(Press-News.org) Making a paper airplane in school used to mean trouble. Today it signals a promising discovery in materials science research that could help next-generation technology -like wearable energy storage devices- get off the ground. Researchers at Drexel University and Dalian University of Technology in China have chemically engineered a new, electrically conductive nanomaterial that is flexible enough to fold, but strong enough to support many times its own weight. They believe it can be used to improve electrical energy storage, water filtration and radiofrequency shielding in technology from portable electronics to coaxial cables.
Finding or making a thin material that is useful for holding and disbursing an electric charge and can be contorted into a variety of shapes, is a rarity in the field of materials science. Tensile strength -the strength of the material when it is stretched- and compressive strength -its ability to support weight- are valuable characteristics for these materials because, at just a few atoms thick, their utility figures almost entirely on their physical versatility.
"Take the electrode of the small lithium-ion battery that powers your watch, for example, ideally the conductive material in that electrode would be very small -so you don't have a bulky watch strapped to your wrist- and hold enough energy to run your watch for a long period of time," said Michel Barsoum, PhD, Distinguished Professor in the College of Engineering. "But what if we wanted to make the watch's wristband into the battery? Then we'd still want to use a conductive material that is very thin and can store energy, but it would also need to be flexible enough to bend around your wrist. As you can see, just by changing one physical property of the material -flexibility or tensile strength- we open a new world of possibilities."
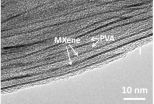
This flexible new material, which the group has identified as a conductive polymer nanocomposite, is the latest expression of the ongoing research in Drexel's Department of Materials Science and Engineering on a family of composite two-dimensional materials called MXenes.
This development was facilitated by collaboration between research groups of Yury Gogotsi, PhD, Distinguished University and Trustee Chair professor in the College of Engineering at Drexel, and Jieshan Qiu, vice dean for research of the School of Chemical Engineering at Dalian University of Technology in China. Zheng Ling, a doctoral student from Dalian, spent a year at Drexel, spearheading the research that led to the first MXene-polymer composites. The researchat Drexel was funded by grants from the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy.
The Drexel team has been diligently examining MXenes like a paleontologist carefully brushing away sediment to unearth a scientific treasure. Since inventing the layered carbide material in 2011 the engineers are finding ways to take advantage of its chemical and physical makeup to create conductive materials with a variety of other useful properties.
One of the most successful ways they've developed to help MXenes express their array of abilities is a process, called intercalation, which involves adding various chemical compounds in a liquid form. This allows the molecules to settle between the layers of the MXene and, in doing so, alter its physical and chemical properties. Some of the first, and most impressive of their findings, showed that MXenes have a great potential for energy storage.
To produce the flexible conductive polymer nanocomposite, the researchers intercalated the titanium carbide MXene, with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) -a polymer widely used as the paper adhesive known as school or Elmer's glue, and often found in the recipes for colloids such as hair gel and silly putty. They also intercalated with a polymer called PDDA (polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride) commonly used as a coagulant in water purification systems.
"The uniqueness of MXenes comes from the fact that their surface is full of functional groups, such as hydroxyl, leading to a tight bonding between the MXene flakes and polymer molecules, while preserving the metallic conductivity of nanometer-thin carbide layers. This leads to a nanocomposite with a unique combination of properties," said Gogotsi.
The results of both sets of MXene testing were recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In the paper, the researchers report that the material exhibits increased ability to store charge over the original MXene; and 300-400 percent improvement in strength.
"We have shown that the volumetric capacitance of an MXene-polymer nanocomposite can be much higher compared to conventional carbon-based electrodes or even graphene," said Chang Ren, Gogotsi's doctoral student at Drexel. "When mixing MXene with PVA containing some electrolyte salt, the polymer plays the role of electrolyte, but it also improves the capacitance because it slightly enlarges the interlayer space between MXene flakes, allowing ions to penetrate deep into the electrode; ions also stay trapped near the MXene flakes by the polymer. With these conductive electrodes and no liquid electrolyte, we can eventually eliminate metal current collectors and make lighter and thinner supercapacitors."
The testing also revealed hydrophilic properties of the nanocomposite, which means that it could have uses in water treatment systems, such as membrane for water purification or desalinization, because it remains stable in water without breaking up or dissolving.
In addition, because the material is extremely flexible, it can be rolled into a tube, which early tests have indicated only serves to increase its mechanical strength. These characteristics mark the trail heads of a variety of paths for research on this nanocomposite material for applications from flexible armor to aerospace components. The next step for the group will be to examine how varying ratios of MXene and polymer will affect the properties of the resulting nanocomposite and also exploring other MXenes and stronger and tougher polymers for structural applications.
INFORMATION:
November 11, 2014 - Several lines of research have opened exciting new frontiers in scientific understanding and clinical management of bipolar disorder. Recent advances in bipolar disease research are described in this month's special issue of Harvard Review of Psychiatry. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Bipolar disease is a "prevalent, complex, and hard-to-treat illness [leading] to extreme and erratic shifts of mood, thinking, and behavior, with a very high risk of suicide as well as increased risks of dying ...
In multiple sclerosis, the immune system goes rogue, improperly attacking the body's own central nervous system. Mobility problems and cognitive impairments may arise as the nerve cells become damaged.
In a new study, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and co-investigators have identified a key protein that is able to reduce the severity of a disease equivalent to MS in mice. This molecule, Del-1, is the same regulatory protein that has been found to prevent inflammation and bone loss in a mouse model of gum disease.
"We see that two completely different ...
DALLAS - November 11, 2014 - UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have determined the specific type of cell that gives rise to large, disfiguring tumors called plexiform neurofibromas, a finding that could lead to new therapies for preventing growth of these tumors.
"This advance provides new insight into the steps that lead to tumor development and suggests ways to develop therapies to prevent neurofibroma formation where none exist today," said Dr. Lu Le, Assistant Professor of Dermatology at UT Southwestern and senior author of the study, published online and ...
As scientists probe the molecular underpinnings of why some people are prone to obesity and some to leanness, they are discovering that weight maintenance is more complicated than the old "calories in, calories out" adage.
A team of researchers led by the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine's Kendra K. Bence have now drawn connections between known regulators of body mass, pointing to possible treatments for obesity and metabolic disorders.
Their work also presents intriguing clues that these same molecular pathways may play a role in learning ...
Salivary mucins, key components of mucus, actively protect the teeth from the cariogenic bacterium, Streptococcus mutans, according to research published ahead of print in Applied and Environmental Microbiology. The research suggests that bolstering native defenses might be a better way to fight dental caries than relying on exogenous materials, such as sealants and fluoride treatment, says first author Erica Shapiro Frenkel, of Harvard University, Cambridge, MA.
S. mutans attaches to teeth using sticky polymers that it produces, eventually forming a biofilm, a protected ...
From this week's Eos: Scientists Engage With the Public During Lava Flow Threat
On 27 June, lava from Kīlauea, an active volcano on the island of Hawai`i, began flowing to the northeast, threatening the residents in Pāhoa, a community in the District of Puna, as well as the only highway accessible to this area. Scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey's Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) and the Hawai`i County Civil Defense have been monitoring the volcano's lava flow and communicating with affected residents through public meetings since 24 August. Eos recently ...
The majority of people - including healthcare professionals - are unable to visually identify whether a person is a healthy weight, overweight or obese according to research by psychologists at the University of Liverpool.
Researchers from the University's Institute of Psychology, Health and Society asked participants to look at photographs of male models and categorise whether they were a healthy weight, overweight or obese according to World Health Organisation (WHO) Body Mass Index (BMI) guidelines.
They found that the majority of participants were unable to correctly ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Tiny, thin microtubes could provide a scaffold for neuron cultures to grow so that researchers can study neural networks, their growth and repair, yielding insights into treatment for degenerative neurological conditions or restoring nerve connections after injury.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the University of Wisconsin-Madison created the microtube platform to study neuron growth. They posit that the microtubes could one day be implanted like stents to promote neuron regrowth at injury sites or to treat disease.
"This ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Crop producers and scientists hold deeply different views on climate change and its possible causes, a study by Purdue and Iowa State universities shows.
Associate professor of natural resource social science Linda Prokopy and fellow researchers surveyed 6,795 people in the agricultural sector in 2011-2012 to determine their beliefs about climate change and whether variation in the climate is triggered by human activities, natural causes or an equal combination of both.
More than 90 percent of the scientists and climatologists surveyed said they ...
Located hundreds of miles inland from the nearest ocean, the Midwest is unaffected by North Atlantic hurricanes.
Or is it?
With the Nov. 30 end of the 2014 hurricane season just weeks away, a University of Iowa researcher and his colleagues have found that North Atlantic tropical cyclones in fact have a significant effect on the Midwest. Their research appears in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
Gabriele Villarini, UI assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering, studied the discharge records collected at 3,090 U.S. Geological Survey ...