Lefties are all right with kangaroos
2015-06-18
(Press-News.org) Kangaroos prefer to use one of their hands over the other for everyday tasks in much the same way that humans do, with one notable difference: generally speaking, kangaroos are lefties. The finding, reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 18--the first to consider handedness in wild kangaroos--challenges the notion that "true" handedness among mammals is a feature unique to primates.
"According to a special-assessment scale of handedness adopted for primates, kangaroos pulled down the highest grades," says Yegor Malashichev of Saint Petersburg State University in Russia. "We observed a remarkable consistency in responses across bipedal species in that they all prefer to use the left, not the right, hand."
Malashichev's interest in handedness goes back at least a decade, when he reported differences in handedness between jumping and walking frogs. Those studies showed that jumping frogs less often show handedness than do walking frogs. His team later showed subtle signs of handedness in marsupials that walk on all fours, including gray short-tailed opossums and sugar gliders, which differed by sex. But no one had taken a careful look at different species of bipedal kangaroos.
One reason true handedness wasn't expected in kangaroos--or other marsupials, for that matter--is because, unlike other mammals, they lack the same neural circuit that bridges the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Studies of kangaroos living in captivity hadn't yielded conclusive evidence either. In the new study, to find out what wild kangaroos really do when left to their own devices, the researchers watched these iconic animals in Tasmania and continental Australia.
"What we observed in reality we did not initially expect," Malashichev says. "But the more we observed, the more it became obvious that there is something really new and interesting in the wild."
They found that wild kangaroos show a natural preference for their left hands when performing particular actions--grooming the nose, picking a leaf, or bending a tree branch, for example. Left-handedness was particularly apparent in eastern grey and red kangaroos.
Red-necked wallabies prefer their left hand for some tasks and their right for others. Generally speaking, they use their left forelimb for tasks that involve fine manipulation and the right for tasks that require more physical strength. The researchers found less evidence for handedness in species that spend their days in the trees.
The findings should encourage more careful study of the marsupial brain, which differs from those of other mammals in many respects. Such studies might even yield important insight into neuropsychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia and autism, the researchers say, noting links between those disorders and handedness.
The researchers will continue to explore handedness in other species that stand upright regularly or from time to time. "This will give us a better resolution for the evolutionary interpretations," Malashichev says.
INFORMATION:
The National Geographic Society Committee for Research and Exploration supported the fieldwork done in this study.
Current Biology, Giljov et al.:" Parallel Emergence of True Handedness in the Evolution of Marsupials and Placentals" http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.05.043
Current Biology, published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. For more information please visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive media alerts for Current Biology or other Cell Press journals, contactpress@cell.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-18
Anti-cancer strategies generally involve killing off tumor cells. However, cancer cells may instead be coaxed to turn back into normal tissue simply by reactivating a single gene, according to a study published June 18th in the journal Cell. Researchers found that restoring normal levels of a human colorectal cancer gene in mice stopped tumor growth and re-established normal intestinal function within only 4 days. Remarkably, tumors were eliminated within 2 weeks, and signs of cancer were prevented months later. The findings provide proof of principle that restoring the ...
2015-06-18
American scientists have discovered that a drug commonly used to treat osteoporosis in humans also stimulates the production of cells that control insulin balance in diabetic mice. While other compounds have been shown to have this effect, the drug (Denosumab) is already FDA approved and could more quickly move to clinical trials as a diabetes treatment. The research is published June 18 in Cell Metabolism.
Diabetes is a major health issue worldwide that arises due to a deficiency of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. In type 1 diabetes, beta cells die from ...
2015-06-18
Cutaneous melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer, is now believed to be divided into four distinct genomic subtypes, say researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, a finding that could prove valuable in the ever-increasing pursuit of personalized medicine.
As part of The Cancer Genome Atlas, researchers identified four melanoma subtypes: BRAF, RAS, NF1 and Triple-WT, which were defined by presence or absence of mutations from analysis of samples obtained from 331 patients. The five-year study resulted from an international collaboration of ...
2015-06-18
PHILADELPHIA -- Most of us need seven to eight hours of sleep a night to function well, but some people seem to need a lot less sleep. The difference is largely due to genetic variability. In research published online June 18th in Current Biology, researchers report that two genes, originally known for their regulation of cell division, are required for normal slumber in fly models of sleep: taranis and Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1).
'There's a lot we don't understand about sleep, especially when it comes to the protein machinery that initiates the process on the ...
2015-06-18
In 2012, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine showed that heart muscle cells made from the skin of people with a cardiac condition called dilated cardiomyopathy beat with less force than those made from the skin of healthy people. These cells also responded less readily to the waves of calcium that control the timing and strength of each contraction.
Now, the same research team has teased apart the molecular basis for these differences and identified a drug treatment that at least partially restores function to diseased cells grown in a laboratory ...
2015-06-18
Adult neural stem cells, which are commonly thought of as having the ability to develop into many type of brain cells, are in reality pre-programmed before birth to make very specific types of neurons, at least in mice, according to a study led by UC San Francisco researchers.
"This work fundamentally changes the way we think about stem cells," said principal investigator Arturo Alvarez-Buylla, UCSF professor of neurological surgery, Heather and Melanie Muss Endowed Chair and a principal investigator in the UCSF Brain Tumor Research Center and the Eli and Edythe Broad ...
2015-06-18
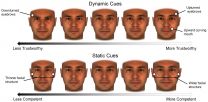
We can alter our facial features in ways that make us look more trustworthy, but don't have the same ability to appear more competent, a team of New York University psychology researchers has found.
The study, which appears in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, a SAGE journal, points to both the limits and potential we have in visually representing ourselves--from dating and career-networking sites to social media posts.
"Our findings show that facial cues conveying trustworthiness are malleable while facial cues conveying competence and ability are significantly ...
2015-06-18
Want to lose abdominal fat, get smarter and live longer? New research led by USC's Valter Longo shows that periodically adopting a diet that mimics the effects of fasting may yield a wide range of health benefits.
In a new study, Longo and his colleagues show that cycles of a four-day low-calorie diet that mimics fasting (FMD) cut visceral belly fat and elevated the number of progenitor and stem cells in several organs of old mice -- including the brain, where it boosted neural regeneration and improved learning and memory.
The mouse tests were part of a three-tiered ...
2015-06-18
Last June, in the early days of the Ebola outbreak in Western Africa, a team of researchers sequenced the genome of the deadly virus at unprecedented scale and speed. Their findings revealed a number of critical facts as the outbreak was unfolding, including that the virus was being transmitted only by person-to-person contact and that it was picking up new mutations through its many transmissions.
While public health officials now believe the worst of the epidemic is behind us, it is not yet over, and questions raised by the previous work still await answers.
To ...
2015-06-18
PHILADELPHIA - Several well-known neurodegenerative diseases, such as Lou Gehrig's (ALS), Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's disease, all result in part from a defect in autophagy - one way a cell removes and recycles misfolded proteins and pathogens. In a paper published this week in Current Biology, postdoctoral fellow David Kast, PhD, and professor Roberto Dominguez, PhD, and three other colleagues from the Department of Physiology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, show for the first time that the formation of ephemeral compartments ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lefties are all right with kangaroos