(Press-News.org) Washington, DC--Taking 3-minute breaks to walk in the middle of a TV marathon or other sedentary activity can improve children's blood sugar compared to continuously sitting, according to a new National Institutes of Health (NIH) study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
A sedentary lifestyle can put children at risk of developing pediatric obesity and metabolic health problems such as diabetes. Nearly 17 percent of children and teens nationwide are obese, according to the Society's Endocrine Facts and Figures report. A 2013 study estimated that elevated body-mass index in childhood was linked to $14.1 billion in prescription drug costs and emergency room and outpatient visits annually according to the report.
"Interrupting a long period of sitting with a few minutes of moderate activity can have short-term benefits on a child's metabolism," said the study's senior author, Jack A. Yanovski, MD, PhD, of the NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). "While we know getting 30 minutes or more of moderate intensity exercise each day improves children's health and metabolism, small behavioral changes like taking short walking breaks can also yield some benefits."
The randomized crossover trial examined sedentary behavior and metabolism in 28 normal-weight children who were between 7 and 11 years old. On two different days, the children either sat continuously for three hours or took 3-minute breaks to walk on a treadmill every half hour during that period. The study participants had their blood sugar and insulin levels tested before and after the experiment. The children drank a sugary soda-like drink prior to sitting so that researchers could measure how their bodies processed the sugar.
When children took breaks to walk, their blood sugar and insulin levels were lower than when they sat continuously. The findings indicate the children's bodies were better able to maintain blood sugar levels when their sitting was interrupted.
"Sustained sedentary behavior after a meal diminishes the muscles' ability to help clear sugar from the bloodstream," said first author, Britni Belcher, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute. "That forces the body to produce more insulin, which may increase the risk for beta cell dysfunction that can lead to the onset of Type 2 diabetes. Our findings suggest even short activity breaks can help overcome these negative effects, at least in the short term."
Additional exercise did not appear to affect the participants' appetites. The researchers provided the children with a buffet meal after the blood sugar testing was completed. The children selected similar amounts and types of foods, regardless of whether they had engaged in continuous or interrupted sitting that day.
INFORMATION:
Other authors of the study include: David Berrigan and Pamela L. Wolters of the National Cancer Institute; Alexia Papachristopoulou, Sheila M. Brady and Ira L. Tigner Jr. of NICHD; Shanna B. Bernstein, Amber B. Courville, Bart E. Drinkard, and Kevin P. Smith of the NIH's Hatfield Clinical Center; Douglas R. Rosing of the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute and Robert J. Brychta, Jacob D. Hattenbach and Kong Y. Chen of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
The study, "Effects of Interrupting Children's Sedentary Behaviors with Activity on Metabolic Function: A Randomized Trial," was published online at http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/jc.2015-2803, ahead of print.
Founded in 1916, the Endocrine Society is the world's oldest, largest and most active organization devoted to research on hormones and the clinical practice of endocrinology. Today, the Endocrine Society's membership consists of over 18,000 scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. Society members represent all basic, applied and clinical interests in endocrinology. The Endocrine Society is based in Washington, DC. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at http://www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at https://twitter.com/#!/EndoMedia.
Washington, DC--For years after it was administered, growth hormone continued to reduce the risk of fractures and helped maintain bone density in postmenopausal women who had osteoporosis, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Osteoporosis is a progressive condition that causes the bones to become weak and more likely to break. More than 10 million American adults have osteoporosis, and 80 percent of the people being treated for the condition nationwide are women, according to the Society's Endocrine ...
NASA's Aqua satellite and NOAA's GOES-West satellite provided temperature and cloud data on newborn Tropical Storm Jimena in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Data from both satellites show the storm continues to consolidate.
Tropical Depression 13E formed about 865 miles (1,390 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, Mexico at 5 p.m. EDT (2100 UTC) on August 26. Six hours later, the depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Jimena at 11 p.m. EDT.
A false-colored infrared image from Aug. 27 at 09:47 UTC (4:57 a.m. EDT) showed high, cold, strong thunderstorms ...
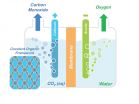
A molecular system that holds great promise for the capture and storage of carbon dioxide has been modified so that it now also holds great promise as a catalyst for converting captured carbon dioxide into valuable chemical products. Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have incorporated molecules of carbon dioxide reduction catalysts into the sponge-like crystals of covalent organic frameworks (COFs). This creates a molecular system that not only absorbs carbon dioxide, but also selectively reduces ...
Researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on August 27 have evidence in support of a clearly defined depth limit for deep-sea fishing in Europe. The findings come just as the European Union considers controversial new legislation to manage deep-sea fisheries, including a ban on trawling below 600 meters.
"The most notable thing to consider about our findings is that the trend in catch composition over the depth range of 600 to 800 meters shows that collateral ecological impacts are significantly increasing while the commercial gain per unit effort ...
Isaac Newton was a classic neurotic. He was a brooder and a worrier, prone to dwelling on the scientific problems before him as well as his childhood sins. But Newton also had creative breakthroughs--thoughts on physics so profound that they are still part of a standard science education.
In a Trends in Cognitive Sciences Opinion paper published August 27, psychologists present a new theory for why neurotic unhappiness and creativity go hand-in-hand. The authors argue that the part of the brain responsible for self-generated thought is highly active in neuroticism, which ...
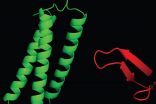
Researchers at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute at Virginia Tech have uncovered key cellular functions that help regulate inflammation -- a discovery that could have important implications for the treatment of allergies, heart disease, and certain forms of cancer.
The discovery, to be published in the Oct. 6 issue of the journal Structure, explains how two particular proteins, Tollip and Tom1, work together to contribute to the turnover of cell-surface receptor proteins that trigger inflammation.
"The inflammatory response can be a double-edged sword," said Daniel ...
Mobility between different physical environments in the cell nucleus regulates the daily oscillations in the activity of genes that are controlled by the internal biological clock, according to a study that is published in the journal Molecular Cell. Eventually, these findings may lead to novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of diseases linked with disrupted circadian rhythm.
So called clock-controlled - or circadian - genes are part of the internal biological clock, allowing humans and other light-sensitive organisms to adjust their daily activity to the cycle ...
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - When a large combat unit, widely dispersed in dense jungle, goes to battle, no single soldier knows precisely how his actions are affecting the unit's success or failure. But in modern armies, every soldier is connected via an audio link that can instantly receive broadcasts - reporting both positive and negative surprises - based on new intelligence. The real-time broadcasts enable dispersed troops to learn from these reports and can be critical since no solider has an overview of the entire unit's situation.
Similarly, as neuroscientists at Cold ...
LA JOLLA--Every organism--from a seedling to a president--must protect its DNA at all costs, but precisely how a cell distinguishes between damage to its own DNA and the foreign DNA of an invading virus has remained a mystery.
Now, scientists at the Salk Institute have discovered critical details of how a cell's response system tells the difference between these two perpetual threats. The discovery could help in the development of new cancer-selective viral therapies and may help explain why aging and certain diseases seem to open the door to viral infections.
"Our ...
Working with human cancer cell lines and mice, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and elsewhere have found a way to trigger a type of immune system "virus alert" that may one day boost cancer patients' response to immunotherapy drugs. An increasingly promising focus of cancer research, the drugs are designed to disarm cancer cells' ability to avoid detection and destruction by the immune system.
In a report on the work published in the Aug. 27 issue of Cell, the Johns Hopkins-led research team says it has found a core group of genes related to both ...