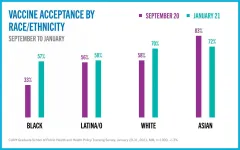(Press-News.org) Wolves are arguably the most well-studied large predators in the world, yet new research shows there is still a lot to learn about their hunting tactics. Typically, wolves hunt large mammals like moose, deer, and bison in packs by outrunning, outlasting, and exhausting their prey. However, throughout the dense boreal forests in North America and Eurasia, during the summer wolves often hunt beavers by themselves.
But how does a wolf catch a semi-aquatic prey that spends little time on land and never ventures far from the safety of its pond? Turns out with patience, and a lot of waiting.
In a new paper published in the journal Behavioral Ecology, researchers from the University of Minnesota and the Voyageurs Wolf Project--which studies wolves in the Greater Voyageurs Ecosystem in the northwoods of Minnesota--show that wolves have evolved ambush hunting tactics specifically tailored for catching and killing beavers.
"Over a five-year period, we estimate that our field research team collectively put in over 15,000 person-hours to search nearly 12,000 locations where wolves had spent time. Through this effort, we ended up documenting 748 locations where wolves waited to ambush beavers but were unsuccessful, and 214 instances where wolves killed beavers," said Sean Johnson-Bice, a co-author of the study. "This dedicated fieldwork has provided unprecedented insight into the hunting tactics wolves use in boreal environments."
Beavers have extremely poor eyesight, so they rely primarily on their well-developed sense of smell to detect predators on land--and wolves appear to have learned this through time. Researchers discovered wolves choose ambushing sites within a few feet of where beavers are active on land because wolves have learned beavers cannot visually detect them. When doing so, wolves almost always choose ambushing sites that are downwind to avoid being smelled by beavers.
"The results are very clear," said Tom Gable, the study's lead-author: "89-94% of the ambushing sites were downwind, where beavers were likely unable to smell wolves."
When staking out beavers, wolves appear to be surprisingly patient. They spend substantial periods of time waiting next to areas where beavers are active on land, such as near beaver dams and trails.
"Wolves waited an average of four hours during each stakeout. But they often waited eight-12 hours or more, and one wolf even waited-in-ambush for 30 hours," said study co-author Austin Homkes.
The researchers note that these behaviors were not unique to a few wolves. Instead, wolves from multiple packs across several years used the same ambushing tactics, indicating that this behavior is widespread throughout the Greater Voyageurs Ecosystem and likely other ecosystems where wolves hunt beavers. Notably, wolves and beavers co-occur across much of the Northern Hemisphere so the implications have wide applicability.
"Gathering data to demonstrate how wind direction influences the ambushing behavior of predators has been difficult for animal ecologists," said co-author Joseph Bump. "Scientists have long-thought that ambush predators are able to strategically choose ambush sites in areas where prey are unable to detect them via scent. Until now though, documenting these hunting tactics in exhaustive detail proved extremely challenging."
Ultimately, the study challenges the classic concept that wolves are solely cursorial predators (i.e., predators that kill their prey by outrunning and outlasting them). Instead, wolf-hunting strategies appear highly flexible, and they are able to switch between hunting modes (cursorial and ambush hunting) depending on their prey.
"It is the first systematic analysis of wolf ambushing behavior," said Gable. "It overturns the traditional notion that wolves rely solely on hunting strategies that involve pursuing, testing, and running down prey."
INFORMATION:
CHICAGO: Elderly patients (70 years and over) with locally advanced esophageal (E) and esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer (located in the stomach and esophagus) should be considered for optimal therapy that has the potential to cure. This therapy regimen includes initial chemoradiotherapy (NACR) and surgical resection, an operation that removes the cancerous part of the organ.
According to researchers, this recommended therapy is often not offered to elderly patients out of concern that they will not tolerate such an intensive treatment regimen. In a new study, they found that older patients who received the therapy had outcomes comparable with those of younger patients (under 70 years old). The single-institution study from the Ochsner Clinic Foundation and The University of ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study finds that providing people who have recently given birth access to long-acting reversible methods of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and contraceptive implants, could help prevent them from unintentionally falling pregnant in the following months.
The study -- which analyzed the effects of a 2012 Medicaid policy implemented in South Carolina -- found that expanded access to particular forms of birth control were especially helpful in preventing unintended pregnancies among adolescents who had just given birth, giving them more control over their own futures.
"The ...
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Feb. 9, 2021) -- Scientists have devised a new approach for detecting and potentially heading off the effects of two rare pediatric diseases before birth.
The study, performed in mouse models of the diseases and published today in Cell Reports, represents an important step toward much-needed early interventions for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome.
Both diseases result in growth-related symptoms in children and often lead to additional problems later in life, such as increased cancer risk from Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome ...
The research team of NUST MISIS has presented an improved structure of perovskite solar cells. Scientists have modified perovskite-based solar cells using MXenes -- thin two-dimensional titanium carbides with high electrical conductivity. The MXenes-based modified cells showed superior performance, with power conversion efficiency exceeding 19% (the reference demonstrated 17%) and improved stabilized power output with respect to reference devices. The results have been published in the Nano energy international scientific journal.
Perovskite solar cells ...
Women whose household drinking water contained nitrate had babies that weighed, on average, 10 grams less than babies born to mothers where household water had no detectible nitrate, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and Aarhus University.
The study, which is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, followed pregnant women living in Denmark. The researchers found that even low nitrate levels -- about half of the allowable level set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, or EPA -- caused an adverse effect.
"While ...
Under the Biden Administration, New Yorkers' acceptance of the Covid-19 vaccine has increased significantly. In September, 55% of residents reported they would take the vaccine when it became available and this January, 64% reported they would take it.
Differences in vaccine acceptance persist across racial and ethnic groups. Among Whites and Asians acceptance is 70-72%; among Blacks and Latina/os it is 57-58%. On a positive note, the largest increase in rate of acceptance was seen among Black respondents, up from 33% in September to 57% in January.
These are key findings from the most recent tracking survey of public perceptions and experiences in New York City during the Covid-19 pandemic, conducted January 29-31 by the City University of New York Graduate School of ...
The colors in a flower patch appear completely different to a bear, a honeybee, a butterfly and humans. The ability to see these colors is generated by specific properties of opsins - light-sensitive proteins in the retina of our eyes. The number of opsins expressed and the molecular structure of the receptor proteins determines the colors we see.
In a paper published February 9 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a team of researchers led by Harvard University develop a novel method to express long wavelength invertebrate opsin proteins in vitro and detail the molecular structure of redshift (long-wavelength) ...
In 2018, a faulty electric transmission line ignited the Camp Fire in Northern California, ultimately consuming 239 square miles and several communities, including the town of Paradise, which was 95 percent destroyed. At least 85 people died.
Structures have been rebuilt, but some things are worse. In a paper published February 2, 2021 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, scientists at University of California San Diego, with colleagues elsewhere, describe chronic mental health problems among some residents who experienced the Camp Fire in varying degrees.
Direct exposure to large-scale fires significantly ...
Photoionization of water involves the migration and solvation of electrons, with many transient and highly active intermediates. The process results in a large blue shift in the absorption spectrum, from the THz or gigahertz region to the visible range. While the behavior of low-density quasifree electrons excited by small pump power density has been investigated extensively, we still know little about the transient evolution of photoexcited plasma in liquid water. Valuable insights were recently provided by an international research team in a study published in Advanced Photonics.
According to Liangliang Zhang, physics professor at Capital Normal University in Beijing and one of the senior authors on the study, the physical mechanism of plasma evolution on the ...
The structure of organic substances tetrahydroisoquinolines (THIQ) includes a benzene ring fused with a nitrogen-containing cycle. These compounds are in high demand in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of myorelaxants, antidepressants, and drugs against hypertension, cough, and insomnia. Although different variations of THIQ structures can be found in natural sources (for example, as parts of phytotoxins), modern-day pharmaceutical manufacturers are also interested in their rare types, such as spirocyclic THIQs. In their molecules, two adjacent cycles share one common atom, thus creating an unusual and very stable 3D structure. This feature ...