(Press-News.org) Mobility between different physical environments in the cell nucleus regulates the daily oscillations in the activity of genes that are controlled by the internal biological clock, according to a study that is published in the journal Molecular Cell. Eventually, these findings may lead to novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of diseases linked with disrupted circadian rhythm.
So called clock-controlled - or circadian - genes are part of the internal biological clock, allowing humans and other light-sensitive organisms to adjust their daily activity to the cycle of daylight and darkness. In the current study, investigators at Sweden's Karolinska Institutet found that daily changes in the spatial localisation of clock-controlled genes in the cell nucleus regulates fluctuations in their activity with a 24-hour period length.
"We have uncovered a novel principle of circadian transcriptional regulation that involves a so-far unexpected dynamics in the sub-nuclear positioning of circadian genes", says principal investigator Anita Göndör at the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology at Karolinska Institutet.
The genetic material is packaged in a structure called chromatin in the cell nucleus. It has been established that the 3-dimensional distribution of chromatin in the nucleus follows a pattern. Open chromatin containing active genes tends to occupy the central parts, whereas chromatin containing genes that are not active tends to localise to the peripheral parts of the nucleus - an environment rich in factors that promote gene silencing.
Researchers investigated physical meetings between regions that are located far apart from each other on the linear chromatin fibre or reside on different chromosomes. By studying such encounters in the 3-dimensional space of the nucleus, they discovered a network of contacts between clock-controlled genes and domains of gene-poor, repressed chromatin in the periphery of the nucleus. They identified two proteins that bring the genes to bed and help them go to sleep at the periphery of the cell nucleus every day: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), a well-known regulator of DNA repair and gene expression, and the transcription factor CTCF. The researchers thus found that PARP1 and CTCF promote the diurnal recruitment of circadian genes to the nuclear periphery to attenuate their expression. They were then released from the periphery in a silent, 'sleeping' state to start a new cycle.
The internal biological clock regulates, among other things, body temperature, metabolism and the levels of several hormones. Disruption of circadian rhythm has been linked to predisposition to multifactorial diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, psychiatric disorders and cancer. The new knowledge may lead up to new strategies for treatment of diseases that are affected by deregulated circadian rhythm.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Pediatric Cancer Foundation, the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Lundberg Foundation, Karolinska Institutet, and the KA Wallenberg Foundation. Researchers from SciLifeLab in Sweden, and University of Pécs, Hungary, also contributed to this recent study.
Publication: 'PARP1- and CTCF-Mediated Interactions between Active and Repressed Chromatin at the Lamina Promote Oscillating Transcription', Honglei Zhao, Emmanouil G. Sifakis, Noriyuki Sumida, Lluís Millán-Ariño, Barbara A. Scholz, J. Peter Svensson, Xingqi Chen, Anna L. Ronnegren, Carolina Diettrich Mallet de Lima, Farzaneh Shahin Varnoosfaderani, Chengxi Shi, Olga Loseva, Samer Yammine, Maria Israelsson, Li-Sophie Rathje, Balázs Németi, Erik Fredlund, Thomas Helleday, Márta P. Imreh, and Anita Göndör. Molecular Cell, publishing in the 17 September, 2015 paper issue, online 27 August 2015.
More about Karolinska Institutet - a medical university: ki.se/english
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - When a large combat unit, widely dispersed in dense jungle, goes to battle, no single soldier knows precisely how his actions are affecting the unit's success or failure. But in modern armies, every soldier is connected via an audio link that can instantly receive broadcasts - reporting both positive and negative surprises - based on new intelligence. The real-time broadcasts enable dispersed troops to learn from these reports and can be critical since no solider has an overview of the entire unit's situation.
Similarly, as neuroscientists at Cold ...
LA JOLLA--Every organism--from a seedling to a president--must protect its DNA at all costs, but precisely how a cell distinguishes between damage to its own DNA and the foreign DNA of an invading virus has remained a mystery.
Now, scientists at the Salk Institute have discovered critical details of how a cell's response system tells the difference between these two perpetual threats. The discovery could help in the development of new cancer-selective viral therapies and may help explain why aging and certain diseases seem to open the door to viral infections.
"Our ...
Working with human cancer cell lines and mice, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and elsewhere have found a way to trigger a type of immune system "virus alert" that may one day boost cancer patients' response to immunotherapy drugs. An increasingly promising focus of cancer research, the drugs are designed to disarm cancer cells' ability to avoid detection and destruction by the immune system.
In a report on the work published in the Aug. 27 issue of Cell, the Johns Hopkins-led research team says it has found a core group of genes related to both ...
Understanding exactly what is taking place inside a single cell is no easy task. For DNA, amplification techniques are available to make the task possible, but for other substances such as proteins and small molecules, scientists generally have to rely on statistics generated from many different cells measured together. Unfortunately, this means they cannot look at what is happening in each individual cell.
Now, thanks to seven years of work done at the RIKEN Quantitative Biology Center and Hiroshima University, scientists can take a peek into a single plant cell and--within ...
In experiments with mouse tissue, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered that the adaptive immune system, generally associated with fighting bacterial and viral infections, plays an active role in guiding the normal development of mammary glands, the only organs--in female humans as well as mice--that develop predominately after birth, beginning at puberty.
The scientists say the findings have implications not only for understanding normal organ development, but also for cancer and tissue-regeneration research, as well as in the highly active field of cancer immunotherapy, ...
Philadelphia, PA, Aug 27, 2015 - Having twins accounts for only 1.5% of all births but 25% of preterm births, the leading cause of infant mortality worldwide. Successful strategies for reducing singleton preterm births include prophylactic use of progesterone and cervical cerclage in patients with a prior history of preterm birth. To investigate whether the use of a cervical pessary might reduce premature births of twins, an international team of researchers conducted a large, multicenter, international randomized clinical trial (RCT) of approximately 1200 twin pregnancies. ...
DURHAM, N.H. - Researchers at the University of New Hampshire are turning to an unusual source --otoliths, the inner ear bones of fish -- to identify the nursery grounds of winter flounder, the protected estuaries where the potato chip-sized juveniles grow to adolesence. The research, recently published in the journal Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, could aid the effort to restore plummeting winter flounder populations along the East Coast of the U.S.
In addition to showing the age of a fish, much like the rings in the cross-section of a tree, otoliths ...
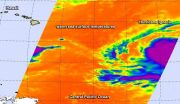
When cloud top temperatures get colder, the uplift in tropical cyclones gets stronger and the thunderstorms that make up the tropical cyclones have more strength. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Ignacio and infrared data revealed cloud top temperatures had cooled from the previous day.
Ignacio strengthened to a hurricane at 11 p.m. EDT on August 26. It became the seventh hurricane of the Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season.
A false-colored infrared image of Hurricane Ignacio was made at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena California, using data ...
Researchers from the Gladstone Institutes have revealed that HIV does not cause AIDS by the virus's direct effect on the host's immune cells, but rather through the cells' lethal influence on one another.
HIV can either be spread through free-floating virus that directly infect the host immune cells or an infected cell can pass the virus to an uninfected cell. The second method, cell to cell transmission, is 100 to 1000 times more efficient, and the new study shows that it is only this method that sets off a cellular chain reaction that ends in the newly infected cells ...
At a time when cancer drug prices are rising rapidly, an innovative new study provides the framework for establishing value-based pricing for all new oncology drugs entering the marketplace. Using a highly sophisticated economic model, researchers from Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology used an example of a new lung cancer drug. The study findings will be published August 27, 2015 in JAMA Oncology.
Researchers focused their investigation on a drug called necitumumab, which is awaiting approval from the U.S. Food and Drug ...