Controlling pain after surgery doesn't have to mean opioids, study shows
Comparison of opioid-sparing approach with standard care shows no difference in patient satisfaction, but less pain among those counseled to use opioids only as backup
2021-01-27
(Press-News.org) As surgeons balance the need to control their patients' post-surgery pain with the risk that a routine operation could become the gateway to long-term opioid use or addiction, a new study shows the power of an approach that takes a middle way.
In a new letter in JAMA Surgery, a team from Michigan Medicine at the University of Michigan reports on findings from a study of 620 patients who had surgery in hospitals across Michigan, had their painkiller use tracked, and took surveys within one to three months after their operations.
Half of the patients received pre-surgery counseling that emphasized non-opioid pain treatment as their first option. Some patients in this group received small, "just in case" prescriptions, but a third of them didn't receive any opioid prescription at all after surgery.
The other patients received standard care - meaning they got the usual amount of opioids given after these operations. Not only did every patient in that group get an opioid prescription, those prescriptions tended to be larger than those in the other group. And most patients didn't take them all - leaving extra pills that can pose a hazard to the patient or others in their household if taken inappropriately, or diverted to illicit use.
The patients in the two groups had the same operations - gallbladder removal, full or partial thyroid removal or hernia repair. But despite the difference in painkiller use, the patients in both groups were equally satisfied with their care and reported similar quality of life when contacted later. And those in the opioid-sparing group actually reported experiencing less pain overall.
First author Maia Anderson, M.D., a resident in the U-M Department of Surgery, says, "It's so exciting to think about the potential for opioid sparing postoperative pathways to not only reduce the risk of opioids for our patients, but also to substantially decrease the risk of opioid diversion into our communities."
Senior author and surgical resident Ryan Howard, M.D., adds, "We know that opioids pose serious risks to patients after surgery. We can protect patients from those risks by reducing or eliminating opioids after surgery. But that idea always raises the concern that patients will have uncontrolled pain and feel miserable. This study suggests that's not the case - patients who get small opioid prescriptions, or even no prescription, are just as satisfied with their recovery after surgery."
Anderson and Howard worked with the three U-M Medical School faculty who direct the Michigan Opioid Prescribing and Engagement Network -- Chad Brummett, M.D., Jennifer Waljee, M.D., M.P.H., M.S. and Michael Englesbe, M.D. -- and with Alex Hallway, B.S., a member of the program's staff who coordinates the effort to right-size surgery-related opioid prescribing in Michigan. Michigan-OPEN has published evidence-based prescribing guidelines for many procedures, as well as materials to support opioid-sparing patient education.
The study used data from the Michigan Surgical Quality Consortium that is working to improve surgical care in 70 hospitals across Michigan. Anderson and Howard are fellows of the U-M Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-27
LA JOLLA--A new study led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) suggests that T cells try to fight SARS-CoV-2 by targeting a broad range of sites on the virus--beyond the key sites on the virus's spike protein. By attacking the virus from many angles, the body has the tools to potentially recognize different SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The new research, published January 27, 2021 in Cell Report Medicine, is the most detailed analysis so far of which proteins on SARS-CoV-2 stimulate the strongest responses from the immune system's "helper" CD4+ T cells and "killer" CD8+ T cells.
"We ...
2021-01-27
INDIANAPOLIS--Researchers at the Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified how breast cancer cells hide from immune cells to stay alive. The discovery could lead to better immunotherapy treatment for patients.
Xinna Zhang, PhD, and colleagues found that when breast cancer cells have an increased level of a protein called MAL2 on the cell surface, the cancer cells can evade immune attacks and continue to grow. The findings are published this month in The Journal of Clinical Investigation and featured on the journal's cover.
The lead author of the study, Zhang is a member of the ...
2021-01-27
Members of Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences are shining new light on an enduring mystery--one that is millions of years in the making.
A team of paleontologists led by Professor Cathryn Newton has increased scientists' understanding of whether Devonian marine faunas, whose fossils are lodged in a unit of bedrock in Central New York known as the Hamilton Group, were stable for millions of years before succumbing to waves of extinctions.
Drawing on 15 years of quantitative analysis with fellow professor Jim Brower (who died in 2018), Newton has continued to probe the structure of these ancient fossil communities, among the most renowned on Earth.
The group's findings, reported by the Geological Society of America (GSA), provide critical ...
2021-01-27
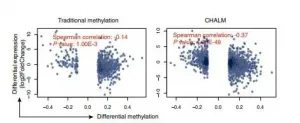
Irvine, CA - January 27, 2021 - A new University of California, Irvine-led study finds a new method for identifying biomarkers may aid in early cancer diagnosis. The study focused on lung cancer, however the Cell Heterogeneity-Adjusted cLonal Methylation (CHALM) method has been tested on aging and Alzheimer's diseases as well and is expected to be effective for studying other diseases.
"We found the CHALM method may be a valuable tool in helping researchers to identify more reliable differentially methylated genes from sequence-based methylation data," ...
2021-01-27
Doctors are increasingly using genetic signatures to diagnose diseases and determine the best course of care, but using DNA sequencing and other techniques to detect genomic rearrangements remains costly or limited in capabilities. However, an innovative breakthrough developed by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center and the VCU Department of Physics promises to diagnose DNA rearrangement mutations at a fraction of the cost with improved accuracy.
Led by VCU physicist Jason Reed, Ph.D., the team developed a technique that combines a process called digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) with high-speed atomic force microscopy (HSAFM) to create an image with such nanoscale resolution that users can measure differences in ...
2021-01-27
Historically redlined neighborhoods are more likely to have a paucity of greenspace today compared to other neighborhoods. The study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the University of California, Berkeley and San Francisco, demonstrates the lasting effects of redlining, a racist mortgage appraisal practice of the 1930s that established and exacerbated racial residential segregation in the United States. Results appear in Environmental Health Perspectives.
In the 1930s, the Home Owners' Loan Corporation (HOLC) assigned risk grades to neighborhoods across the country based on racial demographics and other factors. "Hazardous" areas--often those whose residents included people ...
2021-01-27
LAWRENCE -- For at least a century, ecologists have wondered at the tendency for populations of different species to cycle up and down in steady, rhythmic patterns.
"These cycles can be really exaggerated -- really huge booms and huge busts -- and quite regular," said Daniel Reuman, professor of ecology & evolutionary biology at the University of Kansas and senior scientist at the Kansas Biological Survey. "It attracted people's attention because it was kind of mysterious. Why would such a big thing be happening?"
A second observation in animal populations ...
2021-01-27
(Boston)--Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have identified proteins that are essential for the viability of whole genome doubled tumor cells, yet non-essential to normal cells that comprise the majority of human tissue.
"Exploiting these vulnerabilities represents a highly significant and currently untapped opportunity for therapeutic intervention, particularly because whole genome doubling is a distinguishing characteristic of many tumor types," said corresponding author Neil J. Ganem, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology and medicine, section of hematology and medical oncology, at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM).
The vast majority of human cells are diploid, meaning that they possess two copies of each ...
2021-01-27
The Asia Pacific Consortium on Osteoporosis (APCO) has today launched the first pan-Asia Pacific clinical practice standards for the screening, diagnosis, and management of osteoporosis, targeting a broad range of high-risk groups.
Published in Osteoporosis International today, 'The APCO Framework' comprises 16 minimum clinical standards set to serve as a benchmark for the provision of optimal osteoporosis care in the region.
Developed by APCO members representing key osteoporosis stakeholders, and multiple medical and surgical specialities, this set of clear, concise, relevant and pragmatic clinical standards aims to support national societies, guidelines development authorities, and health care policy makers with ...
2021-01-27
People who take opioid medications for chronic pain may have a hard time finding a new primary care clinic that will take them on as a patient if they need one, according to a new "secret shopper" study of hundreds of clinics in states across the country.
Stigma against long-term users of prescription opioids, likely related to the prospect of taking on a patient who might have an opioid use disorder or addiction, appears to play a role, the University of Michigan research suggests.
Simulated patients who said their doctor or other primary care provider had retired were more likely to be told they could be accepted as new patients, compared with those who said their provider had stopped prescribing opioids to them for an unknown reason.
The U-M primary care provider ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Controlling pain after surgery doesn't have to mean opioids, study shows
Comparison of opioid-sparing approach with standard care shows no difference in patient satisfaction, but less pain among those counseled to use opioids only as backup