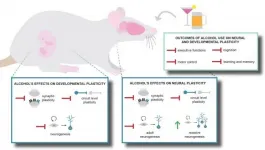
Adult neurogenesis may hold clues for more effective treatment of alcoholism
New research and analysis examine how alcohol exposure impacts many aspects of neuroplasticity in a special issue of Brain Plasticity
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, NL, February 10, 2021 - Neuroplasticity, the remarkable ability of the brain to modify and reorganize itself, is affected by or in response to excessive alcohol, whether through individual consumption or exposure in the womb. It is now well accepted that the birth and integration of new neurons continue beyond development and into adulthood. New discoveries and insights on how alcohol impacts this and other plastic processes are discussed in " END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Preventing COVID-19 and aging: Geroprotector to enhance resilience and vaccine response
2021-02-10
10th of February, Wednesday, Hong Kong - Deep Longevity, a fully-owned subsidiary of Regent Pacific (SEHK:0575.HK), specializing in the development and the application of next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) for aging and longevity research, today announced the publication of an article in Lancet Healthy Longevity titled "The potential of rapalogs to enhance resilience against SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce the severity of COVID-19".
While the pandemic continues to unfold, targeted therapeutic solutions for COVID-19 are still not established. The extremely rapid development of various vaccines as a preventative approach provides ...
COVID-19 telemonitoring program helps reduce hospital admissions and ER visits
2021-02-10
New Rochelle, NY, February 9, 2021--The rapid upscaling of a telemonitoring program in which health care providers performed daily telemedicine check-ins on COVID-19 patients faced a unique set of challenges. How these were resolved, and early outcomes are reported in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health, Click here to read the article now.
"Kaiser Permanente's Virtual Home Care Program (VHCP) was able to rapidly establish a telemedicine-based program for the management of COVID-19 positive patients in the DC and Baltimore Metro regions. Preliminary data suggest that such a program may be effective ...
Astronomers uncover mysterious origins of 'super-Earths'
2021-02-10
Mini-Neptunes and super-Earths up to four times the size of our own are the most common exoplanets orbiting stars beyond our solar system. Until now, super-Earths were thought to be the rocky cores of mini-Neptunes whose gassy atmospheres were blown away. In a new study published in The Astrophysical Journal, astronomers from McGill University show that some of these exoplanets never had gaseous atmospheres to begin with, shedding new light on their mysterious origins.
From observations, we know about 30 to 50 percent of host stars have one or the other, and the two populations appear in about equal proportion. But where did they come from?
One theory is that most exoplanets ...
Lung ultrasound helps predict COVID-19 patient outcomes
2021-02-10
Lung ultrasound, considered a simple method for diagnosing lung disease, can also help predict the clinical progression of severe COVID-19 patients, according to a study conducted at the University of São Paulo's Medical School (FM-USP) in São Paulo City, Brazil.
The principal investigator for the study was Heraldo Possolo de Souza, a professor at FM-USP and an attending physician at its teaching and general hospital, Hospital das Clínicas (HC).
The researchers applied an ultrasound examination protocol covering 12 lung regions in 180 COVID-19 patients undergoing treatment at HC. The results showed that the higher the lung ultrasound score, the greater the risk of admission to an intensive care unit (ICU), intubation, and death.
The study was supported ...
Gulls, sentinels of bacteria in the environment
2021-02-10
Gulls are one of the main wild birds that act as reservoirs of Campylobacter and Salmonella, two most relevant intestinal antibiotic-resistant bacteria causing gastroenteritis in humans. Therefore, according to an article published in the journal Science of the Total Environment seagulls could act as sentinels of the antibiotic pressure in the environment.
The study was carried out by experts of the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the University of Barcelona, and the Institute of Agrifood Research and Technology (IRTA).
Resistant bacteria to antibiotics represent a serious problem for human health and other species since they can harden the treatment ...
The science of siestas: New research reveals the genetic basis for daytime napping
2021-02-10
BOSTON - How often a person takes daytime naps, if at all, is partly regulated by their genes, according to new research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in Nature Communications. In this study, the largest of its kind ever conducted, the MGH team collaborated with colleagues at the University of Murcia in Spain and several other institutions to identify dozens of gene regions that govern the tendency to take naps during the day. They also uncovered preliminary evidence linking napping habits to cardiometabolic health.
"Napping is somewhat controversial," says Hassan Saeed Dashti, PhD, RD, of the MGH Center for Genomic Medicine, co-lead author of the report with Iyas Daghlas, a medical student at ...
Choir singing can improve cognitive functioning among the elderly
2021-02-10
Alongside the effects of lifestyle, including physical exercise and diet, on ageing, research has increasingly turned its attention to the potential cognitive benefits of musical hobbies. However, such research has mainly concentrated on hobbies involving musical instruments.
The cognitive benefits of playing an instrument are already fairly well known: such activity can improve cognitive flexibility, or the ability to regulate and switch focus between different thought processes. However, the cognitive benefits of choir singing have so far been investigated very little.
Now, a study recently ...
New tool helps clinicians assess patients who develop COVID-19 symptoms
2021-02-10
BOSTON - When patients arrive in emergency departments and hospitals with symptoms consistent with COVID-19, it's critical to isolate them to avoid the potential spread of infection, but keeping patients isolated longer than needed could delay patient care, take up hospital beds needed for other patients, and unnecessarily use up personal protective equipment. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now created a tool to guide frontline clinicians through diagnostic evaluations of such patients so that they'll know when it's safe to discontinue precautions. The tool was developed and validated in a study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
In the spring of 2020, due to the risk of false-negative ...
Study reveals platinum's role in clean fuel conversion
2021-02-10
UPTON, NY--Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University (SBU), and other collaborating institutions have uncovered dynamic, atomic-level details of how an important platinum-based catalyst works in the water gas shift reaction. This reaction transforms carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen gas (H2)--an important step in producing and purifying hydrogen for multiple applications, including use as a clean fuel in fuel-cell vehicles, and in the production of hydrocarbons.
But because ...
Russian scientists significantly improved coal-burning efficiency
2021-02-10
A team of Russian scientists from NUST MISIS, Tomsk Polytechnic University (TPU) and Boreskov Institute of Catalysis has suggested a new approach to modifying the combustion behavior of coal. The addition of copper salts reduces the content of unburnt carbon in ash residue by 3.1 times and CO content in the gaseous combustion products by 40%, the scientists found. The research was published in Fuel Processing Technology.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), coal is the predominant energy resource used as the primary fuel for power generation. According to reports, coal supplied over one-third of global electricity generation in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
[Press-News.org] Adult neurogenesis may hold clues for more effective treatment of alcoholismNew research and analysis examine how alcohol exposure impacts many aspects of neuroplasticity in a special issue of Brain Plasticity