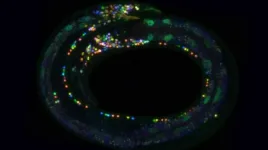
Possible explanation for more efficient maize growth
Biology: Publication in The Plant Cell
2021-01-08
(Press-News.org) Maize has a significantly higher productivity rate compared with many other crops. The particular leaf anatomy and special form of photosynthesis (referred to as 'C4') developed during its evolution allow maize to grow considerably faster than comparable plants. As a result, maize needs more efficient transport strategies to distribute the photoassimilates produced during photosynthesis throughout the plant.
Researchers at HHU have now discovered a phloem loading mechanism that has not been described before - the bundle sheath surrounding the vasculature as the place for the actual transport of compounds such as sugars or amino acids. The development of this mechanism could have been the decisive evolutionary step towards the higher transport rate that has made maize plants especially successful and useful. It is also likely linked to the more effective C4 photosynthesis used by maize compared with other plants, which only use C3 photosynthesis. The study was led by Dr. Ji Yun Kim and Prof. Dr. Wolf B. Frommer from the Institute of Molecular Physiology at HHU.
Plant leaves have different structures on the upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) sides, and each side performs different tasks. In maize, for example, sucrose transporters (SWEET) act in the `bundle sheath cells' (which frame the vascular bundle like a wreath) on the abaxial side of the leaf. In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, sugars released via SWEETs from phloem parenchyma cells are transported directly into the neighbouring companion cells via active transport. In maize, sugar is released in the direction of phloem by two large bundle sheath cells. The large surface of the bundle sheath cells compared to phloem parenchyma allows much higher transport rates. Compared to Arabidopsis, maize could transport sugar more effectively.
Doctoral student and first author Margaret Bezrutczyk from HHU emphasize: "The bundle sheath cells arranged in a wreath look the same at first glance. The single cell sequencing approach we used made it possible for the first time to distinguish between different types of bundle sheath cells in a maize leaf. With this technology, we expect that more cell types, especially those in the vascular bundles will be discovered in the future."
Institute Head Prof. Frommer emphasizes the significance of the finding, saying: "Maize plants are extremely productive due to their C4 photosynthesis. It is conceivable that the productivity of rice or other crops can be increased by transferring the loading mechanism from maize to these crops."
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Margaret Bezrutczyk, Nora R. Zöllner, Colin P. S. Kruse, Thomas Hartwig, Tobias Lautwein, Karl Köhrer, Wolf B. Frommer and Ji-Yun Kim, Evidence for phloem loading via the abaxial bundle sheath cells in maize leaves, The Plant Cell, 2021
DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koaa055
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-08
A unifying explanation of the cause of autism and the reason for its rising prevalence has eluded scientists for decades, but a theoretical model published in the journal Medical Hypotheses describes the cause as a combination of socially valued traits, common in autism, and any number of co-occurring disabilities.
T.A. Meridian McDonald, PhD, a research instructor in Neurology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, has spent 25 years researching autism, from a time she could read literally every research paper on the topic in the 1990s until now, when there is an overload of such studies.
"Up until now there have been a lot of theories about the possible causes ...
2021-01-08
In a letter published in the December issue of the American Heart Association's medical journal Circulation a group of researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) dispute the most recent findings of the incidence of myocarditis in athletes with a history of COVID-19.
The Vanderbilt study, COVID-19 Myocardial Pathology Evaluation in AthleTEs with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (COMPETE CMR), found a much lower degree of myocarditis in athletes than what was previously reported in other studies.
"The differences in the findings are extremely important. The whole world paused after seeing the alarmingly high rates of myocardial inflammation and edema initially published," said ...
2021-01-08
Across the world, health care workers and high-risk groups are beginning to receive COVID-19 vaccines, offering hope for a return to normalcy amidst the pandemic. However, the vaccines authorized for emergency use in the U.S. require two doses to be effective, which can create problems with logistics and compliance. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a nanoparticle vaccine that elicits a virus-neutralizing antibody response in mice after only a single dose.
The primary target for COVID-19 vaccines is the spike protein, which is necessary for SARS-CoV-2's entry into ...
2021-01-08
In 2020, astronomers added a new member to an exclusive family of exotic objects with the discovery of a magnetar. New observations from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory help support the idea that it is also a pulsar, meaning it emits regular pulses of light.
Magnetars are a type of neutron star, an incredibly dense object mainly made up of tightly packed neutron, which forms from the collapsed core of a massive star during a supernova.
What sets magnetars apart from other neutron stars is that they also have the most powerful known magnetic fields in the universe. For context, the strength of our planet's magnetic field has a value of about one Gauss, while a refrigerator magnet measures about ...
2021-01-08
UC San Francisco scientists have discovered a new way to control the immune system's "natural killer" (NK) cells, a finding with implications for novel cell therapies and tissue implants that can evade immune rejection. The findings could also be used to enhance the ability of cancer immunotherapies to detect and destroy lurking tumors.
The study, published January 8, 2021 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, addresses a major challenge for the field of regenerative medicine, said lead author Tobias Deuse, MD, the Julien I.E. Hoffman, MD, Endowed Chair in Cardiac Surgery in the UCSF Department of Surgery.
"As a cardiac surgeon, I would love to put myself out of business by being able to implant healthy cardiac ...
2021-01-08
The SARS-CoV-2 virus was introduced to the United Kingdom well over 1,000 times in early 2020, according to researchers who analyzed more than 50,000 viral sequences from the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK. The virus lineages introduced before the UK's national lockdown in March tended to be larger and more geographically dispersed. Infectious disease epidemics are composed of chains of transmission, yet little is known about how co-circulating transmission lineages vary in size, spatial distribution and persistence. Understanding these features could help target interventions, track variants with different impacts on their human hosts, and more. The UK's COVID-19 epidemic during early 2020 was one of the world's largest. It was also well represented by virus genomic sampling, ...
2021-01-08
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons, or nerve cells, woven together by an estimated 100 trillion connections, or synapses. Each cell has a role that helps us to move muscles, process our environment, form memories, and much more.
Given the huge number of neurons and connections, there is still much we don't know about how neurons work together to give rise to thought or behavior.
Now Columbia scientists have engineered a coloring technique, known as NeuroPAL (a Neuronal Polychromatic Atlas of Landmarks), which makes it possible--at least in experiments with Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a worm species commonly used in biological ...
2021-01-08
Micro-CT scanning and digital reconstructions have been used to compare the skulls of the Tasmanian tiger (thylacine) and wolf across their early development and into adulthood, establishing that not only did the thylacine resemble the wolf as adults, but also as newborns and juveniles.
"Remarkably, the Tasmanian tiger pups were more similar to wolf pups than to other closely related marsupials," Professor Andrew Pask from the University of Melbourne said.
The collaborative study with Flinders University and Museums Victoria complement earlier findings that thylacine and wolf have evolved similar instructions in their genome, which influence cranial stem cells during development.
While ...
2021-01-08
The COVID-19 pandemic is raising fears of new pathogens such as new viruses or drug-resistant bacteria. To this, a Korean research team has recently drawn attention for developing the technology for removing antibiotic-resistant bacteria by controlling the surface texture of nanomaterials.
A joint research team from POSTECH and UNIST has introduced mixed-FeCo-oxide-based surface-textured nanostructures (MTex) as highly efficient magneto-catalytic platform in the international journal Nano Letters. The team consisted of professors In Su Lee and ...
2021-01-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists have figured out a cheaper, more efficient way to conduct a chemical reaction at the heart of many biological processes, which may lead to better ways to create biofuels from plants.
Scientists around the world have been trying for years to create biofuels and other bioproducts more cheaply; this study, published today in the journal Scientific Reports, suggests that it is possible to do so.
"The process of converting sugar to alcohol has to be very efficient if you want to have the end product be competitive with fossil fuels," said Venkat Gopalan, a senior author on the paper and professor of chemistry and biochemistry at The Ohio State University. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Possible explanation for more efficient maize growth
Biology: Publication in The Plant Cell