A 'ghastly future' unless extraordinary action is taken soon on sustainability
Global team of scientists, including UCLA's Daniel Blumstein, points to environmental, population and political challenges
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) Without immediate and drastic intervention, humans face a "ghastly future" -- including declining health, climate devastation, tens of millions of environmental migrants and more pandemics -- in the next several decades, according to an international team of 17 prominent scientists.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blue-light stride in perovskite-based LEDs
2021-01-13
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed efficient blue light-emitting diodes based on halide perovskites. "We are very excited about this breakthrough", says Feng Gao, professor at Linköping University. The new LEDs may open the way to cheap and energy-efficient illumination.
Illumination is responsible for approximately 20% of global electricity consumption, a figure that could be reduced to 5% if all light sources consisted of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The blue-white LEDs currently in use, however, need complicated manufacturing methods and are expensive, which makes it more difficult to achieve ...
Limits of atomic nuclei predicted
2021-01-13
Atomic nuclei are held together by the strong interaction between neutrons and protons. About ten percent of all known nuclei are stable. Starting from these stable isotopes, nuclei become increasingly unstable as neutrons are added or removed, until neutrons can no longer bind to the nucleus and "drip" out. This limit of existence, the so-called neutron "dripline", has so far been discovered experimentally only for light elements up to neon. Understanding the neutron dripline and the structure of neutron-rich nuclei also plays a key role in the research program for the future accelerator facility FAIR at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt.
In a new study, "Ab Initio Limits of Nuclei," ...
A new study identifies possible biomarkers of severe malaria in African children
2021-01-13
The levels of small molecules called microRNAs (miRNAs) circulating in blood could help identify early on children with life-threatening forms of malaria, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health, an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, in collaboration with the Manhiça Health Research Center (CISM) in Mozambique. The results, published in Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, could also help better understand the mechanisms underlying severe malaria.
Malaria mortality among young African children remains unacceptably high. To improve the outcome, it is important to rapidly identify and treat children with severe forms of the disease. ...
Seawater as an electrical cable !? Wireless power transfers in the ocean
2021-01-13
Overview:
Associate professor Masaya Tamura, Kousuke Murai (who has completed the first term of his master's program), and their research team from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have successfully transferred power and data wirelessly through seawater by using a power transmitter/receiver with four layers of ultra-thin, flat electrodes. In the field of wireless power transfers, seawater behaves as a dielectric with extremely high loss, and achievement through capacitive coupling is difficult. Up until now, it had been thought that wireless power transfers could only be achieved through magnetic coupling. ...
New molecular structures associated with ALS
2021-01-13
Researchers from the University of Seville and the University of Pavia have identified a link between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and the accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids in the genome. The accumulation of these hybrids causes increased genomic damage and boosts genetic instability. This finding will make it possible to better understand the molecular basis of the disease, as well as to propose new solutions to curb it.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system, characterised by progressive degeneration ...
Evolution in a test tube: these bacteria survive on deadly copper surfaces
2021-01-13
The descendants of regular wild-type bacteria can evolve to survive for a long time on metallic copper surfaces that would usually kill them within a few minutes. An international research team led by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Bundeswehr Institute of Microbiology was able to produce these tiny survivalists in the lab and has been able to study them more closely. The team reports on its findings in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics. However, in recent decades many pathogenic bacteria have developed an increasing tolerance to common drugs. So-called multidrug-resistant bacteria are of particular concern as ...
How will we achieve carbon-neutral flight in future?
2021-01-13
It is politically agreed and necessary for climate protection reasons that our entire economy becomes climate-neutral in the coming decades - and that applies to air travel, too. This is a technically feasible goal, and there are numerous ways to achieve it. ETH Professor Marco Mazzotti and his team have now compared the options that appear to be the easiest to implement in the short and medium term and evaluated them according to factors such as cost-effectiveness.
The ETH researchers conclude that the most favourable option is to continue powering aircraft with fossil fuels in future, but then remove the associated CO2 emissions from the atmosphere ...
TalTech's neuroscientists investigate the causes of a widespread eye disease
2021-01-13
Fuchs' corneal dystrophy is one of the most common eye diseases diagnosed in almost 5% of the population of Europe aged 40 years or over. It is a hereditary eye disease that causes vision impairment and typically manifests in middle age. The first symptoms of the disease - blisters on the surface of your cornea - resemble cataract at first glance. The disease progresses from the centre of the cornea affecting all layers of the cornea. The progression of the disease varies from individual to individual and in severe cases results in vision loss.
The molecular neurobiology ...
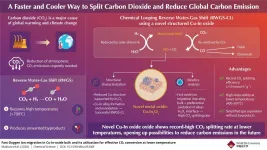
Copper-indium oxide: A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprint
2021-01-13
With ever-worsening climate change, there is a growing need for technologies that can capture and use up the atmospheric CO2 (carbon dioxide) and reduce our carbon footprint. Within the realm of renewable energy, CO2-based e-fuels have emerged as a promising technology that attempts to convert atmospheric CO2 into clean fuels. The process involves production of synthetic gas or syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO)). With the help of the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reaction, CO2 is broken down into the CO necessary for syngas. While promising in its conversion efficiency, the RWGS reaction requires incredibly high temperatures (>700°C) to proceed, while also generating ...
Lipid biomarkers in urine can determine the type of asthma
2021-01-13
In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used a urine test to identify and verify a patient's type of asthma. The study, which has been published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, lays the foundation for a more personalized diagnosis and may result in improved treatment of severe asthma in the future.
About 10 percent of the Swedish population suffers from asthma, a disease that has become increasingly widespread over the past 50 years, with annual global mortality of around 400,000 according to the World Health Organization. Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation in the airways, which can result in symptoms including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
[Press-News.org] A 'ghastly future' unless extraordinary action is taken soon on sustainabilityGlobal team of scientists, including UCLA's Daniel Blumstein, points to environmental, population and political challenges