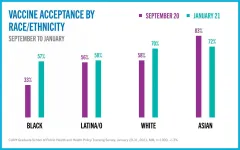Long-term environmental damage from transportation projects in Kenya, scientists warn
2021-02-09
(Press-News.org) The construction of a major railway through Kenya will have long-term environmental impacts on the area, suggesting more work needs to be done to limit the damage on future infrastructure projects, a major study reveals.
The biggest impact of the Standard Gauge Railway (SGR), which runs from Mombasa to Nairobi, was pollution and contamination of soil, water and air, as well as disruption of natural processes.
The research, led by the University of York and part of the Development Corridors Partnership project, also showed environmental issues as a result of breaking up large areas of habitat into smaller, more isolated patches, that may not be able to support long-term natural processes.
The SGR project was given the go-ahead following the completion of two Environmental and Social Impact Assessments, but scientists question how effectively recommendations were implemented in the development, given the evidence of widespread environmental degradation that can be seen in the area.
Professor Robert Marchant, from the University of York's Department of Environment and Geography, said: "African nations are looking forward to large-scale infrastructure investment as a catalyst for economic growth, but our research shows that before this can happen more work is needed to quantify ecological impacts on the land.
"Not only this, but should issues arises once the projects are complete, there must be a ready-to-go mitigation strategy that can be applied to reduce further damage quickly."
The researchers recommend that environmental impacts are integrated into the planning of largescale infrastructure projects at every stage, and call for a particular focus on engaging and consulting key stakeholders in the design and implementation phases of the project.
Dr Tobias Nyumba, Post-Doctoral Researcher at the Development Corridors Partnership, said: "These steps are essential, if a 'transportation corridor' is to become a true 'development corridor', bringing sustainable development and social wellbeing to a country such as Kenya, while minimizing or eliminating environmental damage."
INFORMATION:
As part of the Development Corridors Partnership, which aims to address environmental concerns about large development areas, researchers continue to work with a wide-range of East African and Chinese developers to improved thinking around sustainability.
The paper, funded by Global Challenges Research Fund, is published in the PlosOne journal.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-09
A multi-institutional team became the first to generate accurate results from materials science simulations on a quantum computer that can be verified with neutron scattering experiments and other practical techniques.
Researchers from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory; the University of Tennessee, Knoxville; Purdue University and D-Wave Systems harnessed the power of quantum annealing, a form of quantum computing, by embedding an existing model into a quantum computer.
Characterizing materials has long been a hallmark of classical supercomputers, which encode information using a binary system of bits that are each assigned a value of either 0 or 1. But quantum computers -- in this case, D-Wave's 2000Q - rely on qubits, which can be valued at ...
2021-02-09
Wolves are arguably the most well-studied large predators in the world, yet new research shows there is still a lot to learn about their hunting tactics. Typically, wolves hunt large mammals like moose, deer, and bison in packs by outrunning, outlasting, and exhausting their prey. However, throughout the dense boreal forests in North America and Eurasia, during the summer wolves often hunt beavers by themselves.
But how does a wolf catch a semi-aquatic prey that spends little time on land and never ventures far from the safety of its pond? Turns out with patience, and a lot of waiting.
In a new paper published in the journal Behavioral Ecology, researchers from the University of Minnesota and the Voyageurs Wolf Project--which ...
2021-02-09
CHICAGO: Elderly patients (70 years and over) with locally advanced esophageal (E) and esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer (located in the stomach and esophagus) should be considered for optimal therapy that has the potential to cure. This therapy regimen includes initial chemoradiotherapy (NACR) and surgical resection, an operation that removes the cancerous part of the organ.
According to researchers, this recommended therapy is often not offered to elderly patients out of concern that they will not tolerate such an intensive treatment regimen. In a new study, they found that older patients who received the therapy had outcomes comparable with those of younger patients (under 70 years old). The single-institution study from the Ochsner Clinic Foundation and The University of ...
2021-02-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study finds that providing people who have recently given birth access to long-acting reversible methods of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and contraceptive implants, could help prevent them from unintentionally falling pregnant in the following months.
The study -- which analyzed the effects of a 2012 Medicaid policy implemented in South Carolina -- found that expanded access to particular forms of birth control were especially helpful in preventing unintended pregnancies among adolescents who had just given birth, giving them more control over their own futures.
"The ...
2021-02-09
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Feb. 9, 2021) -- Scientists have devised a new approach for detecting and potentially heading off the effects of two rare pediatric diseases before birth.
The study, performed in mouse models of the diseases and published today in Cell Reports, represents an important step toward much-needed early interventions for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome.
Both diseases result in growth-related symptoms in children and often lead to additional problems later in life, such as increased cancer risk from Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome ...
2021-02-09
The research team of NUST MISIS has presented an improved structure of perovskite solar cells. Scientists have modified perovskite-based solar cells using MXenes -- thin two-dimensional titanium carbides with high electrical conductivity. The MXenes-based modified cells showed superior performance, with power conversion efficiency exceeding 19% (the reference demonstrated 17%) and improved stabilized power output with respect to reference devices. The results have been published in the Nano energy international scientific journal.
Perovskite solar cells ...
2021-02-09
Women whose household drinking water contained nitrate had babies that weighed, on average, 10 grams less than babies born to mothers where household water had no detectible nitrate, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and Aarhus University.
The study, which is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, followed pregnant women living in Denmark. The researchers found that even low nitrate levels -- about half of the allowable level set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, or EPA -- caused an adverse effect.
"While ...
2021-02-09
Under the Biden Administration, New Yorkers' acceptance of the Covid-19 vaccine has increased significantly. In September, 55% of residents reported they would take the vaccine when it became available and this January, 64% reported they would take it.
Differences in vaccine acceptance persist across racial and ethnic groups. Among Whites and Asians acceptance is 70-72%; among Blacks and Latina/os it is 57-58%. On a positive note, the largest increase in rate of acceptance was seen among Black respondents, up from 33% in September to 57% in January.
These are key findings from the most recent tracking survey of public perceptions and experiences in New York City during the Covid-19 pandemic, conducted January 29-31 by the City University of New York Graduate School of ...
2021-02-09
The colors in a flower patch appear completely different to a bear, a honeybee, a butterfly and humans. The ability to see these colors is generated by specific properties of opsins - light-sensitive proteins in the retina of our eyes. The number of opsins expressed and the molecular structure of the receptor proteins determines the colors we see.
In a paper published February 9 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a team of researchers led by Harvard University develop a novel method to express long wavelength invertebrate opsin proteins in vitro and detail the molecular structure of redshift (long-wavelength) ...
2021-02-09
In 2018, a faulty electric transmission line ignited the Camp Fire in Northern California, ultimately consuming 239 square miles and several communities, including the town of Paradise, which was 95 percent destroyed. At least 85 people died.
Structures have been rebuilt, but some things are worse. In a paper published February 2, 2021 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, scientists at University of California San Diego, with colleagues elsewhere, describe chronic mental health problems among some residents who experienced the Camp Fire in varying degrees.
Direct exposure to large-scale fires significantly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Long-term environmental damage from transportation projects in Kenya, scientists warn