(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (Nov. 13, 2014) - While feelings of disgust can increase behaviors like lying and cheating, cleanliness can help people return to ethical behavior, according to a recent study by marketing experts at Rice University, Pennsylvania State University and Arizona State University. The study highlights the powerful impact emotions have on individual decision-making.
"As an emotion, disgust is designed as a protection," said Vikas Mittal, the J. Hugh Liedtke Professor of Marketing at Rice's Jones Graduate School of Business. "When people feel disgusted, they tend to remove themselves from a situation. The instinct is to protect oneself. People become focused on 'self' and they're less likely to think about other people. Small cheating starts to occur: If I'm disgusted and more focused on myself and I need to lie a little bit to gain a small advantage, I'll do that. That's the underlying mechanism."
In turn, the researchers found that cleansing behaviors actually mitigate the self-serving effects of disgust. "If you can create conditions where people's disgust is mitigated, you should not see this (unethical) effect," Mittal said. "One way to mitigate disgust is to make people think about something clean. If you can make people think of cleaning products - for example, Kleenex or Windex - the emotion of disgust is mitigated, so the likelihood of cheating also goes away. People don't know it, but these small emotions are constantly affecting them."
Vikas co-authored the paper with Karen Page Winterich, an associate professor of marketing at Penn State's Smeal College of Business, and Andrea Morales, a professor of marketing at Arizona State's W.P. Carey School of Business. It will be published in the journal Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes.
The researchers conducted three randomized experiments evoking disgust through various means. The study involved 600 participants around the United States; both genders were equally represented. In one experiment, participants evaluated consumer products such as antidiarrheal medicine, diapers, feminine care pads, cat litter and adult incontinence products. In another, participants wrote essays about their most disgusting memory. In the third, participants watched a disgusting toilet scene from the movie "Trainspotting." Once effectively disgusted, participants engaged in experiments that judged their willingness to lie and cheat for financial gain. Mittal and colleagues found that people who experienced disgust consistently engaged in self-interested behaviors at a significantly higher rate than those who did not.
In another set of experiments, after inducing the state of disgust on participants, the researchers then had them evaluate cleansing products, such as disinfectants, household cleaners and body washes. Those who evaluated the cleansing products did not engage in deceptive behaviors any more than those in the neutral emotion condition.
The findings should help managers and organizational leaders understand the impact, both ethical and unethical, of emotions on decision-making, Mittal said.
"At the basic level, if you have environments that are cleaner, if you have workplaces that are cleaner, people should be less likely to feel disgusted," Mittal said. "If there is less likelihood to feel disgusted, there will be a lower likelihood that people need to be self-focused and there will be a higher likelihood for people to cooperate with each other."
Mittal said the deeper meaning of the study's finding is that these powerful emotions can be triggered by various innocuous-sounding things when people are reading the newspaper or listening to the radio. "What we found is that unless you ask people, they often don't know they're feeling disgusted," Mittal said. "Small things can trigger specific emotions, which can deeply affect people's decision-making. The question is how to make people more self-aware and more thoughtful about the decision-making process."
Mittal mentioned Warren Buffett as an example of a smart decision-maker who avoids paying too much attention to the news. "If you're making important decisions, how do you create an environment that is less emotionally cluttered so you can become progressively more thoughtful?"
INFORMATION:
For a copy of the study, "Protect Thyself: How Affective Self-Protection Increases Self-Interested Behavior," e-mail jfalk@rice.edu. For more information about Mittal's research, visit the Jones School's website: http://business.rice.edu/Disgust.
Follow the Jones School via Twitter @RiceMBA.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Mittal bio: http://business.rice.edu/Vikas_Mittal.
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just over 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is highly ranked for best quality of life by the Princeton Review and for best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Half a million objects, including debris, satellites, and the International Space Station, orbit the planet in the thermosphere, the largest layer of Earth's atmosphere. To predict the orbits--and potential collisions--of all this stuff, scientists must forecast the weather in the thermosphere.
Researchers who analyzed the role that gravitational effects of the Moon have on the thermosphere found that satellites taking different paths around the planet--circling over the poles, around the equator, or any route in between--will experience different levels of lunar-induced ...
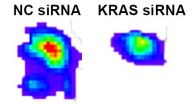
CHAPEL HILL, NC - Researchers from the UNC School of Medicine and colleagues at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new approach to block the KRAS oncogene, one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancer. The approach, led by Chad Pecot, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at UNC, offers another route to attack KRAS, which has proven to be an elusive and frustrating target for drug developers.
The new method relies upon a specifically sequenced type of small interfering RNA - or siRNA. The findings, published in the journal ...
Irvine, Calif., Nov. 13, 2014 -- A new bloodstream infection test created by UC Irvine researchers can speed up diagnosis times with unprecedented accuracy, allowing physicians to treat patients with potentially deadly ailments more promptly and effectively.
The UCI team, led by Weian Zhao, assistant professor of pharmaceutical sciences, developed a new technology called Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. In as little as 90 minutes, IC 3D can detect bacteria in milliliters of blood with single-cell sensitivity; no cell culture is needed.
The work appears ...
The Sudbury Basin located in Ontario, Canada is one of the largest known impact craters on Earth, as well as one of the oldest due to its formation more than 1.8 billion years ago. Researchers who took samples from the site and subjected them to a detailed geochemical analysis say that a comet may have hit the area to create the crater.
"Our analysis revealed a chondritic platinum group element signature within the crater's fallback deposits; however, the distribution of these elements within the impact structure and other constraints suggest that the impactor was a comet. ...
Among overweight and obese adults who had asthma and participated in weight loss programs, more severe asthma, male sex, and improvements in eating behaviors were all linked with better success at losing weight.
The finding that individuals with more severe asthma may have a greater motivation to lose weight suggests that these individuals should be targeted for intervention. Also, gender tailoring of weight loss programs may be useful to enhance weight loss success, said Lisa Wood, senior author of the Respirology study.
INFORMATION: ...
People can gauge the accuracy of their decisions, even if their decision making performance itself is no better than chance, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In the study, people who showed chance-level decision making still reported greater confidence about decisions that turned out to be accurate and less confidence about decisions that turned out to be inaccurate. The findings suggest that the participants must have had some unconscious insight into their decision making, even though ...
Philadelphia, PA (November 13, 2014) -- Patients on dialysis are very vulnerable during emergencies or disasters, but many are unprepared for such situations, according to two studies that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Dialysis patients are highly dependent on technologies to sustain their lives, with ongoing needs for transportation, electricity, and water for the dialysis apparatus. Interruption of these needs by a natural disaster can be devastating.
Naoka Murakami, MD, PhD ...
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2014--Canadians with cystic fibrosis are living almost 20 years longer than they did two decades ago, according to a research paper published today.
The median survival age was 49.7 years in 2012, up from 31.9 years in 1990, Dr. Anne Stephenson, a respirologist and research at St. Michael's Hospital wrote in the European Respiratory Journal. Since the paper was written, Dr. Stephenson has updated the median survival age to include Cystic Fibrosis Canada data from 2013 and reported the median age of survival has in fact reached 50.9 years.
In addition, ...
Scientists from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles describe a new distinctive fly species of the highly diverse genus Megaselia. The study published in the Biodiversity Data Journal proposes an innovative method for streamlining Megaselia species descriptions to save hours of literature reviews and comparisons.
The new species, M. shadeae, is easily distinguished by a large, central, pigmented and bubble-like wing spot. The description is part of the the Zurquí All Diptera Biodiversity Inventory (ZADBI) project, and represents the first of an incredible ...
Mice bred to carry a gene variant found in a third of ALS patients have a faster disease progression and die sooner than mice with the standard genetic model of the disease, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. Understanding the molecular pathway of this accelerated model could lead to more successful drug trials for all ALS patients.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, commonly known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a degeneration of lower and upper motor neurons in the brainstem, spinal cord and the motor cortex. The disease, which affects 12,000 Americans, ...