ET phones home!
Hebrew University finds first evidence of delayed radio flares after star is destroyed by black hole
2021-02-23
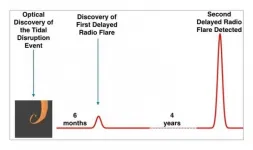
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI) led by Dr. Assaf Horesh have discovered the first evidence of radio flares emitted only long after a star is destroyed by a black hole. Published in the periodical Nature Astronomy, the discovery relied upon ultra-powerful radio telescopes to study these catastrophic cosmic events in distant galaxies called Tidal Disruption Events (TDE). While researchers had known that these events cause the release of radio flares, this latest discovery saw those flares being emitted months or even years after the stellar disruption. The team was led by Dr. Horesh from the Racah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew together with the NASA Swift space telescope director Professor Brad Cenko and Dr. Iair Arcavi from Tel-Aviv University.
"According to existing theories of how these events occur, if no radio emission has been discovered in the immediate wake of the disruption, there is no expectation that one should occur later on" says Dr. Horesh. "However, we decided to conduct one last radio observation six months after the star was destroyed, and surprisingly we discovered bright radio emission. Once we discovered this delayed radio flare, we continued collecting data over a year, during which the radio emission faded away. Moreover, we found a second delayed flare, four years after the initial stellar disruption discovery. This is the first discovery of such delayed radio flares from such events, when a star is disrupted by a black hole."
Flares are believed to be caused by a huge velocity jet launched when the star is destroyed and sucked into the black hole or as a result of the outward explosion of debris from the explosion.
The analysis of the delayed radio flares lead the research team to several conclusions.
First, they now believe that new models have to be developed to explain such a long delay of radio flare emission. Second, it is possible that such delayed radio flares are a common phenomenon, but in order to find more of them teams will need to remain focused on observations surrounding the affected areas long after the initial disruption. Third, it is possible that a substantial amount of the stellar debris is eventually accreted (pulled in) to the black hole, but only long after the star was destroyed.
"What led to the delay and what is the exact physical process responsible for such late-time emission are still open questions", says Dr. Horesh. "In light of this discovery, we are actively searching for more such delayed radio flares in other tidal disruption events."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-23
Selenium contamination of freshwater ecosystems is an ongoing environmental health problem around the world. A naturally occurring trace element, selenium levels are high in some geologic formations like sedimentary shales that form much of the bedrock in the Western United States. Soils derived from this bedrock, and weathering of shale outcrops, can contribute high levels of selenium to surrounding watersheds.
New research out today in Environmental Science & Technology from UConn Assistant Professor of Natural Resources and the Environment Jessica Brandt with Travis Schmidt and colleagues at the United States Geological Survey (USGS) investigates some of the complexities of selenium and how it moves through the ecosystem during runoff ...
2021-02-23
To discover the function of a gene researchers turn it off and observe the consequences. Often genes have multiple functions that differ depending on a tissue and age. Some genes are essential to growth and turning them off too early can have profound consequences that can make observing other functions impossible. To avoid it, researchers have been using conditional gene inactivation which allows turning a gene off only in a specific tissue or later in development, e.g., in adulthood.
One of the systems used for conditional gene inactivation is Cre/lox. "It is the gold standard for the conditional gene inactivation in mice but over time has also become quite important in other model ...
2021-02-23
New storage and information technology requires new higher performance materials. One of these materials is yttrium iron garnet, which has special magnetic properties. Thanks to a new process, it can now be transferred to any material. Developed by physicists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the method could advance the production of smaller, faster and more energy-efficient components for data storage and information processing. The physicists have published their results in the journal "Applied Physics Letters".
Magnetic materials play a major role in the development of ...
2021-02-23
The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists
Personality has been described in all sorts of animal species, from ants to apes. Some individuals are shy and sedentary, while others are bold and active. Now a new study published in Ecology and Evolution has revealed that the way a fish swims tells us a lot about its personality.
This new research suggests experts can reliably measure animal personality simply from the way individual animals move, a type of micropersonality trait, and that the method could be used to help scientists understand about personality differences in wild animals.
A team of biologists and mathematicians from Swansea University and the University of Essex filmed the movements of 15 three-spined stickleback ...
2021-02-23
A new analysis of B cells and more than 1,000 different monoclonal antibodies from 8 patients with COVID-19 shows that, contrary to previous hypotheses, protective B cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein remain stable and continue to evolve over a 5-month period, many months after the initial period of active viral replication. However, a large proportion of the neutralizing antibodies generated from these long-lasting B cells did not efficiently recognize various emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants from Brazil and South Africa. These results - from an academia-industry collaboration - will help inform the design of future COVID-19 vaccines that work to constrain viral evolution and stimulate ...
2021-02-23
Researchers have pinpointed a helper T cell population in the lungs of patients with severe COVID-19 that may be central to the development of hyperinflammation, lung injury, and subsequent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during disease. Their data support the ongoing investigation of anti-cytokine therapies that target this cell subset, called tissue-resident memory-like Th17 cells (Trm17). To date, the bulk of research on immune responses to COVID-19 has mainly focused on T cells in the blood, while the role of tissue-specific immune cells in the inflamed lung has remained unclear. Accumulating evidence suggests that one of the causes of ...
2021-02-23
WHAT:
Using viruses instead of antibiotics to tame troublesome drug-resistant bacteria is a promising strategy, known as bacteriophage or "phage therapy." Scientists at the National Institutes of Health have used two different bacteriophage viruses individually and then together to successfully treat research mice infected with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 (ST258). The bacterium K. pneumoniae ST258 is included on a CDC list of biggest antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. High rates of morbidity and mortality are associated with untreated K. pneumoniae infections.
Phage therapy has been pursued for about a century, though conclusive research studies are rare and clinical results--from ...
2021-02-23
Imagine if surgeons could transplant healthy neurons into patients living with neurodegenerative diseases or brain and spinal cord injuries. And imagine if they could "grow" these neurons in the laboratory from a patient's own cells using a synthetic, highly bioactive material that is suitable for 3D printing.
By discovering a new printable biomaterial that can mimic properties of brain tissue, Northwestern University researchers are now closer to developing a platform capable of treating these conditions using regenerative medicine.
A key ingredient to the discovery is the ability to control the self-assembly processes of molecules within the ...
2021-02-23
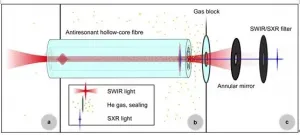
Bright, coherent soft X-ray radiation (SXR) is used in many scientific applications such as advanced absorption spectroscopy or lens-less imaging, and in fundamental research e.g. to produce extremely short isolated optical pulses. Therefore, the generation, control, and detection of this type of short-wavelength light is highly important in fields like fundamental atomic physics, solid-state physics, the semiconductor industry, material science and biology.
To date, high photon flux in the soft X-ray spectral region is mostly delivered by large-scale facilities like synchrotrons or free electron lasers. An alternative is to use high-order harmonic generation (HHG) sources, which are currently driven by pulsed laser systems with ...
2021-02-23
Diabetes is on the rise worldwide. It is a permanent condition that requires care over a life time. To help manage it, an artificial pancreas system, which automatically measures blood sugar levels to infuse the appropriate amount of insulin into the blood, has now become smarter thanks to AI learning.
A research team, led by Professor Sung-Min Park and Ph.D. candidate Seunghyun Lee and M.S. candidate Jiwon Kim of POSTECH's Department of Convergence IT Engineering and Electrical Engineering, has newly developed a reinforcement learning (RL) based AI algorithm that calculates the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] ET phones home!
Hebrew University finds first evidence of delayed radio flares after star is destroyed by black hole