(Press-News.org) Washington, DC - September 4, 2015 - Decontamination protocols eradicated both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and antibiotic resistant, pathogenic intestinal bacteria, the Enterobacteriaceae, from a pig farm. The research appears online September 4th in ASM's journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The study involved a farm on which both pathogens had been discovered through routine monitoring. The farmer had approached the investigators for help. The Enterobacteriaceae were expressing resistance genes called extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL-E). β-lactamases disable a broad, very important class of antibiotics called β-lactams, which inhibit bacterial wall synthesis.
For their part, the investigators wanted to find out whether intensive decontamination performed by a commercially available service would effectively expunge the pathogens contaminating the farm environment. They collected samples at different time points both before and after decontamination, from the pigs, the air, water, and manure, and from the farm personnel. "Later, we compared the time points and the different media to evaluate the efficacy and durability of the decontamination measures on the farm," said corresponding author Isabelle Bekeredjian-Ding, MD, MPH, Head of Microbiology, Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, the German Federal regulatory agency for Vaccines and Biomedicines, Langen, Germany.
Following decontamination, the investigators could no longer detect the MRSA and ESBL-E strains of bacteria in the farm environment, in the farm personnel, or on the new pigs that repopulated the stables, said Bekeredjian-Ding.
"However, we found a new MRSA strain that we had never detected previously, said Bekeredjian-Ding. "This strain colonized the pigs and contaminated the environment just two days after the arrival of the new pigs." The investigators also found the new strain colonizing the noses of farmworkers. Thus, the major challenge to farm hygiene may be preventing reintroduction of a new or old resistant strain from an external source, said first author Ricarda M. Schmithausen, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital Bonn Institute of Medical Microbiology, Immunology and Parasitology.
A year after decontamination, the farmer told the investigators that the farm had been able to greatly reduce use of antibiotics, that incidence of diarrhea among the animals had dropped to zero, and that the mortality rate among piglets had fallen below two percent. Thus, despite its high cost, decontamination had resulted in significant benefits to the farm, said coauthor Brigitte Petersen, Professor and Head of Preventive Health Management at the Agricultural Faculty, the University of Bonn.
Decontaminating the pig farm involved high pressure cleaning and then drying the stables, followed by treatment with a complex solution containing amphoteric surfactants and complexing agents. That was followed by a two day-long disinfection process using a complex formula that comprised formaldehyde and dimethyl ammonium chloride, as well as other compounds. Finally, the manure pit, ventilation system, and feeding installation were nebulized for 48 hours at 1,000o C. The process also included constructing new stables, from metal and plastic, which are more easily disinfected than wooden structures.
"Our results show that the control of MRSA colonization can be achieved with basic but rather aggressive infection control measures," the investigators conclude.
INFORMATION:
The American Society for Microbiology is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications and educational opportunities. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - Sept. 4, 2015 - A commonly prescribed antidepressant may alter brain structures in depressed and non-depressed individuals in very different ways, according to new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
The study - conducted in nonhuman primates with brain structures and functions similar to those of humans - found that the antidepressant sertraline, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) marketed as Zoloft, significantly increased the volume of one brain region in depressed subjects but decreased the volume of two brain areas in ...
Far above the wildfires raging in Washington's forests, a less noticeable consequence of this dry year is taking place in mountain ponds. The minimal snowpack and long summer drought that have left the Pacific Northwest lowlands parched also affect the region's amphibians due to loss of mountain pond habitat.
According to a new paper published Sept. 2 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, this summer's severe conditions may be the new normal within just a few decades.
"This year is an analog for the 2070s in terms of the conditions of the ponds in response to climate," ...
The misery of motion sickness could be ended within five to ten years thanks to a new treatment being developed by scientists.
The cause of motion sickness is still a mystery but a popular theory among scientists says it is to do with confusing messages received by our brains from both our ears and eyes, when we are moving.
It is a very common complaint and has the potential to affect all of us, meaning we get a bit queasy on boats or rollercoasters. However, around three in ten people experience hard-to-bear motion sickness symptoms, such as dizziness, severe nausea, ...
This news release is available in Japanese.
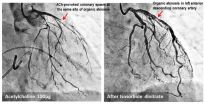
Researchers at Kumamoto University in Japan have found that patients with coronary spasm have a higher risk of experiencing future heart attack particularly when a spasm occurs at the site of atherosclerotic coronary artery narrowing, i.e., coronary atherosclerotic stenosis.
Angina is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart, and vasospastic angina patients account for about 40% of all angina patients. The incidence and progression of the disease can be reduced through appropriate drug treatment ...
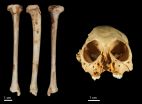
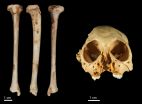
ALLENDALE, Mich. -- An international team of scientists, including a Grand Valley State University professor and alumni, recently discovered a species of monkey fossil the team has dated to be more than one million years old.
The discovery was made after the team recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The species was roughly the size of a small cat, dwelled in trees, and lived largely on a diet of fruits and leaves.
"We know that there ...
As climate change accelerates ice melt in the Arctic, polar bears may find caribou and snow geese replacing seals as an important food source, shows a recent study published in the journal PLOS ONE. The research, by Linda Gormezano and Robert Rockwell at the American Museum of Natural History, is based on new computations incorporating caloric energy from terrestrial food sources and indicates that the bears' extended stays on land may not be as grim as previously suggested.
"Polar bears are opportunists and have been documented consuming various types and combinations ...
Natural wonders like tumbling waterfalls, jutting rock faces and banks of wildflowers have long drawn visitors to America's national parks and inspired efforts to protect their beauty.
According to a study published Sept. 4 in Park Science, visitors also value and seek to protect a different kind of threatened natural resource in the parks: dark nighttime skies.
Almost 90 percent of visitors to Maine's Acadia National Park interviewed for the study agreed or strongly agreed with the statements, "Viewing the night sky is important to me" and "The National Park Service ...
(Boston)--Patients with spinal stenosis (SS) experienced good short term benefit, lasting from weeks to months, after receiving epidural steroid injections (ESI).
These findings, which appear in a letter in the journal Pain Medicine, contradict a previously published New England Journal Medicine (NEJM) study that found epidural steroid injections were not helpful in spinal stenosis cases.
It has been one year since the publication of "A Randomized Trial of Epidural Glucocorticoid Steroid Injections for Spinal Stenosis." This was a large scale clinical trial evaluating ...
An international team of scientists have dated a species of fossil monkey found across the Caribbean to just over 1 million years old.
The discovery was made after the researchers recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
In a paper published this week in the well renowned international journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the team use three-dimensional ...
Tropical Storm Kevin's center was several hundred miles south-southwest of Baja California when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw some associated high clouds streaming over the peninsula.
The MODIS and the AIRS instruments aboard Aqua captured visible and infrared images of Kevin on September 3 at 20:50 UTC (4:50 p.m. EDT). The visible image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided look at Kevin's clouds. MODIS showed a somewhat elongated tropical storm with a fragmented band of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level ...