Low risk of severe COVID-19 in children
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Sweden kept preschools, primary and lower secondary schools open during the spring of 2020. So far, little research has been done on the risk of children being seriously affected by COVID-19 when the schools were open. A study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has now shown that one child in 130,000 was treated in an intensive care unit on account of COVID-19 during March-June. The study has been published in New England Journal of Medicine.
So far, more than 80 million people have become ill with COVID-19 and globally, almost two million people have died from the disease. Many countries have closed down parts of society in order to reduce the spread of infection. One such measure has been to close schools.
According to the United Nations body UNESCO, schools in 195 countries have been fully or partially closed. Even now, hundreds of millions of children around the globe are unable to go to their schools because of enforced closures.
In Sweden, distance learning was put in place for upper secondary schools but not for preschools, primary or lower secondary schools which instead remained open.
So far, there have been no data on how open schools affect the risk of children being seriously affected by COVID-19. Because of that, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have conducted a registry study to find out how many children aged 1-16 years were treated in an intensive care unit for COVID-19 or for multi-inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) which has been linked to COVID-19.
Between 1 March and 30 June 2020, 15 children with COVID-19 or MIS-C were treated in intensive care units in Sweden.
"That is the equivalent of 0.77 intensive care patients per 100,000 children in that age group. Four of the children had underlying diseases. None of the children died within two months after their period of intensive care," says Jonas F. Ludvigsson, paediatrician at Örebro University Hospital, Professor at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, and the first author of the study.
Seven of the 15 children had MIS-C. Four children needed invasive mechanical ventilation. The most common length of time in an intensive care unit was four days.
"It is very gratifying that serious COVID-19, defined here as needing treatment in an intensive care unit, is so rare among children despite schools being open during the pandemic. The next step will be to follow up the children who were treated in an intensive care unit for COVID-19 to see if they have recovered fully. My gut feeling is that children who have been seriously ill because of MIS-C seem to recover fully eventually," says Jonas F. Ludvigsson.
This study was made possible through collaboration between the Swedish Intensive Care Registry and the Swedish Paediatric Rheumatology Registry. Jonas F. Ludvigsson is managing an unrelated study on behalf of the Swedish Quality Registry for IBD, SWIBREG. There are no other reported conflicts of interests.
INFORMATION:
Publication: "Open schools, COVID-19 and child and teacher morbidity: A nationwide study." Jonas F. Ludvigsson, Lars Engerström, Charlotta Nordenhäll, Emma Larsson. New England Journal of Medicine, online 6 January 2021, doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2026670.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-07
Men and women aged over 50 can reap similar relative benefits from resistance training, a new study led by UNSW Sydney shows.
While men are likely to gain more absolute muscle size, the gains relative to body size are on par to women's.
The findings, recently published in END ...
2021-01-07
Social media misinformation can negatively influence people's attitudes about vaccine safety and effectiveness, but credible organizations -- such as research universities and health institutions -- can play a pivotal role in debunking myths with simple tags that link to factual information, University of California, Davis, researchers, suggest in a new study.
Researchers found that fact-check tags located immediately below or near a post can generate more positive attitudes toward vaccines than misinformation alone, and perceived source expertise makes a difference.
"In fact, fact-checking labels ...
2021-01-07
An international team of researchers led by Swinburne University of Technology has demonstrated the world's fastest and most powerful optical neuromorphic processor for artificial intelligence (AI), which operates faster than 10 trillion operations per second (TeraOPs/s) and is capable of processing ultra-large scale data.
Published in the prestigious journal Nature, this breakthrough represents an enormous leap forward for neural networks and neuromorphic processing in general.
Artificial neural networks, a key form of AI, can 'learn' and perform complex operations with wide applications to computer vision, natural language processing, facial recognition, speech translation, ...
2021-01-07
El Niño events have long been perceived as a driver for low rainfall in the winter and spring in Hawai'i, creating a six-month wet-season drought. However, a recent study by researchers in the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) revealed the connection between Hawai'i winter rainfall and El Niño is not as straightforward as previously thought.
Studies in the past decade suggested that there are at least two types of El Niño: the Eastern Pacific and Central Pacific, when the warmest pool of water is located in the eastern or central portions of the ocean basin, respectively. El Niño events usually ...
2021-01-07
WASHINGTON--Black and Hispanic people with COVID-19 and diabetes are more likely than Caucasians to die or have serious complications, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. ...
2021-01-07
With an estimated lifespan between 25 to 40 years, the queen conch (Strombus gigas) is a prized delicacy long harvested for food and is revered for its beautiful shell. Second only to the spiny lobster, it is one of the most important benthic fisheries in the Caribbean region. Unfortunately, the species faces a challenge of survival: how to endure and thrive, as populations are in a steady state of decline from overfishing, habitat degradation and hurricane damage. In some places, the conch populations have dwindled so low that the remaining conch cannot find breeding partners. This dire situation is urgent in ecological and economic terms.
To preserve this most significant molluscan fishery in the Caribbean, ...
2021-01-07
Osaka, Japan - Medical professionals all want to be able to quickly and correctly diagnose diseases. Their future ability to do so will depend on identifying what biochemicals are present in tissue sections, where the biomolecules are, and at what concentrations. For this purpose, mass spectrometry imaging--which can identify multiple biochemicals in a single experiment--will be useful. However, the stability of biomolecular sampling needs improvement to obtain the chemical distribution information with high spatial resolution.
In the recent study published in Analytical Chemistry, researchers from Osaka University used mass spectrometry to image the distribution of ...
2021-01-07
A scalpel-free alternative to brain surgery has the potential to benefit people with Parkinson's disease symptoms that are much more severe on one side of the body, new research suggests.
More testing is needed, but the approach, which uses a technology called focused ultrasound, could offer a new option for patients whose symptoms are poorly controlled by medications and those who cannot or do not wish to undergo traditional brain surgery.
"This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," ...
2021-01-07
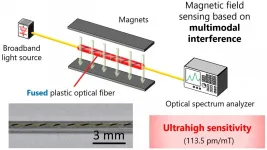
The invention of optical fibers has revolutionized not only telecommunications but also sensing technology. Optical fiber sensors can measure strain, temperature, pressure, and many other physical parameters along the fibers, but they are currently immune to electromagnetic noise -- interference from other external electric or magnetic interactions. It is a desirable trait, until the effect of the electromagnetic field on the fibers needs to be measured. Now, an international team of researchers has used what was previously considered a 'damaged' part of an optical fiber to develop such a magnetic field sensor.
They published details of their approach on Nov. 5 in Advanced Photonics Research.
"This nature of immunity ...
2021-01-07
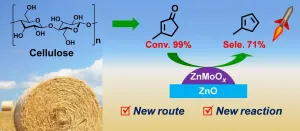
Methylcyclopentadiene (MCPD) is an important monomer in the production of RJ-4 fuel, a high-energy-density rocket fuel, and various valuable products.
Currently, MCPD is mainly obtained from the by-products of petroleum cracking tar at a very low yield of ~ 0.7 kg ton-1 and high price of ~10,000 USD ton-1. The exploration of highly efficient processes to convert renewable biomass to MCPD is stimulated by the energy and environment problems.
Recently, a group led by Prof. LI Ning and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) synthesized bio-based MCPD via direct hydrodeoxygenation of 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP) derived from cellulose.
Their study was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
The researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Low risk of severe COVID-19 in children