(Press-News.org) UC San Francisco has received a National Cancer Institute grant of $5 million over the next five years to lead a massive effort to integrate the data from all experimental models across all types of cancer. The web-based repository is an important step in moving the fight against cancer toward precision medicine.
The goal is to accelerate cancer research to improve the way we diagnose, treat and conduct further research on the disease. The resulting database, called the Oncology Models Forum (OMF), will be accessible to researchers through the National Institutes of Health, to encourage scientists to use existing validated cancer models, rather than creating new ones.
"There are incredible new discoveries happening in cancer research today, such as detecting cancer cells and DNA in the blood stream, and even harnessing the immune system to fight cancers," said Atul Butte, MD, PhD, director of the Institute for Computational Health Sciences at UCSF and principal investigator for the grant. "These research methodologies generate enormous amounts of data that can and should be harnessed by researchers and engineers to yield new drugs and diagnostics."
Cell lines and mice have been placeholders for studying human cancer for decades, resulting in thousands of mouse models for all cancer types. While results from those studies are chronicled in scientific papers and journals, it is difficult to know how relevant the data from these experimental systems are to the actual research and development of drugs and diagnostics in actual human cancers.
This is particularly important, Butte said, because there can be a gap of up to 10 years between the early basic science discoveries from experimental systems and the actual clinical trial of the drug candidates that are developed from that science, with many drug candidates failing in those clinical trials. As a result, it is critically important to ensure that early scientific discoveries are in fact relevant to human cancers, to provide every possible hope that the eventual drugs developed from those discoveries will work in clinical trials and be available to cancer patients.
The project aims to create an online cache of molecular data that oncologists and cancer researchers could use to validate the current models that best translate to humans, make predictions about the disease and move toward a collaborative, precision medicine approach to cancer. Ultimately, Butte said, the effort also has the potential to create computer-based cancer models that greatly reduce the need for using animals in research.
The project, led by the UCSF Institute for Computational Health Sciences, will collaborate with Alejandro Sweet-Cordero, MD, Julien Sage, PhD, and Nigam Shah, PhD, at Stanford University, who will provide support with the latest genetically-engineered cancer models, as well as standardized nomenclatures. It also will include bioinformatics specialists from the Northrop Grumman Corp., who will help build and maintain the online database.
INFORMATION:
UC San Francisco (UCSF) is a leading university dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. It includes top-ranked graduate schools of dentistry, medicine, nursing and pharmacy, a graduate division with nationally renowned programs in basic, biomedical, translational and population sciences, as well as a preeminent biomedical research enterprise and two top-ranked hospitals, UCSF Medical Center and UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital San Francisco.
Current drugs may stop working against the most common type of brain tumor in children, medulloblastoma, but the tumor could be targeted in a new way, according to Stanford University scientists.
In research to be published in the journal eLife, a team led by Prof. Matthew P. Scott at the University's School of Medicine tested a drug called Roflumilast in mice with a brain tumor that is resistant to Vismodegib, the drug in current use. Roflumilast is normally used to treat inflammatory lung diseases. It dramatically inhibited tumor growth from the first day of treatment. ...
This news release is available in French.
Montreal, September 15th 2015 - It is estimated that half of all cancer patients suffer from a muscle wasting syndrome called cachexia. Cancer cachexia impairs quality of life and response to therapy, which increases morbidity and mortality of cancer patients. Currently, there is no approved treatment for muscle wasting but a new study from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) and University of Alberta could be a game changer for patients, improving both quality of life and longevity. The ...
To better inform the tradeoffs involved in land use choices around the world, experts have assessed the value of ecosystem services provided by land resources such as food, poverty reduction, clean water, climate and disease regulation and nutrients cycling.
Their report today estimates the value of ecosystem services worldwide forfeited due to land degradation at a staggering US $6.3 trillion to $10.6 trillion annually, or the equivalent of 10-17% of global GDP.
Furthermore, the problem threatens to force the migration of millions of people from affected areas. ...
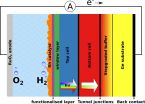
Solar energy is abundantly available globally, but unfortunately not constantly and not everywhere. One especially interesting solution for storing this energy is artificial photosynthesis. This is what every leaf can do, namely converting sunlight to chemical energy. That can take place with artificial systems based on semiconductors as well. These use the electrical power that sunlight creates in individual semiconductor components to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. Hydrogen possesses very high energy density, can be employed in many ways and could replace fossil ...
Amsterdam, NL, September 9, 2015 - The potential benefits of dietary cocoa extract and/or its final product in the form of chocolate have been extensively investigated in regard to several aspects of human health. Cocoa extracts contain polyphenols, which are micronutrients that have many health benefits, including reducing age-related cognitive dysfunction and promoting healthy brain aging, among others.
Dr. Giulio Maria Pasinetti, MD, PhD, Saunders Family Chair and Professor of Neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Director of Biomedical Training ...
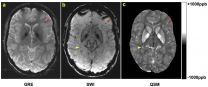
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Imaging patients soon after traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs can lead to better (more accurate) detection of cerebral microhemorrhages, or microbleeding on the brain, according to a study of military service members, published online in the journal Radiology.
Cerebral microhemorrhages occur as a direct result of TBI and can lead to severe secondary injuries such as brain swelling or stroke. The ability to monitor the evolution of microhemorrhages could provide important information regarding disease progression or recovery.
According to the Centers ...
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (SEPTEMBER 15, 2015). Management of Myelomeningocele Study (MOMS) investigators analyzed updated data on the effects of prenatal myelomeningocele closure on the need for placement of a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt within the first 12 months of life. These researchers reaffirm the initial MOMS finding that prenatal repair of a myelomeningocele results in less need for a shunt at 12 months and introduce the new finding that prenatal repair reduces the need for shunt revision in those infants who do require shunt placement. The researchers also found ...
In what is believed to be the largest, most detailed study of its kind in the United States, scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center and elsewhere have confirmed that tiny chemical particles in the air we breathe are linked to an overall increase in risk of death.
The researchers say this kind of air pollution involves particles so small they are invisible to the human eye (at less than one ten-thousandth of an inch in diameter, or no more than 2.5 micrometers across).
In a report on the findings, published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives online Sept. ...
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, September 15, 2015 -- Prolonged sitting time as well as reduced physical activity contribute to the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a study of middle-aged Koreans. These findings support the importance of both reducing time spent sitting and increasing physical activity, say researchers. Their results are published in the Journal of Hepatology.
Physical activity is known to reduce the incidence and mortality of various chronic diseases. However, more than one half of the average person's waking day involves sedentary ...
PHILADELPHIA -- Recent data suggest that epigenetic therapies are likely to provide additional clinical benefit to cancer patients when rationally combined with immunotherapeutic drugs, according to a review published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"The term epigenetics refers to the study of cellular changes in gene expression that are heritably transmitted during cell replication," said Michele Maio, MD, PhD, chair of medical oncology and immunotherapy, Ospedale Santa Maria alle Scotte, Istituto Toscano Tumori, ...