(Press-News.org) DNA from the 8,500-year-old skeleton of an adult man found in 1996, in Washington, is more closely related to Native American populations than to any other population in the world, according to an international collaborative study conducted by scientists at the University of Copenhagen and the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The finding challenges a 2014 study that concluded, based on anatomical data, that Kennewick Man was more related to indigenous Japanese or Polynesian peoples than to Native Americans. The study is likely to reignite a long-standing legal dispute regarding the skeleton's provenance and its eventual fate.
"Using ancient DNA, we were able to show that Kennewick Man is more closely related to Native Americans than any other population," said postdoctoral scholar Morten Rasmussen, PhD. "Due to the massive controversy surrounding the origins of this sample, the ability to address this will be of interest to both scientists and tribal members."
Rasmussen is the lead author of the research, published online June 17 in Nature. The senior author of the study is Eske Willerslev, PhD, from the University of Copenhagen's Centre for GeoGenetics. Rasmussen initiated the study at the Centre for GeoGenetics and completed the analysis of the DNA sequences at Stanford, working with Carlos Bustamante, PhD, professor of genetics.
The skeleton, known as Kennewick Man, is called the Ancient One by Native American groups, which believe the bones are those of a long-ago ancestor. In 2004, five Native American tribes of the Pacific Northwest requested repatriation of the remains for reburial, but the proceedings were halted to allow further investigation into the skeleton's origins.
Bits of ancient DNA
Now an exhaustive genetic study of the tiny bits of ancient DNA from a bone in the skeleton's hand refutes the conclusions of the 2014 study. The researchers used the latest in DNA isolation and sequencing techniques to pick out and analyze the skeleton's DNA.
"Although the exterior preservation of the skeleton was pristine, the DNA in the sample was highly degraded and dominated by DNA from soil bacteria and other environmental sources," said Rasmussen. "With the little material we had available, we applied the newest methods to squeeze every piece of information out of the bone."
The researchers compared the DNA sequences from the skeleton with those of modern Native Americans. They concluded that, although it is impossible to assign Kennewick Man to a particular tribe, he is closely related to members of the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation in Washington.
Willerslev and Bustamante are well-known for their studies of ancient DNA. Willerslev and Rasmussen recently published the genome of a young child, known as the Anzick boy, buried more than 12,000 years ago in Montana. That study showed that the boy was also closely related to modern Native American groups, in particular those of South and Central America. In 2012, Bustamante and colleagues used DNA from the 5,300-year-old Iceman mummy called Otzi to show the man likely hailed from the Mediterranean island of Sardinia rather than the frigid Alps, where his body was found.
"Advances in DNA sequencing technology have given us important new tools for studying the great human diasporas and the history of indigenous populations," said Bustamante. "Now we are seeing its adoption in new areas, including forensics and archeology. The case of Kennewick Man is particularly interesting given the debates surrounding the origins of Native American populations. Morten's work aligns beautifully with the oral history of native peoples and lends strong support for their claims. I believe that ancient DNA analysis could become standard practice in these types of cases since it can provide objective means of assessing both genetic ancestry and relatedness to living individuals and present-day populations."
INFORMATION:
Stanford graduate student David Poznik is also a co-author of the study.
The research was supported by the Danish Council for Independent Research, the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología in Mexico, the National Science Foundation and a Marie Curie Intra-European Fellowship.
Information about Stanford's Department of Genetics, which also supported the work, is available at http://genetics.stanford.edu.
The Stanford University School of Medicine consistently ranks among the nation's top medical schools, integrating research, medical education, patient care and community service. For more news about the school, please visit http://med.stanford.edu/school.html. The medical school is part of Stanford Medicine, which includes Stanford Health Care and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford. For information about all three, please visit http://med.stanford.edu.
NASA provided four different views of Tropical Depression Bill as it continued traveling through the south-central U.S. and into the Ohio Valley. NASA's Aqua and Terra satellite provided infrared and visible imagery while NASA/NOAA's GOES Project animated NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery to show the storm's progression since landfall. The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core satellite also showed rainfall estimates and locations.
On June 18, the National Weather Service, Weather Prediction Center (NWS/WPC) noted that flood and flash flood watches and warnings ...
Kangaroos prefer to use one of their hands over the other for everyday tasks in much the same way that humans do, with one notable difference: generally speaking, kangaroos are lefties. The finding, reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 18--the first to consider handedness in wild kangaroos--challenges the notion that "true" handedness among mammals is a feature unique to primates.
"According to a special-assessment scale of handedness adopted for primates, kangaroos pulled down the highest grades," says Yegor Malashichev of Saint Petersburg State ...
Anti-cancer strategies generally involve killing off tumor cells. However, cancer cells may instead be coaxed to turn back into normal tissue simply by reactivating a single gene, according to a study published June 18th in the journal Cell. Researchers found that restoring normal levels of a human colorectal cancer gene in mice stopped tumor growth and re-established normal intestinal function within only 4 days. Remarkably, tumors were eliminated within 2 weeks, and signs of cancer were prevented months later. The findings provide proof of principle that restoring the ...
American scientists have discovered that a drug commonly used to treat osteoporosis in humans also stimulates the production of cells that control insulin balance in diabetic mice. While other compounds have been shown to have this effect, the drug (Denosumab) is already FDA approved and could more quickly move to clinical trials as a diabetes treatment. The research is published June 18 in Cell Metabolism.
Diabetes is a major health issue worldwide that arises due to a deficiency of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, beta cells die from ...
Cutaneous melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer, is now believed to be divided into four distinct genomic subtypes, say researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, a finding that could prove valuable in the ever-increasing pursuit of personalized medicine.
As part of The Cancer Genome Atlas, researchers identified four melanoma subtypes: BRAF, RAS, NF1 and Triple-WT, which were defined by presence or absence of mutations from analysis of samples obtained from 331 patients. The five-year study resulted from an international collaboration of ...
PHILADELPHIA -- Most of us need seven to eight hours of sleep a night to function well, but some people seem to need a lot less sleep. The difference is largely due to genetic variability. In research published online June 18th in Current Biology, researchers report that two genes, originally known for their regulation of cell division, are required for normal slumber in fly models of sleep: taranis and Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1).
'There's a lot we don't understand about sleep, especially when it comes to the protein machinery that initiates the process on the ...
In 2012, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine showed that heart muscle cells made from the skin of people with a cardiac condition called dilated cardiomyopathy beat with less force than those made from the skin of healthy people. These cells also responded less readily to the waves of calcium that control the timing and strength of each contraction.
Now, the same research team has teased apart the molecular basis for these differences and identified a drug treatment that at least partially restores function to diseased cells grown in a laboratory ...
Adult neural stem cells, which are commonly thought of as having the ability to develop into many type of brain cells, are in reality pre-programmed before birth to make very specific types of neurons, at least in mice, according to a study led by UC San Francisco researchers.
"This work fundamentally changes the way we think about stem cells," said principal investigator Arturo Alvarez-Buylla, UCSF professor of neurological surgery, Heather and Melanie Muss Endowed Chair and a principal investigator in the UCSF Brain Tumor Research Center and the Eli and Edythe Broad ...
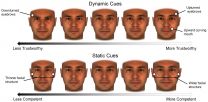
We can alter our facial features in ways that make us look more trustworthy, but don't have the same ability to appear more competent, a team of New York University psychology researchers has found.
The study, which appears in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, a SAGE journal, points to both the limits and potential we have in visually representing ourselves--from dating and career-networking sites to social media posts.
"Our findings show that facial cues conveying trustworthiness are malleable while facial cues conveying competence and ability are significantly ...
Want to lose abdominal fat, get smarter and live longer? New research led by USC's Valter Longo shows that periodically adopting a diet that mimics the effects of fasting may yield a wide range of health benefits.
In a new study, Longo and his colleagues show that cycles of a four-day low-calorie diet that mimics fasting (FMD) cut visceral belly fat and elevated the number of progenitor and stem cells in several organs of old mice -- including the brain, where it boosted neural regeneration and improved learning and memory.
The mouse tests were part of a three-tiered ...