty tissue is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, neurological disorders, and cancer. People become overweight and obese when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure, and excess calories ...
2014-10-09
Harvard stem cell researchers today announced that they have made a giant leap forward in the quest to find a truly effective treatment for type 1 diabetes, a condition that affects an estimated three million Americans at a cost of about $15 billion annually:
With human embryonic stem cells as a starting point, the scientists are for the first time able to produce, in the kind of massive quantities needed for cell transplantation and pharmaceutical purposes, human insulin-producing beta cells equivalent in most every way to normally functioning beta cells.
Doug Melton, ...
2014-10-09
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (October 9, 2014) – Within almost every human cell is a nucleus six microns in diameter—about one 300th of a human hair's width—that is filled with roughly three meters of DNA. As the instructions for all cell processes, the DNA must be accessible to the cell's transcription machinery yet be compressed tightly enough to fit inside the nucleus. Scientists have long theorized that the way DNA is packaged affects gene expression. Whitehead Institute researchers present the first evidence that DNA scaffolding is responsible for enhancing and ...
2014-10-09
BOSTON – The surprising discovery of a previously unidentified class of lipid molecules that enhance insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control offers a promising new avenue for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes.
The new findings, made by a team of scientists from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and the Salk Institute, are described in the October 9 online issue of the journal Cell.
"We were blown away to discover this completely new class of molecules," says senior author Barbara Kahn, MD, Vice Chair of the Department of Medicine ...
2014-10-09
Beer yeasts produce chemicals that mimic the aroma of fruits in order to attract flies that can transport the yeast cells to new niches, report scientists from VIB, KU Leuven and NERF in the reputed journal Cell Reports. Interestingly, these volatile compounds are also essential for the flavor of beverages such as beer and wine.
Kevin Verstrepen (VIB/KU Leuven): "The importance of yeast in beer brewing has long been underestimated. But recent research shows that the choice of a particular yeast strain or variety explains differences in taste between different beers and ...
2014-10-09
A key mechanism behind diabetes may start in the brain, with early signs of the disease detectable through rising levels of molecules not previously linked to insulin signaling, according to a study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai published today in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Past studies had found that levels of a key set of protein building blocks, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), are higher in obese and diabetic patient, and that this rise occurs many years before someone develops diabetes. Why and how BCAA breakdown may be ...
2014-10-09
NEW YORK, NY (October 9, 2014)—Using an innovative algorithm that analyzes gene regulatory and signaling networks, Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers have found that loss of a gene called KLHL9 is the driving force behind the most aggressive form of glioblastoma, the most common form of brain cancer. The CUMC team demonstrated in mice transplants that these tumors can be suppressed by reintroducing KLHL9 protein, offering a possible strategy for treating this lethal disease. The study was published today in the online issue of Cell.
The team used ...
2014-10-09
VIDEO:
Salk researchers explain how a new class of lipids may be tied to diabetes.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston have discovered a new class of molecules—produced in human and mouse fat—that protects against diabetes.
The researchers found that giving this new fat, or lipid, to mice with the equivalent of type 2 diabetes lowered their elevated blood sugar, ...
2014-10-09
New Rochelle, NY, October 9, 2014—Excessive and often lethal blood levels of bilirubin can result from mutations in a single gene that are the cause of the metabolic disease known as Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1 (CNS1). A new gene therapy approach to correcting this metabolic error achieved significant, long-lasting reductions in bilirubin levels in a mouse model of CNS1 and is described in an Open Access article in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Human Gene Therapy website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/hum.2013.233. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers uncover how 'love hormone' regulates sexual behavior