Stricter limits for ozone pollution would boost need for science, measurements
2015-06-04
(Press-News.org) A tougher federal standard for ozone pollution, under consideration to improve public health, would ramp up the importance of scientific measurements and models, according to a new commentary published in the June 5 edition of Science by researchers at NOAA and its cooperative institute at the University of Colorado Boulder.
The commentary, led by Owen Cooper of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences and NOAA's Earth System Research Laboratory, looks at how a new, stricter ozone standard would pose challenges for air quality managers at state and local levels. Last November, the Environmental Protection Agency proposed lowering the primary ozone standard from 75 parts per billion (ppb) to 70 or 65 ppb, based on ozone's known effects on children, the elderly, and people who have lung diseases such as asthma. A decision by the EPA Administrator is expected in October 2015.
The problem for state and local officials is that ozone pollution has several sources, some of which are beyond their borders. At any given place, a certain amount of the ozone pollution comes from local emissions by vehicles and other sources. Additional amounts can blow in from pollution sources across the ocean or in other parts of the United States. And some ozone is produced from natural sources or descends from the upper atmosphere's ozone layer.
Sorting all this out is where science comes in, says Cooper. "It's not easy, but we do know how to figure out where the ozone comes from. This source information is exactly what air quality managers will need to know when the margin for allowable locally produced ozone shrinks."
Ozone is a pollutant that has respiratory health effects in humans and also impairs plant growth and damages crops. It is produced when emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the presence of sunlight. Controls on NOx and VOC emissions from vehicles, power plants, and other sources have enabled many U.S. counties to meet the 75 ppb standard, but the number of counties in "nonattainment" status (currently at 227) would jump to 358 or 558 if the standard is revised to 70 or 65 ppb, respectively.
The new commentary suggests that to quantify how much ozone flows into the United States from all upwind sources, additional measurements would be needed, from instruments on the ground, on balloons, and on aircraft. These observations could help scientists and air quality managers evaluate the performance of the computer models that are used to determine sources of ozone at a particular location. Once the models can successfully replicate the observed ozone levels, scientists and air quality managers will have greater confidence in the model estimates of how much of that observed ozone is beyond the reach of domestic control measures.
That information is critical because the U.S. regulatory framework has procedures for exceptions and other allowances if non-local factors are significant for a given locality. And, those outside factors have been growing in recent decades, with sources in South and East Asia pushing up the baseline of ozone that enters the western U.S., for example.
"The ozone baseline is rising, especially in high-elevation regions of the western U.S. that are more strongly influenced by high ozone coming from upwind sources or from the stratosphere. Lowering the federal ozone standard to protect public health will reduce the wiggle room for air quality managers. We point out that measurements and science will be crucial to successfully navigating the new regulatory landscape," said Cooper said.
The EPA has stated that in their upcoming regulations and guidance, they will assist states in ensuring that sources of ozone that are outside of U.S. borders do not create unnecessary control obligations.
INFORMATION:
CIRES is a partnership of NOAA and the University of Colorado Boulder.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-04
Modern mountain climbers typically carry tanks of oxygen to help them reach the summit. It's the combination of physical exertion and lack of oxygen at high altitudes that creates one of the biggest challenges for mountaineers.
University of Washington researchers and collaborators have found that the same principle will apply to marine species under global warming. The warmer water temperatures will speed up the animals' metabolic need for oxygen, as also happens during exercise, but the warmer water will hold less of the oxygen needed to fuel their bodies, similar to ...
2015-06-04
If you want to live, you need to breathe and muster enough energy to move, find nourishment and reproduce. This basic tenet is just as valid for us human beings as it is for the animals inhabiting our oceans. Unfortunately, most marine animals will find it harder to satisfy these criteria, which are vital to their survival, in the future. That was the key message of a new study recently published in the journal Science, in which American and German biologists defined the first universal principle on the combined effects of ocean warming and oxygen loss on the productivity ...
2015-06-04
From a single drop of blood, researchers can now simultaneously test for more than 1,000 different strains of viruses that currently or have previously infected a person. Using a new method known as VirScan, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and Harvard Medical School tested for evidence of past viral infections, detecting on average 10 viral species per person. The new work sheds light on the interplay between a person's immunity and the human virome -- the vast array of viruses that can infect humans - with implications both for the clinic and for the ...
2015-06-04
PHILADELPHIA - Around-the-clock rhythms guide nearly all physiological processes in animals and plants. Each cell in the body contains special proteins that act on one another in interlocking feedback loops to generate near-24 hour oscillations called circadian rhythms. These dictate behaviors controlled by the brain, such as sleeping and eating, as well as metabolic, hormonal, and other rhythms that are intrinsic to the organs of the body. For example, when you eat may have affects on rhythms controlling fat or sugar metabolism, illustrating how circadian and metabolic ...
2015-06-04
This news release is available in Japanese.
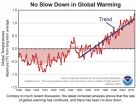
An analysis using updated global surface temperature data disputes the existence of a 21st century global warming slowdown described in studies including the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessment. The new analysis suggests no discernable decrease in the rate of warming between the second half of the 20th century, a period marked by manmade warming, and the first fifteen years of the 21st century, a period dubbed a global warming "hiatus." Numerous studies have been done to explain the possible ...
2015-06-04
This news release is available in Japanese.
Many species are migrating toward Earth's poles in response to climate change, and their habitats are shrinking in the process, researchers say. Two new reports focusing on marine organisms, which have been moving pole-ward at higher rates than terrestrial creatures, show how factors, including those not directly related to climate change, are limiting the ranges of corals and fish. Paul Muir and colleagues investigated 104 species of reef corals -- collectively known as the staghorn corals -- and confirmed the hypothesis ...
2015-06-04
This news release is available in Japanese. With less than a drop of blood, a new technology called VirScan can identify all of the viruses that individuals have been exposed to over the course of their lives. Researchers used the screening technique with 569 people from around the world and found that, on average, their participants had been exposed to about 10 viral species over their lifetimes. VirScan provides a powerful and inexpensive tool for studying interactions between the human virome -- the collection of viruses known to infect humans, some of which don't ...
2015-06-04
This news release is available in Japanese. Some of the world's last isolated tribes are emerging from the Amazon rainforest, forcing scientists and policymakers in South America to reconsider their policies regarding contact with such people. In this special package of news, Science correspondents Andrew Lawler and Heather Pringle report from Peru and Brazil, respectively -- two countries that are dealing with a spate of first encounters. Lawler describes contact between isolated tribespeople emerging from the forest and indigenous Peruvian villagers, who themselves ...
2015-06-04
New technology developed by Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) researchers makes it possible to test for current and past infections with any known human virus by analyzing a single drop of a person's blood. The method, called VirScan, is an efficient alternative to existing diagnostics that test for specific viruses one at a time.
With VirScan, scientists can run a single test to determine which viruses have infected an individual, rather than limiting their analysis to particular viruses. That unbiased approach could uncover unexpected factors affecting individual ...
2015-06-04
Friction is all around us, working against the motion of tires on pavement, the scrawl of a pen across paper, and even the flow of proteins through the bloodstream. Whenever two surfaces come in contact, there is friction, except in very special cases where friction essentially vanishes -- a phenomenon, known as "superlubricity," in which surfaces simply slide over each other without resistance.
Now physicists at MIT have developed an experimental technique to simulate friction at the nanoscale. Using their technique, the researchers are able to directly observe individual ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stricter limits for ozone pollution would boost need for science, measurements